Registered User mNo edit summary |
Registered User mNo edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude>{{ApplicableFor | ||
{{ | |MPUs list=STM32MP15x | ||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x | |||
}}</noinclude> | |||
}} | |||
</noinclude> | |||
==Article purpose== | ==Article purpose== | ||
The purpose of this article is to | The purpose of this article is to | ||
* briefly introduce the VREFBUF peripheral and its main features | * briefly introduce the VREFBUF peripheral and its main features | ||
* indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | * indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | ||
* explain how each instance can be allocated to the | * explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components | ||
* explain, when needed, how to configure the VREFBUF peripheral. | * explain, when needed, how to configure the VREFBUF peripheral. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 30: | ||
==Peripheral usage and associated software== | ==Peripheral usage and associated software== | ||
===Boot time=== | ===Boot time=== | ||
The VREFBUF is usually not used at boot time. But it may be needed by the SSBL (see [[Boot | The VREFBUF is usually not used at boot time. But it may be needed by the SSBL (see [[Boot chain overview]]), to supply the internal ADC<ref name="adc_internal"/> for example. | ||
===Runtime=== | ===Runtime=== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 46: | ||
====Software frameworks==== | ====Software frameworks==== | ||
{{: | {{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_software_table_template}} | ||
| Analog | | Analog | ||
| [[VREFBUF internal peripheral|VREFBUF]] | | [[STM32MP15 VREFBUF internal peripheral|VREFBUF]] | ||
| | | | ||
| Linux [[Regulator overview|regulator]] framework | | Linux [[Regulator overview|regulator]] framework | ||
| Line 71: | Line 63: | ||
====Peripheral assignment==== | ====Peripheral assignment==== | ||
{{: | {{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | ||
<onlyinclude> | <onlyinclude> | ||
| rowspan="1" | Analog | | rowspan="1" | Analog | ||
| rowspan="1" | [[VREFBUF internal peripheral|VREFBUF]] | | rowspan="1" | [[STM32MP15 VREFBUF internal peripheral|VREFBUF]] | ||
| VREFBUF | | VREFBUF | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 86: | Line 78: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
<noinclude> | |||
[[Category:Analog peripherals|VREFBUF internal peripheral STM32MP15]] | |||
{{PublicationRequestId | 8312 | 2018-08-07 | AlainF}} | |||
{{ArticleBasedOnModel| Internal peripheral article model}} | |||
{{ReviewsComments|JCT 1840: alignment needed with the last version of the model<br> | |||
[[Category:ToBeAlignedWithModel]] | |||
}} | |||
</noinclude> | |||
Revision as of 15:37, 1 February 2022
1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this article is to
- briefly introduce the VREFBUF peripheral and its main features
- indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- explain, when needed, how to configure the VREFBUF peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit | edit source]
The VREFBUF peripheral is an internal voltage regulator.
2.1. Features[edit | edit source]
The VREFBUF is supplied via the VDDA pin. When enabled, it can provide a reference voltage in the range of: 1,5V, 1,8V, 2,048V or 2,5V.
The VREFBUF can be used to provide an analog voltage reference for:
- ADC internal peripheral[1]
- DAC internal peripheral[2]
- External components through the dedicated VREF+ pin.
The VREFBUF can be left unused. In this case, an external voltage regulator can provide reference voltage to VREF+ pin.
Refer to the STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to know which features are really implemented.
2.2. Security support[edit | edit source]
The VREFBUF is a non-secure peripheral.
3. Peripheral usage and associated software[edit | edit source]
3.1. Boot time[edit | edit source]
The VREFBUF is usually not used at boot time. But it may be needed by the SSBL (see Boot chain overview), to supply the internal ADC[1] for example.
3.2. Runtime[edit | edit source]
3.2.1. Overview[edit | edit source]
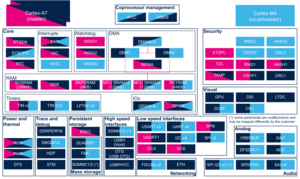
The VREFBUF can be allocated to the Arm® Cortex®-A7 non-secure to be used under Linux® with regulator framework[3].
The VREFBUF is a system resource[4] which needs to be also controlled by the resource manager[4] in case its consumers (e.g. ADC[1], DAC[2] or an external device connected to VREF+ pin) are spread across:
For this reason, the direct control of VREFBUF from the Arm® Cortex®-M4 is not recommended in STM32Cube[5] by default. |
The Peripheral assignment chapter describes which peripheral instance can be assigned to which context.
3.2.2. Software frameworks[edit | edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Analog | VREFBUF | Linux regulator framework | |||
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit | edit source]
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration by itself can be performed via the STM32CubeMX tool for all internal peripherals. It can then be manually completed (especially for external peripherals) according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article.
- For the Linux kernel configuration, please refer to device internal regulator. An example can be found also in ADC DT configuration example
- In case the control of VREFBUF consumers are spread across the various cores, see also Resource manager for coprocessing
3.2.4. Peripheral assignment[edit | edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Analog | VREFBUF | VREFBUF | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | ||
4. References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 ADC internal peripheral
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 DAC internal peripheral
- ↑ Regulator overview, Linux® regulator framework overview
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Resource manager for coprocessing, focus on system resources
- ↑ STM32CubeMP1 architecture