1. Yocto-based OpenSTLinux embedded software overview[edit | edit source]
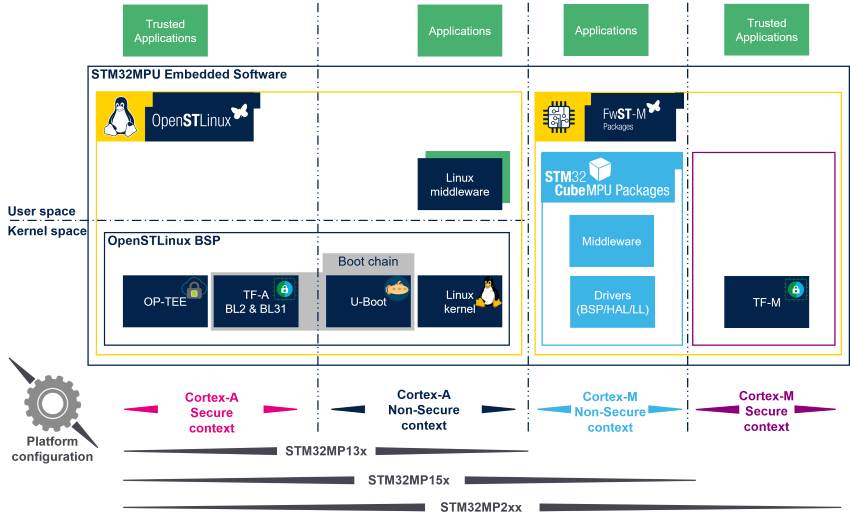
The diagram below shows Yocto-based OpenSTLinux embedded software distribution main components:
- The OpenSTLinux distribution running on the Arm® Cortex®-A, includes:
- The OpenSTLinux BSP with:
- The boot chain based on TF-A BL2 (FSBL-A) running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in secure mode and U-Boot (SSBL-A) running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in nonsecure mode.
- The secure monitor based on TF-A BL31 or OP-TEE , depending on Cortex®-A architecture, running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in secure mode.
- The OP-TEE secure OS running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in secure mode.
- The Linux® kernel running on the Arm® Cortex®-A in nonsecure mode.
- The Linux middleware relying on the OpenSTLinux BSP to provide API to the Applications that typically interact with the user via the display, the touchscreen, etc.
- The OP-TEE Trusted Applications (TA) relying on the OP-TEE core for secrets operations (not visible from the Linux and other software components).
- The OpenSTLinux BSP with:
- The FwST-M Packages that are composed of the firmwares running on Arm® Cortex®-M (not available on STM32MP13x lines
 ) include:
) include:
- The FwST-M BSP with:
- The boot chain based on MCUboot (FSBL-M) running on the Arm® Cortex®-M in secure mode, for STM32MP2 series M33-TD flavor
 only.
only. - The TF-M secure OS running on the Arm® Cortex®-M in secure mode, for STM32MP2 series only. It provides local secure services to STM32Cube MPU Package.
- The STM32Cube MPU Packages drivers (BSP, HAL, LL) running on the Arm® Cortex®-M nonsecure mode.
- The boot chain based on MCUboot (FSBL-M) running on the Arm® Cortex®-M in secure mode, for STM32MP2 series M33-TD flavor
- The STM32Cube MPU Packages middleware relying on the FwST-M BSP, like STM32 microcontrollers, completed with Arm® Cortex®-M remote processor management for interaction with the Cortex®-A.
- The FwST-M BSP with:
The OpenSTLinux distribution is generated with OpenEmbedded build framework : the BSP components are modified open source software components, stored on GitHub, whereas the middleware is directly inherited from communities. See our Open Source Software (OSS) philosophy just below for further information.
The figure below is clickable so that the user can directly jump to one of the sub-levels listed above.
2. Open Source Software (OSS) philosophy[edit | edit source]
The Open source software source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to study, change and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose[1].
STMicroelectronics maximizes the using of open source software and contributes to those communities. Notice that, due to the software review life cycle, it can take some time before getting all developments accepted in the communities, so STMicroelectronics can also temporarily provide some source code on github[2], until it is merged in the targeted repository.
3. References[edit | edit source]
