1. Framework purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this article is to introduce the "Thermal framework".
Thermal framework is a subsystem made for handling thermal sensors and cooling devices (fan, processor...), it is made of 3 subsystems:
- thermal zone
- cooling device
- thermal-sensor via hwmon API or thermal API
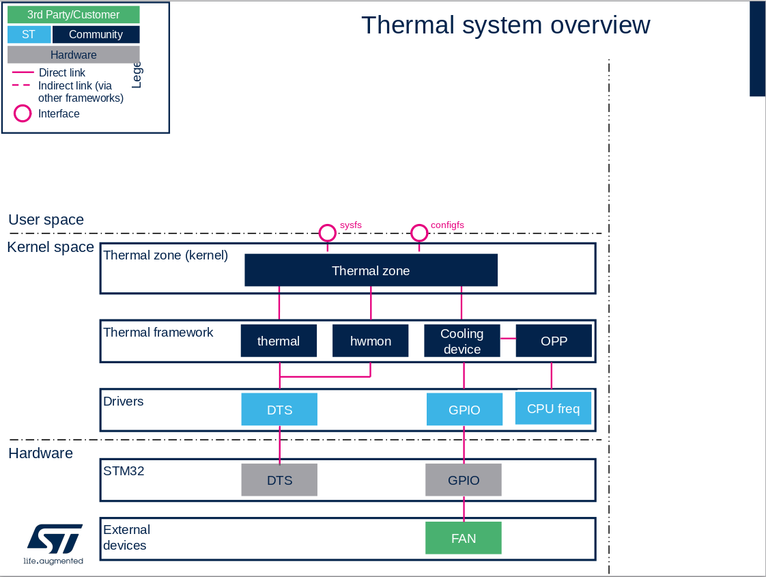
2. System overview[edit | edit source]
2.1. Component description[edit | edit source]
- thermal-zone is a container used to describe all thermal data for the platform
- thermal framework offers an API to read temperature and to handle thresholds with interrupts.
- hwmon framework offers an API to read temperature: no threshold, only polling.
- cooling-device device is used to dissipate heat either:
- actively for example with a FAN controlled by GPIOs
- passively via OPP by forcing a lower CPU voltage or frequencies as a cooling state.
- driver DTS: the STM32 MPU thermal/hwmon device driver
- DTS internal peripheral: Digital temperature sensor (DTS)
2.2. Thermal-zone role[edit | edit source]
The thermal zone is also responsible for:
- driving cooling devices depending on thermal sensor information,
- handling a critical trip point that consist of calling shutdown,
- polling thermal sensors that do not handle trip points with IRQs (that are implemented under hwmon framework).
A system may contains several thermal zones. For example one for CPU, one for GPU. Each zone is made of:
- a thermal sensor with some polling periods descriptions,
- some active or passive trip points with a temperature and hysteresis for each,
- a cooling map that describe the action for each trip point.
2.3. API description[edit | edit source]
The thermal API is not documented in the Linux Kernel documentation, except the 2 pages:
- Generic Thermal Sysfs driver How To: driver-api/thermal/sysfs-api.html
- The sysfs ABI: admin-guide/abi-testing.html?sensor#abi-file-testing-sysfs-class-thermal
3. Configuration[edit | edit source]
3.1. Kernel configuration[edit | edit source]
The thermal API and the DTS driver are activated by default in ST deliveries.
Configuration flag:
- CONFIG_THERMAL
- CONFIG_HWMON
- CONFIG_STM32_THERMAL on STM32MP1 series
- CONFIG_SENSORS_MR75203 on STM32MP2 series
Nevertheless, if a specific configuration is required, you can use Linux Menuconfig tool: Menuconfig or how to configure kernel and select:
[*] Device Drivers -->
[*] Thermal drivers (THERMAL [=y]) -->
[*] STMicroelectronics thermal drivers
[*] Hardware Monitoring support (HWMON [=y])
<*> Moortec Semiconductor MR75203 PVT Controller
3.2. Device tree configuration[edit | edit source]
The thermal zone is represented by the Thermal zone binding: Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal-zones.yaml
The thermal sensor is represented by the Thermal sensor binding: Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal-sensor.yaml
The thermal cooling device is represented by the Thermal cooling device binding: Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/thermal-cooling-devices.yaml
The DTS bindings are described in:
- on STM32MP1 series: Documentation/devicetree/bindings/thermal/st,stm32-thermal.yaml
- on STM32MP2 series: Documentation/devicetree/bindings/hwmon/moortec,mr75203.yaml
4. How to use the Thermal framework[edit | edit source]
4.1. critical trip point[edit | edit source]
A typical use case is to handle CPU overheat by calling shutdown when the temperature reaches a certain level. This is done in "critical" trip point. The example below makes that shutdown is called as soon as temperature reaches 105°C:
trips {
cpu-crit {
temperature = <105000>;
hysteresis = <0>;
type = "critical";
};
4.2. passive trip point[edit | edit source]
Another typical use case is passive power dissipation, consisting in limiting CPU frequency when the CPU is too hot. This is done in "passive" trip point.
The example below sets the highest allowed OPP as OPP number 1 (one) as soon as the temperature is higher than 95°C:
trips {
cpu_alert: cpu-alert {
temperature = <95000>;
hysteresis = <10000>;
type = "passive";
};
};
cooling-maps {
map0 {
trip = <&cpu_alert>;
cooling-device = <&cpu0 1 1>;
};
};
The cooling agent is provided CPUFreq Linux framework (see documentation for details cpu-freq/index.html, thermal/cpu-cooling-api.html for details), with cooling state set at min=1 and max=1, the minimal OPP is forced.
5. How to trace and debug the framework[edit | edit source]
5.1. How to trace[edit | edit source]
Dynamic debug can be enabled in the "thermal_sys" module like in the command below:
echo 'module thermal_sys +ptmlf' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
5.2. How to debug[edit | edit source]
When the thermal driver implements hwmon API, the temperature can be read from the sysfs like in the command below:
cat /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/thermal_zone0/hwmon0/temp1_input
6. Generic source code location[edit | edit source]
- thermal core and drivers: drivers/thermal/
- thermal interface: drivers/thermal/thermal_core.h
- STM32MP1 series DTS driver: drivers/thermal/st/stm_thermal.c
- hwmon drivers: drivers/hwmon/
- STM32MP2 series DTS driver: drivers/hwmon/mr75203.c
7. References[edit | edit source]