This article describes the content of X-LINUX-RT expansion package release version v6.1.0, which can be applied on top of STM32 MPU ecosystem release note - v6.1.0.
1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
Purpose of this article is to:
- Introduce the X-LINUX-RT expansion package,
- Define the hardware & software deliverables to use the X-LINUX-RT package,
- Describe all steps to integrate the X-LINUX-RT package and associated expected results,
- Give some use case examples enabled by the X-LINUX-RT package.
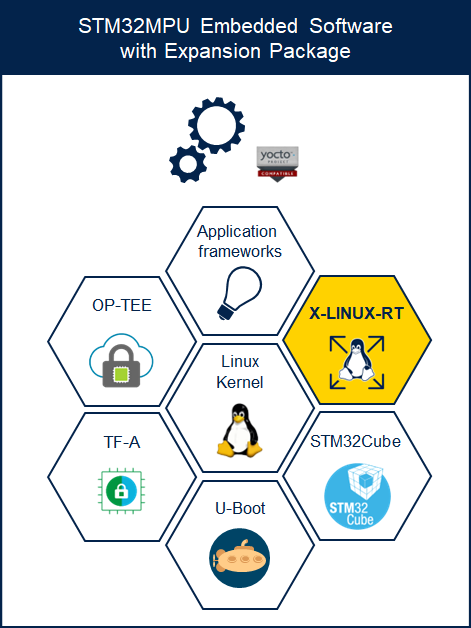
2. X-LINUX-RT expansion package description[edit | edit source]
2.1. Overview[edit | edit source]
X-LINUX-RT is an STM32 MPU OpenSTLinux expansion package that targets the real-time (RT) feature in the Linux® kernel.
An RT system is a system that responds to a request in a time lapse and not as fast as possible. It targets:
- Determinism
- LATENCY but not SPEED
For a better understanding about real-time Linux, refer to the Linux RT foundation website[1].
The X-LINUX-RT expansion package is delivered as a new meta layer. The following chapters show how to build it with the OpenSTLinux Distribution Package.
2.2. Main software modifications[edit | edit source]
2.2.1. Linux kernel configuration[edit | edit source]
The Linux kernel configuration must be modified to enable:
- CONFIG_EXPERT: Dependency for enabling PREEMPT_RT
- CONFIG_PREEMPT_RT: RT feature in kernel
- CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS: High resolution timer support
and disable:
- CONFIG_CPU_FREQ: Dynamic CPU Operating Performance Points support (Frequency scaling)
- CONFIG_CPU_IDLE: CPU idle Power Management support
This is done by applying the config fragment file fragment-07-rt.config available when applying this expansion package (see 0011-v6.6-stm32mp-rt-r2.patch ).
2.2.2. OP-TEE OS configuration[edit | edit source]
2.2.2.1. OP-TEE OS Profile[edit | edit source]
It is recommended to set OP-TEE OS in a system_services profile in order to optimize the system latency (Refer to STM32MPU_OP-TEE_profiles for more details about OP-TEE profiles).
It is configured by default in context of OpenSTLinux Distribution Package, and has to be considered in case of OpenSTLinux Developer Package as described in below chapters.
2.2.2.2. OP-TEE OS board device trees[edit | edit source]
Because there is no more frequency scaling, and to ensure an optimal lifetime for the microprocessor, the frequency is fixed following the recommended industrial profile.
2.3. Main restrictions[edit | edit source]
X-LINUX-RT is an expansion package only available as a Distribution Package. There are no X-LINUX-RT Starter Package nor X-LINUX-RT Developer Package.
Nevertheless, you can learn how to install the X-LINUX-RT feature in your OpenSTLinux Developer Package.
2.4. Versioning[edit | edit source]
The latest version of the X-LINUX-RT expansion package is named openstlinux-6.6-yocto-scarthgap-mpu-v25.06.11 and must be used with components delivered for ecosystem release v6.1.0 ![]() .
.
2.5. Associated licenses[edit | edit source]
This software package is licensed under a SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR ST MATERIALS (SLA). Customers should only use this package in compliance with the software license agreement (SLA), STM32CubeMP15 licenses, and STM32CubeMP2 licenses.
3. Prerequisites[edit | edit source]
3.1. Hardware prerequisites[edit | edit source]
- Below is the list of supported STM32 MPU boards. Click on the associated links to jump to the articles describing how to set up the boards:
3.2. Software prerequisites[edit | edit source]
Be familiar with:
- OpenSTLinux Distribution Package. Refer to the STM32MPU Distribution Package article for more information.
- OpenSTLinux Developer Package. Refer to the STM32MPU Developer Package article for more information.
- Get the OpenSTLinux ecosystem release v6.1.0
 (steps to follow described in chapters below).
(steps to follow described in chapters below). - Be familiar with the changes implied by enabling CFG_PREEMPT_RT in the Linux kernel.
4. Hardware Setup[edit | edit source]
Boards should be assembled as defined in #Hardware prerequisites.
5. Software setup[edit | edit source]
5.1. How to get software[edit | edit source]
X-LINUX-RT expansion package is delivered in a git repository on Github: https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/meta-st-x-linux-rt.git (Scarthgap branch for compatibility with this ecosystem release v6.1.0 ![]() )
)
There is a dependency with External_DT component(branch v6-stm32mp) manage by this expansion package.
It can be integrated using OpenSTLinux Distribution Package to build new OpenSTLinux images.
5.1.1. How to install the Distribution Package[edit | edit source]
5.1.1.1. Install the OpenSTLinux Distribution Package[edit | edit source]
Install the OpenSTLinux Distribution Package v6.1.0.
5.1.1.2. Download the X-LINUX-RT meta layer[edit | edit source]
- Clone the meta-st-x-linux-rt git repositories
pushd <Distribution Package installation directory>/layers/meta-st git clone https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/meta-st-x-linux-rt.git -b openstlinux-6.6-yocto-scarthgap-mpu-v25.06.11 popd
5.1.1.3. Build the Distribution Package[edit | edit source]
- Source the build environment with the correct board and layer
DISTRO=openstlinux-weston MACHINE=stm32mp13-rt source layers/meta-st/scripts/envsetup.sh
DISTRO=openstlinux-weston MACHINE=stm32mp1-rt source layers/meta-st/scripts/envsetup.sh
- For STM32MP2 series (for ecosystem release v6.1.0
 ):
):
DISTRO=openstlinux-weston MACHINE=stm32mp2-rt source layers/meta-st/scripts/envsetup.sh
- Build the image
bitbake st-image-weston
| Note that building the image might take a long time depending on the host computer performance. |
5.1.2. How to populate the flash memory with the image[edit | edit source]
You can refer to Flashing the built image to program your board with X-LINUX-RT binaries.
5.1.3. How to run X-LINUX-RT package software[edit | edit source]
To run X-LINUX-RT package software: boot the image loaded on the board as explained in previous chapters.
5.2. How to check that RT feature is enabled[edit | edit source]
To check that the RT feature is enabled and functional, the following command can be executed when the board is running, to check the kernel version:
uname -s -r -v
| Without the RT feature |
Linux 6.6.78 #1 SMP PREEMPT Fri May 23 14:04:26 UTC 2025 |
|---|---|
| With the RT feature |
Linux 6.6.78-rt51 #1 SMP PREEMPT_RT Fri May 23 18:27:50 UTC 2025 |
6. How to run Cyclictest[edit | edit source]
6.1. Use cases execution and expected results[edit | edit source]
Cyclictest accurately and repeatedly measures the difference between the time at which a thread is intended to wake up and the time at which it actually wakes up.
For a better understanding of cyclictest, refer to the cyclictest webpage in the Linux RT foundation website[2].
For example on STM32MP257F-DK ![]() (2 cores with smp), the following command can be used for one hour test: (--quiet option can be added to improve measurement)
(2 cores with smp), the following command can be used for one hour test: (--quiet option can be added to improve measurement)
cyclictest --mlockall --smp -p 90
| Without the RT feature |
... T: 0 ( 2095) P:90 I:1000 C: 28659 Min: 7 Act: 7 Avg: 12 Max: 1166 T: 1 ( 2096) P:90 I:1500 C: 19106 Min: 7 Act: 8 Avg: 54 Max: 652 ... |
|---|---|
| With the RT feature |
... T: 0 ( 2131) P:99 I:100 C:36000000 Min: 7 Act: 10 Avg: 10 Max: 78 T: 1 ( 2132) P:99 I:100 C:36000000 Min: 7 Act: 11 Avg: 10 Max: 87 ... |
6.2. Use case restrictions[edit | edit source]
Low Power modes Stop and Standby are supported but not S2Idle mode.
7. How to go further[edit | edit source]
7.1. How to improve system latency with perf-rt flavor[edit | edit source]
To improve latency, a new DISTRO, named openstlinux-rt, is provided with the X-LINUX RT package.
This DISTRO is based on following characteristics:
- It uses SysVinit[3] instead of SystemD
- There is no Weston
- A new Linux kernel config fragment file fragment-10-rt-perf.config is applied (provided by patch file present in this expansion package, see 0011-v6.6-stm32mp-rt-r2.patch ). It
- Limits the runtime interactions of the Linux kernel with OP-TEE are to the minimum (boot and low-power sequences). This avoids context switches between the secure and non-secure worlds that heavily impact the kernel latency.
- Disable tickless Linux kernel by setting CONFIG_HZ_PERIODIC=y. This increases the power consumption but reduces from-idle transition latency
- Removes power domains management
- Provides other optimization
- It uses <board_type>-perf-rt.dts device trees across all software components (prodived in External_DT component).
- Only for MACHINE stm32mp13-rt-perf, stm32mp1-rt-perf or stm32mp2-rt-perf
- IWDG watchdog management is transferred to the Linux kernel
7.1.1. Build openstlinux-rt[edit | edit source]
If not done yet, set up the X-LINUX-RT Distribution Package as described #How to install the Distribution Package chapter.
To select the openstlinux-rt DISTRO, run following command:
DISTRO=openstlinux-rt MACHINE=<your machine> source layers/meta-st/scripts/envsetup.sh
- <your machine> one of stm32mp13-rt-perf, stm32mp1-rt-perf or stm32mp2-rt-perf
Build the image
bitbake st-image-core
7.1.2. Flash openstlinux-rt[edit | edit source]
Then flash it, as explained here.
7.1.3. Performances measurement[edit | edit source]
To check RT performances improvement, run new cyclictest command
cyclictest --mlockall --smp -p 99 -i 100 -d 0 -A 0 -D 1h ... T: 0 ( 1849) P:99 I:100 C:36000000 Min: 7 Act: 9 Avg: 8 Max: 25 T: 1 ( 1850) P:99 I:100 C:36000000 Min: 7 Act: 9 Avg: 8 Max: 29 ...
7.2. How to install X-LINUX-RT in the OpenSTLinux Developer Package[edit | edit source]
In order to build Linux RT, some patches provided in X-LINUX-RT meta layer must be applied on top of the Linux kernel component.
7.2.1. Install the OpenSTLinux SDK[edit | edit source]
The OpenSTLinux SDK contains all the basis needed for the X-LINUX-RT expansion package.
It must be downloaded and installed (refer to the STM32MPU_Developer_Package#Installing_the_SDK chapter).
Once the installation is done, a directory is present, containing the OpenSTLinux SDK.
7.2.2. Download the OpenSTLinux Developer Package[edit | edit source]
The OpenSTLinux Developer Package, containing all the BSP components source code, must be downloaded and extracted, refer
- first to STM32MPU_Developer_Package#Installing_the_Starter_Package,
- then to the STM32MPU_Developer_Package#Installing_the_OpenSTLinux_BSP_packages chapter only.
7.2.3. Deploy Linux kernel component and generate the native Linux kernel configuration[edit | edit source]
Refer to README.HOW_TO.txt.{stm32mp1,stm32mp2,stm32mp2-m33td} helper file up Configure kernel source code section. This file is present in the Linux kernel installation directory.
7.2.4. Download the X-LINUX-RT meta layer[edit | edit source]
Clone the meta-st-x-linux-rt git repository
cd <Developer Package installation directory> git clone https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/meta-st-x-linux-rt.git -b openstlinux-6.6-yocto-scarthgap-mpu-v25.06.11
7.2.5. Apply X-LINUX-RT delivery sources[edit | edit source]
Only Linux kernel is patched and its configuration is updated for the RT feature.
7.2.5.1. Apply patches[edit | edit source]
The patches delivered in <Developer Package installation directory>/meta-st-x-linux-rt/recipes-kernel/linux/6.6/ must be applied.
- 0010-Rebase-on-v6.6.78-rt51.patch
- 0011-v6.6-stm32mp-rt-r2.patch
For that:
- Enter into the directory containing the Linux kernel sources (refer to previous step #Deploy Linux kernel component and generate the native Linux kernel configuration)
- Apply the patches:
for p in `ls -1 <Developer Package installation directory>/meta-st-x-linux-rt/recipes-kernel/linux/6.6/*.patch`; do patch -p1 < $p; done
The Linux kernel source is ready to be configured before build.
A Linux kernel config fragment must be copied to the source code:(arm directory for STM32MP1 series and arm64 for STM32MP2 series)
cp <Developer Package installation directory>/meta-st-x-linux-rt/recipes-kernel/linux/6.6/fragment-10-network-improvment.config <Linux kernel source directory>/arch/{arm,arm64}/configs/
7.2.5.2. Add and apply new config fragments[edit | edit source]
Some of new fragments now present inside the Linux kernel source must be applied.
scripts/kconfig/merge_config -m -r -O ${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR} ${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR}/.config arch/{arm,arm64}/configs/fragment-07-rt.config arch/{arm,arm64}/configs/fragment-07-rt-sysvinit.config arch/{STLightGreen|{arm,arm64}}}/configs/fragment-10-network-improvment.config
(yes || true) | make oldconfig O="${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR}"
- Only for STM32MP13x lines
 , apply the fragment <Developer Package installation directory>/stm32mp-openstlinux-6.6-yocto-scarthgap-mpu-v25.08.27/sources/ostl-linuxlinux-stm32mp-6.6.78-stm32mp-r2-r0/optional-fragment-06-nosmp.config as explained in the README.HOW_TO.txt.{stm32mp1,stm32mp2,stm32mp2-m33td} helper file.
, apply the fragment <Developer Package installation directory>/stm32mp-openstlinux-6.6-yocto-scarthgap-mpu-v25.08.27/sources/ostl-linuxlinux-stm32mp-6.6.78-stm32mp-r2-r0/optional-fragment-06-nosmp.config as explained in the README.HOW_TO.txt.{stm32mp1,stm32mp2,stm32mp2-m33td} helper file.
scripts/kconfig/merge_config -m -r -O ${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR} ${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR}/.config ../optional-fragment-06-nosmp.config
(yes || true) | make oldconfig O="${OUTPUT_BUILD_DIR}"
7.2.5.3. Build Linux kernel[edit | edit source]
- The Linux kernel can now be built and deployed, as explained in Building and deploying the Linux kernel for the first time.
8. References[edit | edit source]
9. Archives  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
| STM32MPU release | OpenSTLinux release note |
|---|---|
| STM32 MPU-Ecosystem-v6.0.0 | X-LINUX-RT expansion package - v6.0.0 |