Registered User mNo edit summary |
Registered User mNo edit summary Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ApplicableFor | |||
{{ | |MPUs list=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x, STM32MP21x, STM32MP23x, STM32MP25x | ||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x, STM32MP21x, STM32MP23x, STM32MP25x | |||
}} | }} | ||
==Article purpose== | ==Article purpose== | ||
The purpose of this article is to | The purpose of this article is to: | ||
* briefly introduce the | * briefly introduce the HDP peripheral and its main features, | ||
* indicate the | * indicate the peripheral instances assignment at boot time and their assignment at runtime (including whether instances can be allocated to secure contexts), | ||
* list the software frameworks and drivers managing the peripheral, | |||
* explain | * explain how to configure the peripheral. | ||
==Peripheral overview== | ==Peripheral overview== | ||
The '''HDP''' peripheral is used to output some internal signals on up to 8 [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] pins. | The '''HDP''' peripheral is used to output some internal signals on up to 8 [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] pins.<br /> | ||
Follow the sequence below to connect a GPIO to an internal signal via the HDP: | Follow the sequence below to connect a GPIO to an internal signal via the HDP: | ||
* First of all, look for the internal signal you want to monitor in the HDP signal multiplexing table of the [[ | * First of all, look for the internal signal you want to monitor in the HDP signal multiplexing table of the [[STM32 MPU resources#Reference manuals|STM32MPU reference manuals]]: | ||
** Search for the HDP signal on which you can get it among eight possible choices. | ** Search for the HDP signal on which you can get it among eight possible choices. | ||
** Note the corresponding '''HDPx multiplexing value''' to select. | ** Note the corresponding '''HDPx multiplexing value''' to select. | ||
* Then, look for the most suitable [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] pin on which you can output HDPx in the [[ | * Then, look for the most suitable [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] pin on which you can output HDPx in the [[STM32 MPU resources#Datasheets|datasheets]]: | ||
** Note the [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''bank''' and '''pin'''. | ** Note the [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''bank''' and '''pin'''. | ||
** Note the corresponding [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''alternate function''' (AF) to select. | ** Note the corresponding [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''alternate function''' (AF) to select. | ||
The [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''bank''', '''pin''', '''alternate function''' and '''HDPx multiplexing value''' are the information required to configure each HDP signal. | The [[GPIO internal peripheral|GPIO]] '''bank''', '''pin''', '''alternate function''' and '''HDPx multiplexing value''' are the information required to configure each HDP signal. | ||
Refer to the [[STM32 MPU resources#Reference manuals|STM32 MPU reference manuals]] for the complete list of features, and to the software frameworks and drivers, introduced below, to see which features are implemented. | |||
Refer to [[ | |||
{{ | ==Peripheral usage== | ||
This chapter is applicable in the scope of the '''OpenSTLinux BSP''' running on the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A processor(s), and the '''FwST-M Package''' running on the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M processor. | |||
===Boot time assignment=== | |||
The HDP peripheral is not used at boot time. | |||
===Runtime assignment=== | |||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}}==== | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP1_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp13_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp13_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[HDP internal peripheral|HDP]] | |||
| HDP | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp13_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
=== | ====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}}==== | ||
{{#lst:STM32MP1_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp15_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp15_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[HDP internal peripheral|HDP]] | |||
| HDP | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp15_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
== | ====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=21}}==== | ||
=== | The table below is applicable to any {{TrustedDomainFlavor | flavor=Any-TD}}. | ||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp21_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp21_a35_runtime /> | |||
<section begin=stm32mp21_m33_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[HDP internal peripheral | HDP]] | |||
| HDP | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp21_m33_runtime /> | |||
<section end=stm32mp21_a35_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
=== | ====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=23}}==== | ||
==== | The table below is applicable to any {{TrustedDomainFlavor | flavor=Any-TD}}. | ||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp23_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp23_a35_runtime /> | |||
<section begin=stm32mp23_m33_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[HDP internal peripheral | HDP]] | |||
| HDP | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp23_m33_runtime /> | |||
<section end=stm32mp23_a35_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=25}}==== | |||
The table below is applicable to any {{TrustedDomainFlavor | flavor=Any-TD}}. | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp25_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp25_a35_runtime /> | |||
<section begin=stm32mp25_m33_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Trace & Debug | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[HDP internal peripheral | HDP]] | |||
| HDP | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp25_m33_runtime /> | |||
<section end=stm32mp25_a35_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
==Software frameworks and drivers== | |||
Below are listed the software frameworks and drivers managing the HDP peripheral for the embedded software components listed in the above tables. | |||
* '''Linux<sup>®</sup>''': [[HDP Linux driver|HDP Linux driver]] | |||
==== | ==How to assign and configure the peripheral== | ||
The peripheral assignment can be done via the [[STM32CubeMX]] graphical tool (and manually completed if needed).<br /> | |||
< | This tool also helps to configure the peripheral: | ||
* partial device trees (pin control and clock tree) generation for the OpenSTLinux software components, | |||
* HAL initialization code generation for the STM32CubeMPU Package. | |||
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context in which the peripheral is assigned. | |||
<noinclude> | |||
[[Category:Trace and debug peripherals]] | |||
{{ArticleBasedOnModel| Internal peripheral article model}} | |||
{{PublicationRequestId | 8314 | 2018-08-02 | AnneJ}} | |||
</ | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:33, 24 June 2025
1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the HDP peripheral and its main features,
- indicate the peripheral instances assignment at boot time and their assignment at runtime (including whether instances can be allocated to secure contexts),
- list the software frameworks and drivers managing the peripheral,
- explain how to configure the peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit | edit source]
The HDP peripheral is used to output some internal signals on up to 8 GPIO pins.
Follow the sequence below to connect a GPIO to an internal signal via the HDP:
- First of all, look for the internal signal you want to monitor in the HDP signal multiplexing table of the STM32MPU reference manuals:
- Search for the HDP signal on which you can get it among eight possible choices.
- Note the corresponding HDPx multiplexing value to select.
- Then, look for the most suitable GPIO pin on which you can output HDPx in the datasheets:
The GPIO bank, pin, alternate function and HDPx multiplexing value are the information required to configure each HDP signal.
Refer to the STM32 MPU reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software frameworks and drivers, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
3. Peripheral usage[edit | edit source]
This chapter is applicable in the scope of the OpenSTLinux BSP running on the Arm® Cortex®-A processor(s), and the FwST-M Package running on the Arm® Cortex®-M processor.
3.1. Boot time assignment[edit | edit source]
The HDP peripheral is not used at boot time.
3.2. Runtime assignment[edit | edit source]
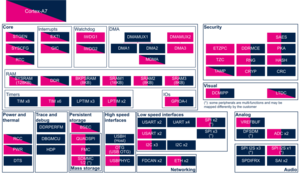
3.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 nonsecure (Linux) | |||
| Trace & Debug | HDP | HDP | ☐ | ||
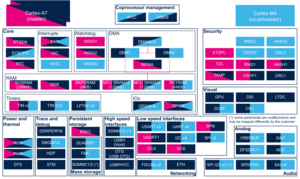
3.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 nonsecure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Trace & Debug | HDP | HDP | ☐ | |||
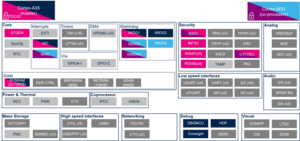
3.2.3. On STM32MP21x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
The table below is applicable to any TD flavor (A35-TD or M33-TD) ![]() .
.
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 nonsecure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 nonsecure (STM32Cube) | |||
| Trace & Debug | HDP | HDP | ⬚OP-TEE | ☐ | ⬚ | ⬚ | |
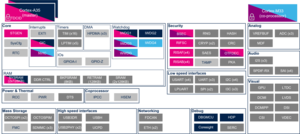
3.2.4. On STM32MP23x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
The table below is applicable to any TD flavor (A35-TD or M33-TD) ![]() .
.
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 nonsecure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 nonsecure (STM32Cube) | |||
| Trace & Debug | HDP | HDP | ⬚OP-TEE | ☐ | ⬚ | ⬚ | |
3.2.5. On STM32MP25x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
The table below is applicable to any TD flavor (A35-TD or M33-TD) ![]() .
.
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 nonsecure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 nonsecure (STM32Cube) |
Cortex-M0+ (STM32Cube) | |||
| Trace & Debug | HDP | HDP | ⬚OP-TEE | ☐ | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
4. Software frameworks and drivers[edit | edit source]
Below are listed the software frameworks and drivers managing the HDP peripheral for the embedded software components listed in the above tables.
- Linux®: HDP Linux driver
5. How to assign and configure the peripheral[edit | edit source]
The peripheral assignment can be done via the STM32CubeMX graphical tool (and manually completed if needed).
This tool also helps to configure the peripheral:
- partial device trees (pin control and clock tree) generation for the OpenSTLinux software components,
- HAL initialization code generation for the STM32CubeMPU Package.
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context in which the peripheral is assigned.