1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
X-LINUX-AWS is an OpenSTLinux distribution Expansion Package that enables the development of your IoT solution by bringing AWS IoT Greengrass[1] software, which transforms your STM32MPU into an IoT edge device that connects to the AWS cloud (AWS IoT Core™).
The purpose of this article is to explain step by step:
- How to install X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package on top of OpenSTLinux distribution.
- How to configure your Greengrass core device to connect to AWS IoT Core[2]
- How to secure the device identity and cloud connection with the use of OP-TEE or TPM for cryptographic operations, private key and certificate storage
- How to create a local MQTT network to connect local devices to your Greengrass core device
2. X-LINUX-AWS package software description[edit | edit source]
2.1. Overview[edit | edit source]
2.1.1. Connectivity[edit | edit source]
X-LINUX-AWS enables your STM32 Arm® Cortex® MPUs ![]() to:
to:
- Connect to AWS IoT Core as an IoT edge device (gateway)
- Connect client devices to local MQTT network
See all Greengrass features[3].
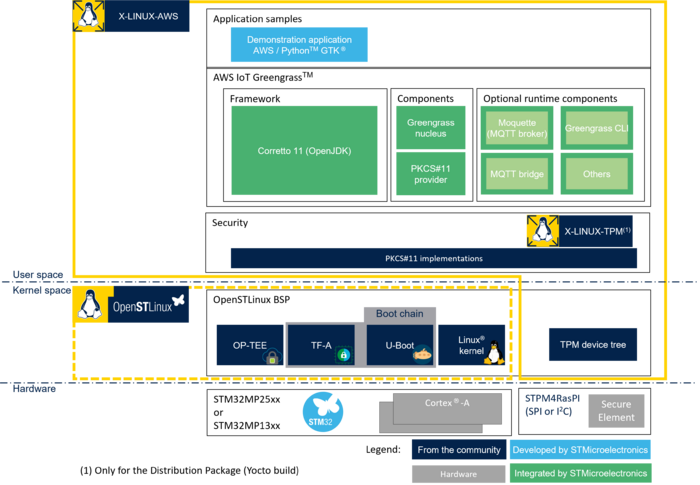
2.1.2. Software architecture[edit | edit source]
The X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package provides open source components that enable you to develop your own IoT solution.
As an example, the X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package provides a graphic demonstration application on top of Greengrass to interact with client devices and AWS IoT Core.
2.2. Versioning[edit | edit source]
The latest version of the X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package is 5.1.0.
Since its release v5.1.0, the major and minor versioning of the X-LINUX-AWS OpenSTLinux Expansion Package are aligned on the major and minor versioning of the OpenSTLinux Distribution. This prevents painful backward compatibility attempts and makes dependencies straightforward. The X-LINUX-AWS generic versioning vx.y.z is built as follows:
- x: major version matching the OpenSTLinux Distribution major version. Each new major version is incompatible with previous OpenSTLinux Distribution versions.
- y: minor version matching the OpenSTLinux Distribution minor version. Each new minor version might be incompatible with previous OpenSTLinux Distribution versions.
- z: patch version to introduce bug fixes. A patch version is implemented in a backward compatible manner.
2.3. Associated licenses[edit | edit source]
See X-LINUX-AWS licenses.
3. Prerequisites[edit | edit source]
- Knowledge of the AWS IoT Greengrass and AWS cloud account configuration is advised.
- An AWS account is needed to connect your board as a Greengrass core device. See how to get started and set up an AWS account[4].
Most of the cloud account configuration is described in this article. Additional information can be found in AWS IoT Greengrass Developer Guide Version 2[5].
3.1. Hardware prerequisites[edit | edit source]
- STM32 MPU Board
- TPM development kit (required if TPM is chosen as a secure solution, only available with X-LINUX-AWS Distribution Package).
- Internet access.
- For Wi-Fi® connection, see how to setup a WLAN connection.
- Connecting under proxy is not documented in this article. See how to configure a network proxy[6].
3.2. Software prerequisites[edit | edit source]
The X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package runs with OpenSTLinux ecosystem release v5.0.0 ![]() to v5.1.0
to v5.1.0 ![]() .
.
An AWS IoT Core access and AWS CLI[7] is needed to setup your STM32 MPU.
3.3. Known limitations[edit | edit source]
4. X-LINUX-AWS package software installation[edit | edit source]
There are two possibilities to install the additional X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package software to port on top of OpenSTLinux; select the one corresponding to your needs among:
- X-LINUX-AWS Starter package: quickly and easily bring Greengrass IoT AWS on the STM32 MPU with OP-TEE as a secure solution.
- X-LINUX-AWS Distribution package: an OpenEmbedded meta-layer must be added on top of the STM32 MPU Distribution Package to bring Greengrass IoT AWS with OP-TEE and TPM as secure solution.
5. X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package software setup[edit | edit source]
Once the X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package is installed on your STM32MPU board over Starter or Distribution Package, follow the guidelines below to set up your firmware.
5.1. AWS IoT and IAM resources configuration[edit | edit source]
Follow the instructions from Greengrass v2 Manual installation[8] to:
- Retrieve AWS IoT data endpoint.
- Retrieve AWS IoT credential endpoint.
- Create an AWS IoT thing
- Create an AWS IoT thing group and attach the thing to the group.
- Create an AWS IoT policy.
- Create a Token Exchange Role Alias.
- Create and attach a Token Exchange Role Alias Policy.
5.2. AWS IoT Greengrass core device configuration[edit | edit source]
Refer to How_to_get_Terminal and How_to_perform_ssh_connection articles to get your board IP address and know how to perform ssh or scp commands.
Example:
BOARD_IP=192.168.3.24
5.2.1. Without security[edit | edit source]
Expand to see detailed commands.
5.2.2. With secure key storage[edit | edit source]
This section describes how to generate and use secure credentials using OP-TEE or TPM.
TPM cannot be used if the software has been installed from the Starter Package.
- Board setup
Example:
PKCS11_SLOT=1
PKCS11_TOKEN_LABEL=GG_token
PKCS11_SO_PIN=1234567890
PKCS11_USER_PIN=12345
PKCS11_KEY_LABEL=GG_key
PKCS11_KEY_ID=0
GREENGRASS_CORE=MyGreengrassCore
CSR=/tmp/mykey_csr.pem
CERT=/tmp/core.pem
REGION=us-west-2
TOKEN_EXCHANGE_ROLE_ALIAS=GreengrassCoreTokenExchangeRoleAlias
DATA_ENDPOINT=xxxxxxxxxxxxx-ats.iot.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
CRED_ENDPOINT=xxxxxxxxxxxx.credentials.iot.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
Specific for OP-TEE: PKCS11_MODULE_LIB=/usr/lib/libckteec.so.0 OPENSSL_CONF_FILE=/etc/pki/openssl-pkcs11-provider-optee.cnf
Specific for TPM: PKCS11_MODULE_LIB=/usr/lib/pkcs11/libtpm2_pkcs11.so OPENSSL_CONF_FILE=/etc/pki/openssl-pkcs11-provider-tpm2.cnf
- PC setup
Example:
CSR=/tmp/mykey_csr.pem
CSR_ON_PC=/tmp/core.pem
CERT_ON_PC=/tmp/core.pem
CERT=/tmp/core.pem
GREENGRASS_CORE=MyGreengrassCore
AWS_IOT_POLICY=GreengrassV2IoTThingPolicy
TOKEN_EXCHANGE_ROLE_ALIAS_POLICY=GreengrassCoreTokenExchangeRoleAliasPolicy
- Initialize PKCS#11 token by providing a PIN SO (Security Officer):
pkcs11-tool --module ${PKCS11_MODULE_LIB} --init-token --slot ${PKCS11_SLOT} --label ${PKCS11_TOKEN_LABEL} --so-pin ${PKCS11_SO_PIN}
- Provide a user pin to the created token
pkcs11-tool --module ${PKCS11_MODULE_LIB} --label ${PKCS11_TOKEN_LABEL} --slot ${PKCS11_SLOT} --login --so-pin ${PKCS11_SO_PIN} --init-pin --pin ${PKCS11_USER_PIN}
- Generate a RSA-2048 private key with decrypt and sign usages:
pkcs11-tool --module ${PKCS11_MODULE_LIB} -l --slot ${PKCS11_SLOT} --pin ${PKCS11_USER_PIN} --keypairgen --key-type rsa:2048 --label ${PKCS11_KEY_LABEL} --id ${PKCS11_KEY_ID} --usage-decrypt --usage-sign
- Set token user pin that will be used by OpenSSL configuration file:
echo ${PKCS11_USER_PIN} > /etc/pki/pin.txt
- Generate a certificate signing request (CSR) with OpenSSL and PKCS#11 provider:
OPENSSL_CONF=${OPENSSL_CONF_FILE} openssl req -new -key "pkcs11:type=private;object=${PKCS11_KEY_LABEL};token=${PKCS11_TOKEN_LABEL}" -subj "/CN=${GREENGRASS_CORE}" -out ${CSR}
- Generate a certificate from CSR with the AWS console.
scp root@${BOARD_IP}:${CSR} ${CSR_ON_PC}
aws iot create-certificate-from-csr --certificate-signing-request file://${CSR_ON_PC} --certificate-pem-outfile ${CERT_ON_PC} --set-as-active
scp ${CERT_ON_PC} root@${BOARD_IP}:${CERT}
- Get certificate ARN from the response and store it in a variable:
Example:
CERT_ARN="arn:aws:iot:us-west-2:xxxxxxxx:cert/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
- Attach the certificate to the AWS IoT thing.
aws iot attach-thing-principal --thing-name ${GREENGRASS_CORE} --principal ${CERT_ARN}
- Attach the AWS IoT thing policy to the AWS IoT thing's certificate.
aws iot attach-policy --policy-name ${AWS_IOT_POLICY} --target ${CERT_ARN}
- Attach the AWS IoT Role policy to the AWS IoT thing's certificate
aws iot attach-policy --policy-name ${TOKEN_EXCHANGE_ROLE_ALIAS_POLICY} --target ${CERT_ARN}
- Import certificate into OP-TEE (Label and Id must be the same as the ones of the private key):
pkcs11-tool --module ${PKCS11_MODULE_LIB} --slot ${PKCS11_SLOT} --pin ${PKCS11_USER_PIN} --write-object ${CERT} --type cert --label ${PKCS11_KEY_LABEL} --id ${PKCS11_KEY_ID}
- Stop the Greengrass service.
systemctl stop greengrass
- Remove the old configuration.
rm /opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.tlog*
- Edit the configuration file.
sed -i "s/thingName: .*/thingName: \"${GREENGRASS_CORE}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/privateKeyPath: .*/privateKeyPath: \"pkcs11:object=${PKCS11_KEY_LABEL};type=private\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/certificateFilePath: .*/certificateFilePath: \"pkcs11:object=${PKCS11_KEY_LABEL};type=cert\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/slot: .*/slot: \"${PKCS11_SLOT}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/userPin: .*/userPin: \"${PKCS11_USER_PIN}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/library: .*/library: \"${PKCS11_MODULE_LIB//\//\\/}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/awsRegion: .*/awsRegion: \"${REGION}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/iotCredEndpoint: .*/iotCredEndpoint: \"${DATA_ENDPOINT}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/iotDataEndpoint: .*/iotDataEndpoint: \"${CRED_ENDPOINT}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
sed -i "s/iotRoleAlias: .*/iotRoleAlias: \"${TOKEN_EXCHANGE_ROLE_ALIAS}\"/g" \
/opt/greengrass/v2/config/config.yaml
- Start the Greengrass service.
systemctl start greengrass
5.3. AWS IoT Greengrass core device connection[edit | edit source]
Once correctly configured and the Greengrass service restarted, your device is connected to AWS IoT and appears as connected in the AWS IoT Console as a Greengrass core device.
You can also check in the logs that the device is successfully connected to AWS IoT Core:
grep -r "Successfully connected to AWS IoT Core" /opt/greengrass/v2/logs
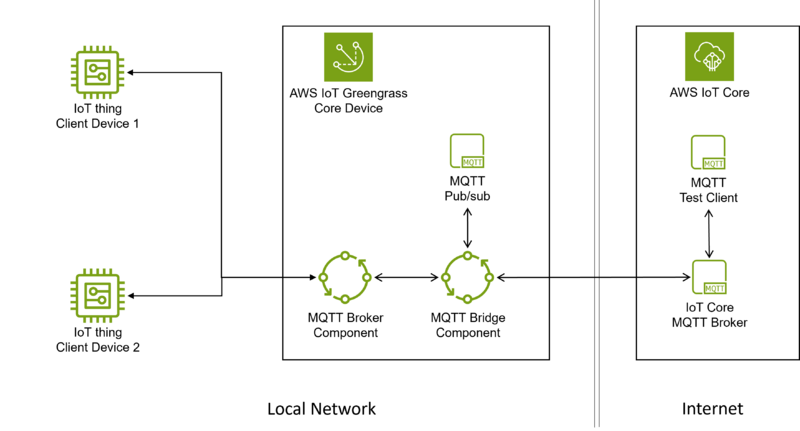
6. How to set up local MQTT network[edit | edit source]
This section describes how to set up a local MQTT network by deploying and configuring on the Greengrass core device:
- A local MQTT broker
- A local MQTT bridge
It also describes how to connect two client devices according to the following topology:
6.1. Core device and client device configuration[edit | edit source]
6.1.1. Component deployment[edit | edit source]
To support client device connection to the Greengrass core device, the following components must be deployed on the Greengrass core device:
| Component | Tested with version | Custom configuration | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| aws.greengrass.clientdevices.Auth | 2.4.3 | Yes | - |
| aws.greengrass.clientdevices.mqtt.Moquette | 2.3.5 | No | - |
| aws.greengrass.clientdevices.mqtt.Bridge | 2.3.0 | Yes | - |
| aws.greengrass.Cli | 2.11.2 | No | - |
| aws.greengrass.Nucleus | 2.11.3 | No | This component is already installed. However it makes sure your device is up to date. |
| aws.greengrass.ShadowManager | 2.3.3 | No | (Optional) Allows the update the device shadow of client devices connected to your core device. |
Configurations:
- aws.greengrass.clientdevices.Auth configured, for example, with a permissive configuration that allows all authorized client devices to connect and publish/subscribe to all topics:
{
"deviceGroups": {
"formatVersion": "2021-03-05",
"definitions": {
"MyPermissiveDeviceGroup": {
"selectionRule": "thingName: *",
"policyName": "MyPermissivePolicy"
}
},
"policies": {
"MyPermissivePolicy": {
"AllowAll": {
"statementDescription": "Allow client devices to perform all actions.",
"operations": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"*"
]
}
}
}
}
}
- aws.greengrass.clientdevices.mqtt.Bridge configured, for example, with a policy that allows the bridge to forward messages:
| Topic | To client devices | To core device | To IoT Core |
|---|---|---|---|
| From client devices | NA | from_local/hello/world topic | from_local/hello/world topic |
| From core device | from_core/hello/world topic | NA | from_core/hello/world topic |
| From IoT Core | from_cloud/hello/world topic | from_cloud/hello/world topic | NA |
{
"mqttTopicMapping": {
"ClientDevicesToCloud": {
"topic": "from_local/hello/world",
"source": "LocalMqtt",
"target": "IotCore"
},
"ClientDevicesToCore": {
"topic": "from_local/hello/world",
"source": "LocalMqtt",
"target": "Pubsub"
},
"CloudToCore": {
"topic": "from_cloud/hello/world",
"source": "IotCore",
"target": "Pubsub"
},
"CloudToClientDevices": {
"topic": "from_cloud/hello/world",
"source": "IotCore",
"target": "LocalMqtt"
},
"CoreToCloud": {
"topic": "from_core/hello/world",
"source": "Pubsub",
"target": "IotCore"
},
"CoreToClientDevices": {
"topic": "from_core/hello/world",
"source": "Pubsub",
"target": "LocalMqtt"
}
}
}
Refer to the connect client devices documentation[9] for more details.
6.1.2. Endpoint management[edit | edit source]
You can either use the IP detector component (aws.greengrass.clientdevices.IPDetector) to automatically manage endpoints if you have a simple network setup, or you can manage it manually:
- Replace "192.0.2.0" by the IP address of your board
- If not overwritten, by default the port of the MQTT broker component (Moquette) is 8883
aws greengrassv2 update-connectivity-info \
--thing-name MyGreengrassCore \
--cli-input-json '{
"connectivityInfo": [
{
"hostAddress": "192.0.2.0",
"portNumber": 8883,
"id": "localIP_192.0.2.0"
}
]
}'
Refer to the manage core device endpoints documentation[10] for more details.
6.1.3. Client device configuration[edit | edit source]
This section explains how to connect two devices to the Greengrass core by using the Eclipse Mosquitto™ client. These two devices run on a computer connected to the same local network as the Greengrass core device.
- Create an AWS IoT policy for the Greengrass client devices
aws iot create-policy --policy-name ClientDeviceIoTThingPolicy --policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iot:*",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "greengrass:Discover",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}'
- Configure Greengrass service role
- Create a role with a trust policy that allows AWS IoT Greengrass to assume the role.
- Replace region and account-id with your values
- You may also change the role name
- Create a role with a trust policy that allows AWS IoT Greengrass to assume the role.
aws iam create-role --role-name Greengrass_ServiceRole --assume-role-policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "greengrass.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"ArnLike": {
"aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:greengrass:region:account-id:*"
},
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "account-id"
}
}
}
]
}'
- Copy the role ARN from the role metadata in the output. You use the ARN to associate the role with your account.
- Attach the AWSGreengrassResourceAccessRolePolicy policy to the role.
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name Greengrass_ServiceRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSGreengrassResourceAccessRolePolicy
- Associate the Greengrass service role with AWS IoT Greengrass for your AWS account.
- Replace role-arn with the ARN of the service role
- Associate the Greengrass service role with AWS IoT Greengrass for your AWS account.
aws greengrassv2 associate-service-role-to-account --role-arn role-arn
Refer to the connect client devices to core devices documentation[11] for more details.
6.1.4. Client device creation[edit | edit source]
- Create two client devices on AWS IoT Core.
aws iot create-thing --thing-name ClientDevice1
aws iot create-thing --thing-name ClientDevice2
- Add the client devices to the Greengrass core group.
aws iot add-thing-to-thing-group --thing-name ClientDevice1 --thing-group-name MyGreengrassCoreGroup
aws iot add-thing-to-thing-group --thing-name ClientDevice2 --thing-group-name MyGreengrassCoreGroup
- Create key and certificate, attach it to the created policy, and attach it to each device.
mkdir device-client-1-certs
aws iot create-keys-and-certificate --set-as-active --certificate-pem-outfile device-client-1-certs/device.pem.crt --private-key-outfile device-client-1-certs/private.pem.key
aws iot attach-thing-principal --thing-name ClientDevice1 --principal cert_client_device_1_arn
aws iot attach-policy --policy-name ClientDeviceIoTThingPolicy --target cert_client_device_1_arn
mkdir device-client-2-certs
aws iot create-keys-and-certificate --set-as-active --certificate-pem-outfile device-client-2-certs/device.pem.crt --private-key-outfile device-client-2-certs/private.pem.key
aws iot attach-thing-principal --thing-name ClientDevice2 --principal cert_client_device_2_arn
aws iot attach-policy --policy-name ClientDeviceIoTThingPolicy --target cert_client_device_2_arn
- Associate client devices with core device:
aws greengrassv2 batch-associate-client-device-with-core-device \
--core-device-thing-name MyGreengrassCore \
--entries thingName=ClientDevice1 thingName=ClientDevice2
- Retrieve IP address, port number and CA of Greengrass core device using Greengrass discovery RESTful API[12].
curl -i \
--cert device-client-1-certs/device.pem.crt \
--key device-client-1-certs/private.pem.key \
https://greengrass-ats.iot.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:8443/greengrass/discover/thing/ClientDevice1
curl -i \
--cert device-client-2-certs/device.pem.crt \
--key device-client-2-certs/private.pem.key \
https://greengrass-ats.iot.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:8443/greengrass/discover/thing/ClientDevice2
Store CA into a file named ca.pem for example.
You also can retrieve these information from the board:
- IP address
ip a
- CA
cat /opt/greengrass/v2/work/aws.greengrass.clientdevices.Auth/ca.pem
- Port: by default 8883 (if no configuration modification has been done on the MQTT broker (aws.greengrass.clientdevices.mqtt.Moquette)).
6.2. MQTT subscribe and publish[edit | edit source]
6.2.1. Subscribe[edit | edit source]
- Launch ClientDevice1 as MQTT subscriber:
mosquitto_sub \
-h ${GG_CORE_IP} \
-p 8883 \
--cert device-client-1-certs/device.pem.crt \
--key device-client-1-certs/private.pem.key \
--cafile ca.pem \
-t "+/hello/world" \
-u ClientDevice1 \
-i ClientDevice1
- Launch Greengrass CLI with the subscribe command:
/opt/greengrass/v2/bin/greengrass-cli pubsub sub -t "+/hello/world"
- Subscribe to the topic "+/hello/world" on AWS IoT MQTT test client in a web browser.
6.2.2. Publish[edit | edit source]
- Publish a message from the Device Client 2
mosquitto_pub \
-h ${GG_CORE_IP} \
-p 8883 \
--cert device-client-2-certs/device.pem.crt \
--key device-client-2-certs/private.pem.key \
--cafile ca.pem \
-t "from_local/hello/world" \
-m "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from device" \
-u ClientDevice2 \
-i ClientDevice2
- Publish a message from the Greengrass core device:
/opt/greengrass/v2/bin/greengrass-cli pubsub pub -t "from_core/hello/world" -m "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from GG core device"
- Publish a message from the AWS IoT MQTT test client in a web browser:
- topic: "from_cloud/hello/world"
- message: "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from IoT Core"
6.2.3. Expected results[edit | edit source]
Messages:
- "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from Client device" on topic "from_local/hello/world"
- "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from GG Core device" on topic "from_core/hello/world"
- "Hello X-LINUX-AWS from IoT Core" on topic "from_cloud/hello/world"
have been received by:
- ClientDevice1
- Core Device
- IoT Core
7. Demonstration application[edit | edit source]
The X-LINUX-AWS Expansion Package is provided with a demonstration application in GTK demo launcher shown with the AWS logo:
Click on the AWS logo to launch the demonstration application.
Double-click anywhere on the screen to exit the application.
This demonstration application is composed of five tabs:
7.1. Settings tab[edit | edit source]
- It displays the current settings applied to the Greengrass core device.
- These settings are read from file /opt/greengrass/v2/config/effectiveConfig.yaml
- The view can be refreshed by clicking on the bottom button Read.
7.2. Components tab[edit | edit source]
- It displays the current components installed on the Greengrass core device.
- The list can be refreshed by clicking on the bottom button Refresh.
- This list is obtained with the Greengrass CLI component:
/opt/greengrass/v2/bin/greengrass-cli component list
7.3. LAN tab[edit | edit source]
- It displays the board IP address.
- The IP addresses can be refreshed by clicking on the bottom button Refresh.
- The IP address for the first Ethernet interface is obtained with:
ip -4 addr show end0 | grep -oP '(?<=inet\s)\d+(\.\d+){3}'
7.4. MQTT Pub tab[edit | edit source]
- It allows the publication of an MQTT message on a topic, both editable, by clicking on the bottom button Publish.
- "Published" is displayed once done successfully.
- Publishing is done using the Greengrass CLI component:
/opt/greengrass/v2/bin/greengrass-cli pubsub pub -t topic -m message
7.5. MQTT Sub tab[edit | edit source]
- It allows the subscription to an editable MQTT topic by clicking on the bottom button Subscribe.
- "Subscribed" is displayed once done successfully.
- Subscription can be stopped by clicking on the bottom button Unsubscribe.
- Subscribing is done using the Greengrass CLI component:
/opt/greengrass/v2/bin/greengrass-cli pubsub sub -t topic
8. References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ AWS IoT Greengrass
- ↑ AWS IoT Core™
- ↑ Greengrass features
- ↑ How to get started and set up an AWS account
- ↑ AWS IoT Greengrass Developer Guide Version 2
- ↑ How to configure a network proxy
- ↑ AWS CLI
- ↑ Greengrass v2 Manual installation
- ↑ Connect client devices documentation
- ↑ Manage core device endpoints documentation
- ↑ Connect client devices to core devices documentation
- ↑ Greengrass discovery RESTful API