1. Article Purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- explain the different lifecycle available on STM32MPU
- explain when the will be used
- how to manage the transitions.
2. Lifecycle purpose[edit source]
The MPU lifecycle manage the device behavior of some security features during different development phases. It enables some secure mechanisms that are specific on every device family to enforce the security of the system.
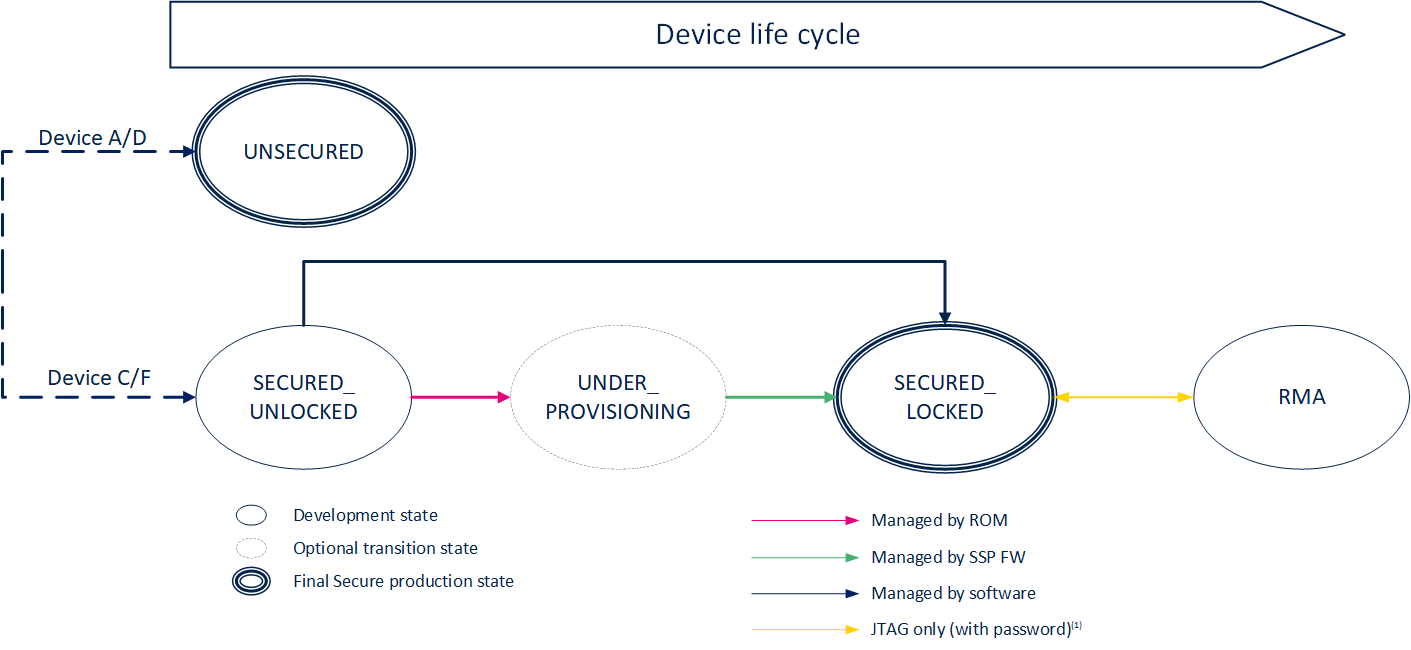
3. Lifecycle overview[edit source]
The lifecycle of the STM32 MPU is following the below diagram state:
Each state of the diagram refers implies a specific device behavior:
3.1. Closed Unlocked[edit source]
In this state, the device is not protected. It is used as an unsecure device usage. It allows to use unsigned firmware for booting. This state is the final state for
All OTP are available for usage.
On STM32MP13xC/F lines ![]() , STM32MP15xC/F lines
, STM32MP15xC/F lines ![]() , STM32MP25xC/F lines
, STM32MP25xC/F lines ![]() , it is possible to evaluate the secure features without locking the device.
, it is possible to evaluate the secure features without locking the device.
3.2. Closed Locked Unprovd[edit source]
The Secure provisioning state is a specific state where the device is only limited to execute the SSP use case.
In this state, the device certificate is generated and can be exported. All the OTP are available for provisioning. As soon as the SSP process is done, the firmware will directly set the lifecycle to the next state.
3.3. Closed Locked Provd[edit source]
This state is a final secure state. Once the device achieve this state, all the hardware secure mechanism are enabled:
- Secure boot is enabled: The first booted images must be signed with the provisioned keys.
- Isolation mechanism are in place and must be guarantee to guarantee the low power mechanism:
- Backup registers security is enforced.
- Peripheral assignment.
On STM32MP25x lines ![]() , the configuration that impact the ROM code is detailed in the ROM isolation description.
, the configuration that impact the ROM code is detailed in the ROM isolation description.
3.4. RMA[edit source]
RMA is a specific analysis state where it becomes possible to debug device issues. It is protected by a password and required a specific processing to enter in this state describe in AN5827. It ensure that all the secrets stored in the Upper OTP are no more accessible (including the hardware unique key usage).
The switch between RMA and Secure closed device state is limited by a counter:
4. Encoding lifecycle[edit source]
The lifecycle uses a set of OTP words to encode the different states.
4.1. STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Closed Unlocked | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | CFG0 | ||
| Bit [9:0] | OTP Mode | b0000010111 | |
| Closed Locked Unprovd | |||
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | CFG0 | ||
| Bit [9:0] | OTP Mode | b0000010111 | |
| 9 | CFG9 | ||
| Bit [5] | SSP_REQ | b1 | |
| Closed Locked Provd | |||
| OTP Word | Name | Value | |
| 0 | CFG0 | ||
| Bit [9:0] | OTP Mode | b0000111111 | |
| 9 | CFG9 | ||
| Bit [6:5] | SSP_REQ / SSP_SUCCESS | b11 | |
4.2. STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Closed Unlocked | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | CFG0 | ||
| Bit [6] | Closed_device | 0 | |
| Closed Locked Unprovd | |||
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | CFG0 | ||
| Bit [6] | Closed_device | 0 | |
| 8 | CFG8 | ||
| Bit [8] | SSP_REQ | b1 | |
| Closed Locked Provd | |||
| OTP Word | Name | Value | |
| 0 | CGF0 | ||
| Bit [6] | Closed_device | b1 | |
| 8 | CFG8 (Only in case of SSP) | ||
| Bit [9:8] | SSP_REQ / SSP_SUCCESS | b11 | |
4.3. STM32MP25x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Closed Unlocked | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | OTP_HW_WORD0 | 0xAAAA5555 | |
| Closed Locked Unprovd | |||
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | OTP_HW_WORD0 | 0xAAAA5555 | |
| 18 | BOOTROM_CONFIG_9 | ||
| Bit [3:0] | secure_boot | 0xF | |
| 124 | HCONF1 | ||
| Bit 20 | DISABLE_SCAN | 1 | |
| Closed Locked Provd | |||
| OTP Word | Bit | Name | Value |
| 0 | OTP_HW_WORD0 | 0xAAAA5555 | |
| 18 | BOOTROM_CONFIG_9 | ||
| Bit [3:0] | secure_boot | 0xF | |
| Bit [7:4] | prov_done | 0xF | |
| Bit [15:12] | otp_prov_done (only if SSP used) | 0xF | |
| 124 | HCONF1 | ||
| Bit 20 | DISABLE_SCAN | 1 | |
5. How to change the lifecycle[edit source]
Different ways are available to change the device lifecycle:
- In a trusted environment:
- STM32DDRFW-UTIL which allows OTP update directly on board or connected to STM32CubeProgrammer.
- stm32key command part of U-Boot firmware included in the OpenSTLinux.
- In an untrusted environment:
- SSP process that directly managed the lifecycle transition.