1. Article purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the Resource Isolation Framework and its main features,
- list the different elements that make it up
- explain how RIF is integrated at system level
2. What is Resource Isolation Framework ?[edit source]
The Resource Isolation Framework (aka RIF) is a fully integrated firewall solution, isolating execution contexts from each other. It allows to protect access to:
- Internal memories
- External memories
- Internal peripherals
- Peripheral features when a peripheral is providing multiple features that could be assigned to different execution contexts
and from:
- any bus master peripherals
2.1. Some key definitions[edit source]
It is important to define few acronyms used in RIF:
- CID = Compartment IDentifier: Identifier added to any bus master peripheral transaction for emitter identification and filtering.
- TDCID = Trusted Domain CID: It is the master owning the highest access rights of the platform, capable to configure critical secure and system resources. It is the boot processor part of the trusted boot. Value is fixed after ROM code execution.
- DDCID = Debug Domain CID: It is dedicated CID value, assignable only to DAP interface which provide open access to any resource via Jtag interface to ease platform debug. This configuration is only possible when device is in "CLOSED_UNSECURED" state and debug opened by TDCID secure OS during platform boot.
2.2. RIF concept[edit source]
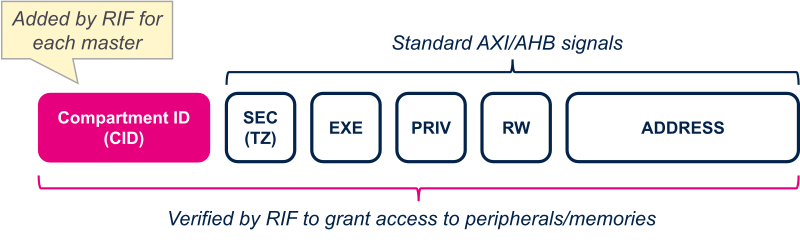
RIF could be seen as an extension of the bus interconnect, adding information at each transaction to identify emitter and being to able to filter transaction in parallel of address decoding.
To do that, a Compartment Identifier (CID) is assigned to each bus master (CPU and peripherals) in addition to secure, read/write, execute and address fields.
The following figure shows all the elements that compose a transaction and which are used to filter access on the different resources of the device.
2.3. RIF composition[edit source]
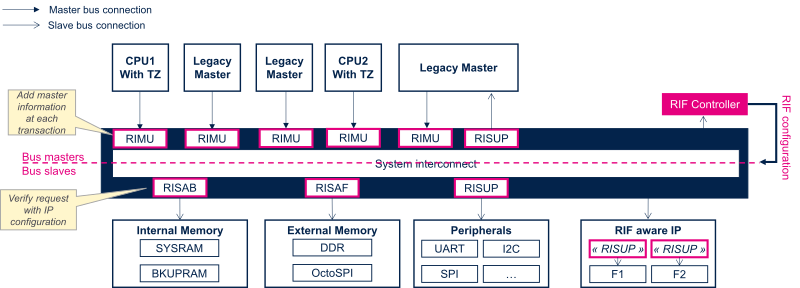
RIF is made up of different elements:
- RIMU = Resource Isolation Master Unit: They are located in front of each bus master port to make transaction unique.
- RISUP = Resource Isolation Slave Unit Peripheral: They are located in front of each slave bus connector to filter transaction according to defined rules.
- RISAL = Resource Isolation Save Address Light: Located in front of low power internal memories to filter access based on variable sized address space regions.
- RIFSC= RIF Security Controller: Provide configuration registers for all RIMU, RISUP and RISAL. Configuration is persistent in low power modes.
- RISAF= Resource Isolation Save Address Full: Located in front of external memories to filter access based on variable sized address space regions. Configuration lost in low power Standby(1/2) modes.
- RISAB= Resource Isolation Save Address Block: Located in front of internal SRAM to filter access based on fixed-sized embedded memory blocks Configuration lost in low power Standby(1/2) modes.
- IAC = Illegal Access Controller: allow to configure and monitor RIF error events.
In addition, some peripherals can't directly rely on this infrastructure because isolation granularity is not at peripheral level but feature one. For example RTC is offering secure time but also several alarms. It should be possible to assign each RTC feature to a specific execution context. To do that, RIF concept has been integrated directly inside the peripheral itself. Such peripherals are named RIF-aware peripherals. RIF-aware peripherals are in general system and communication peripherals like RCC, PWR, EXTI, GPIO, RTC, IPCC, HSEM, ...
The following figure shows a generic implementation of the RIF in a device.
2.4. RIF protection model[edit source]
2.4.1. RIF peripheral protection model[edit source]
RIF offers different protection level for each protected peripheral resource.
RIF filtering rules are based on:
- Secure level
- Privilege level
- CID
CID filtering has 3 modes:
- Disabled : any masters fitting secure and privilege levels can access the resource
- Enabled in static mode: One authorized CID value defined. Only masters fitting CID value, secure and privilege levels can access the resource
- Enabled in semaphore mode: Authorized CIDs are defined in semaphore CID list. Masters with authorized CID should take RIF HW semaphore.
Note: Semaphore mode is not present in some RIF-aware peripherals (EXTI, RTC, ...).
Note: In semaphore mode, if semaphore CID list is empty, resource can't be accessed by any master.
2.4.2. RIF memory protection model[edit source]
RIF offers different protection level for each chunk of memory. Chunk of memory depends on memory type and associated RISAx protection unit. It could be:
- fixed pages and blocks for internal memories protected by RISAB
- configurable region for internal and external memories protected by RISAL or by RISAF
For each chunk of memory it is possible to define some RIF rules based on:
- Global Secure level
- Global Privilege level (if CID filtering disabled)
- CID filtering activation
- Read access per CID (if filtering activated)
- Write access per CID (if filtering activated)
- Privilege level per CID (if CID filtering activated)
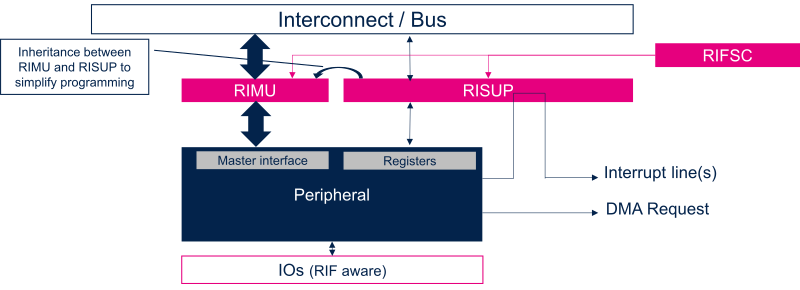
2.5. Master peripherals RIF protection[edit source]
Master peripherals own two bus connections:
- one control port to access configuration registers. This port is protected by a RISUP to filter accesses according to rules defined in RIFSC.
- one initiator port to generate bus read/write accesses. This port is extended by a RIMU to add transaction identifiers (CID, Secure bit, Privilege bit)
To simplify programming model, some inheritance and consistency checks have been implemented between the RISUP and the RIMU associated to a master peripheral:
- CID inheritance : Master peripheral takes the CID of the processor controlling it.
- Secure bit consistency: Master secure bit can be set only if it is controlled by a secure processor execution context
2.6. Relationship between RIF and RCC[edit source]
RCC is a RIF-aware peripheral. That means RCC is integrating some RIF RISUP to protect access to its different features. RCC is offering reset and clock control for all the different peripherals present in the device. To ease programming consistency between RIFSC and RCC RIF protection, a HW inheritance between peripheral RISUP and RCC peripheral configuration register. That means only execution context owning the peripheral can control associated clocks and reset.
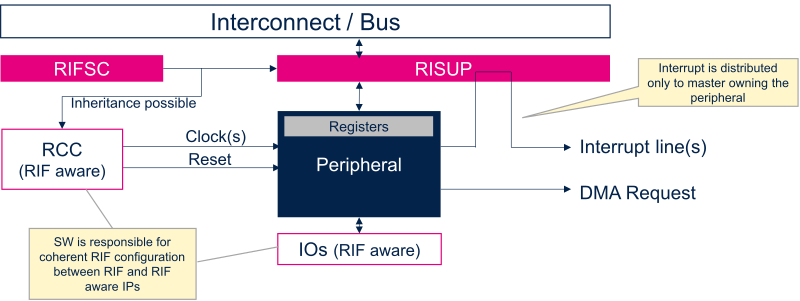
This inheritance is not implemented for RIF-aware and system peripherals which are used at the same time by different execution contexts. Indeed, RCC supports peripheral auto clock gating according as soon as peripheral owner is entering in (LP/LPLV)Stop low power mode. This feature is not valid for RIF-aware and system peripherals and RCC implements a specific owning mechanism to link clock gating on state of the system instead of state of one processor.
2.7. RIF and low power modes[edit source]
The following table sums up which part of RIF configuration is preserved in the different low power modes.
| RIF component | Run(1/2) | (LP/LPLV)Stop(1/2) | Standby(1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RIFSC | Preserved | Preserved | Preserved |
| RISAB | Preserved | Preserved | Lost |
| RISAF | Preserved | Preserved | Lost |
2.8. RIF and debug[edit source]
Thanks to RIF, it is possible to force Jtag DAP access rights according to selected debug profile. The following table sums the possible configuration:
| Debug profile | Cortex-A debug | Cortex-M debug | DAP access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microcontroller debug | No debug | Secure | Same as Cortex-M |
| Non-secure | |||
| Microprocessor debug | Secure | No debug | Same a Cortex-A |
| Non-secure | |||
| Global debug | Secure | Same as Cortex-M or same as Cortex-A or DDCID | |
| Non-secure | |||
Setting DAP master CID to DDCID allows to access any platform resources via DAP interface, whatever their associated RIF rules configuration. This allows to debug the platform without having to modify RIF configuration for debug purpose.
Of course secure and privilege level of DAP interface could also be configured.
3. How to configure RIF[edit source]
3.1. RIF configuration responsibility[edit source]
RIF main configuration is under the TDCID responsibility. Registers can't be access by other masters. That means RIF configuration should be done by secure bootloader and secure OS running on main processor.
Nevertheless, all RIF registers are in read for all, that means any execution context can read them to check if it can access a resource or not.
It is also possible to delegate some sub-configurations to some execution contexts. For examples:
- Secure master having access to a resource can change security level
- Privileged master having access to a resource can change privilege level
- Memory region could be delegated to one owner (defined by CID, secure and privilege levels) which can define new access rights. It is useful for memory sharing management.
3.2. RIF default configuration[edit source]
RIF registers have default value with following rules:
- for peripherals protected by RISUP and features of RIF-aware peripherals
- Non-secure level
- Unprivilege level
- CID filtering disabled
- for GPIO
- Secure level
- Unprivilege level
- CID filtering disabled
- for RISAF protected memories
- base region 0 accessible only to TDCID secure privilege execution context
- for RISAB protected internal memories
- depends on internal memory main allocation, please refer to RISAB internal peripheral article
- for RISAL protected internal memories
- assigned to non-secure, unprivilege, Cortex-M processors (Cortex-M processors depending on devices, please refer to RISAL internal peripheral article)
3.3. How to generate RIF configuration[edit source]
The RIF configuration could be done via STM32CubeMX graphical tool. Indeed STM32CubeMX integrates natively RIF information in its different configuration panels:
- Peripheral assignment between the different execution contexts allows to generate RIFSC RISUP configuration
- RIF-aware configuration panels allow to assign each feature to the different execution contexts and so to generate associated configuration
- RIF panel provides a way to configure the different master interfaces and to generate RIFSC RIMU configuration, to create the different memory regions and to generate associated RISAF, RISAB and RISAL
The advantage of using STM32CubeMX is that consistencies between the different RIF components and between the different SW components running on the platform including ROM code are guarantee.