1. Article purpose[edit source]
The main purpose of this article is to present how an Hardware Unique Key (HUK) can be used on the STM32MPU platforms.
2. HUK overview[edit source]
The Hardware Unique Key is a symmetric encryption key stored in the OTP of the platform. The HUK is different for each chip produced.
Because the HUK is unique for a chip, encrypting data with it ensure that it cannot be decrypted by any other chip. Hence, the HUK is used to secure information that need to be kept inside the chip. This prevent any hacker to clone the encrypted data to use it on another chip. For example, The HUK is used to encrypt the secure storage.
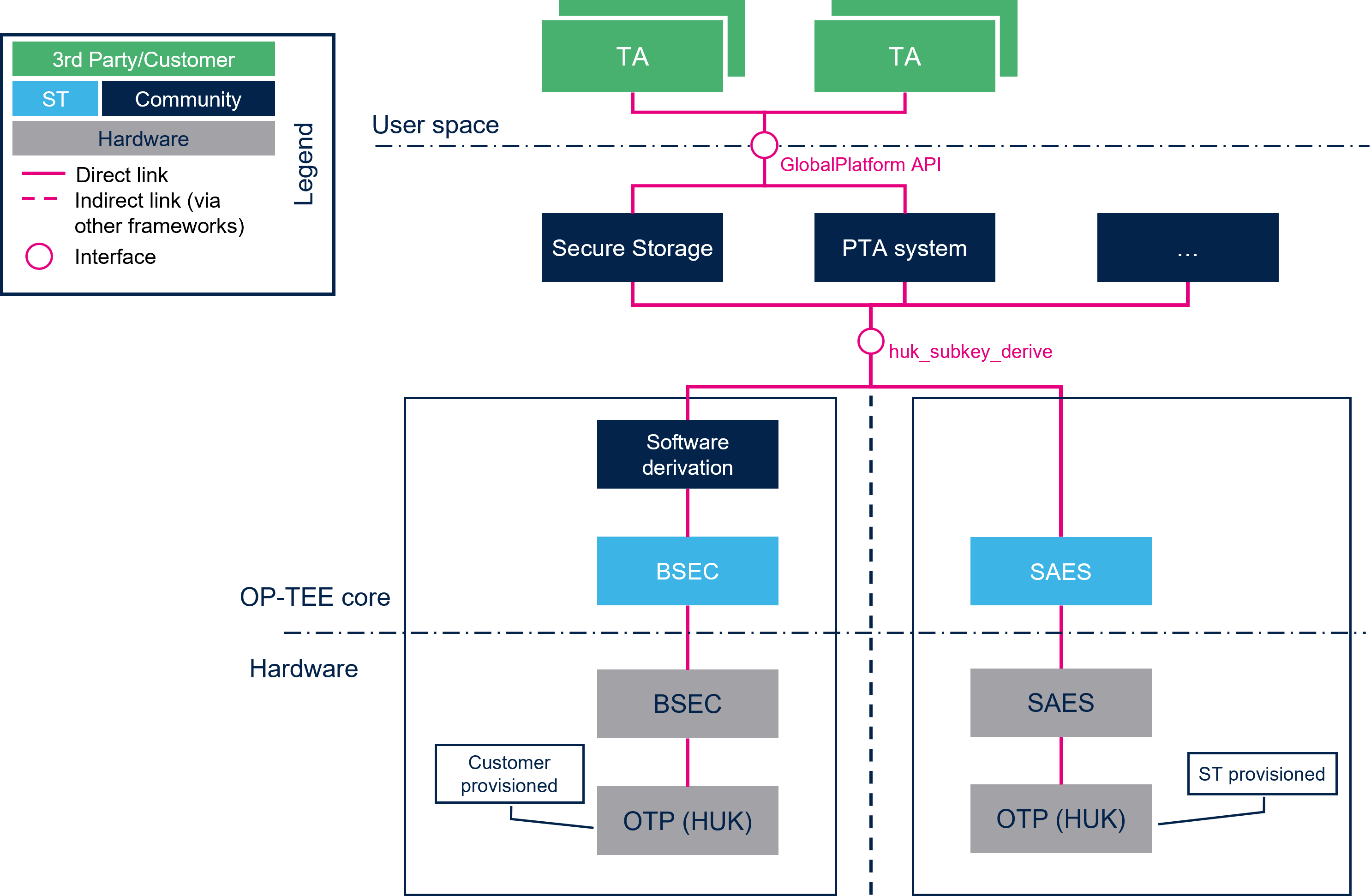
In most cases, we want to use different keys for several use cases to prevent an attacker to access all the data encrypted if one key is found.
Hence we do not want to use the HUK as is. We will use keys derived from the HUK (DHUK). The HUK is also called Root HUK because it is use as a root key to obtain a DHUK.
2.1. HUK : Hardware protected[edit source]
On STM32MP13xC/F lines ![]() , STMicroelectronics provisions an HUK in the OTPs. These OTPs cannot be read with the BSEC IP. The OTPs storing the HUK are directly wired to SAES.
, STMicroelectronics provisions an HUK in the OTPs. These OTPs cannot be read with the BSEC IP. The OTPs storing the HUK are directly wired to SAES.
SAES computes internally a derived HUK (DHUK). The value of DHUK depends on the privilege level, key selection, key selected mode, the chaining mode, and on whether SAES peripheral is secure or non-secure.
2.2. HUK : Software implementation[edit source]
On STM32MP15x lines ![]() , STMicroelectronics does not pre-provision an HUK. It is a customer choice to define and provision one in the OTP.
, STMicroelectronics does not pre-provision an HUK. It is a customer choice to define and provision one in the OTP.
The provisioning can be done with the fuse command in U-Boot or with STM32CubeProgrammer.
The key derivation is computed thanks to software algorithms from the HUK provisioned by the customer.
3. OP-TEE API[edit source]
OP-TEE provides the following function to perform a software key derivation.
TEE_Result huk_subkey_derive(enum huk_subkey_usage usage, const void *const_data, size_t const_data_len, uint8_t *subkey, size_t subkey_len);
The function huk_subkey_derive call the function tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key to read the HUK. The default implementation provided in OP-TEE returned a statically defined key. This function is redefined for platforms that allows the HUK to be read by the software (STM32MP15x lines ![]() ).
).
TEE_Result tee_otp_get_hw_unique_key(struct tee_hw_unique_key *hwkey);
3.1. HUK : Hardware protected[edit source]
On platforms that provides SAES (STM32MP13xC/F lines ![]() ), the key derivation is done by the hardware. Hence the function huk_subkey_derive is redefined in the SAES driver.
), the key derivation is done by the hardware. Hence the function huk_subkey_derive is redefined in the SAES driver.
3.2. HUK : Software implementation[edit source]
If a customer choose to add an HUK, he must configure OP-TEE to indicate in which OTPs the HUK is located. The location of the HUK in the OTP can be set in the DT of OP-TEE or in the build command line.
The location of the HUK in the OTP can be represented with an additional NVMEM data cell in BSEC. The following code is an example to register a 128 bits HUK provisionned in OTPs 60 to 63.
&bsec {
huk_otp: huk-otp@f0 {
reg = <0xf0 0x10>;
};
};
To read the location of the HUK in the DT, OP-TEE must be compiled with the following directives :
CFG_STM32MP15_HUK=y CFG_STM32_HUK_FROM_DT=y
The location of HUK in the OTP can be provided in the OP-TEE build command. There are two possibilities :
- The HUK is stored in contiguous OTPs. In this case you can use the first OTP storing the HUK. The following directives locates the HUK in OTP 60 to 63.
CFG_STM32MP15_HUK=y CFG_STM32MP15_HUK_OTP_BASE=0xf0
- The HUK is scattered in a non contiguous field. For example, the following directives locates the HUK in OTPs 60 63 64 65
CFG_STM32MP15_HUK=y CFG_STM32MP15_HUK_BSEC_KEY_0=0xf0 CFG_STM32MP15_HUK_BSEC_KEY_1=0xfc CFG_STM32MP15_HUK_BSEC_KEY_2=0x100 CFG_STM32MP15_HUK_BSEC_KEY_3=0x104
4. References[edit source]