This article gives information about the ARM® CoreSight™ subsystem.
It explains what are the principle peripherals of this subsystem, how they interact, and how to activate them.
1. Framework purpose[edit source]
ARM® CoreSight™ products include a wide range of trace macrocells for ARM® processors, system and software instrumentation and a comprehensive set of IP blocks to enable the debug & trace of the most complex, multi-core SoCs.
ARM® has defined an open CoreSightarchitecture to allow SoC designers to add debug & trace capabilities for other IP cores in to the CoreSight infrastructure.
2. System overview[edit source]
2.1. Components description[edit source]
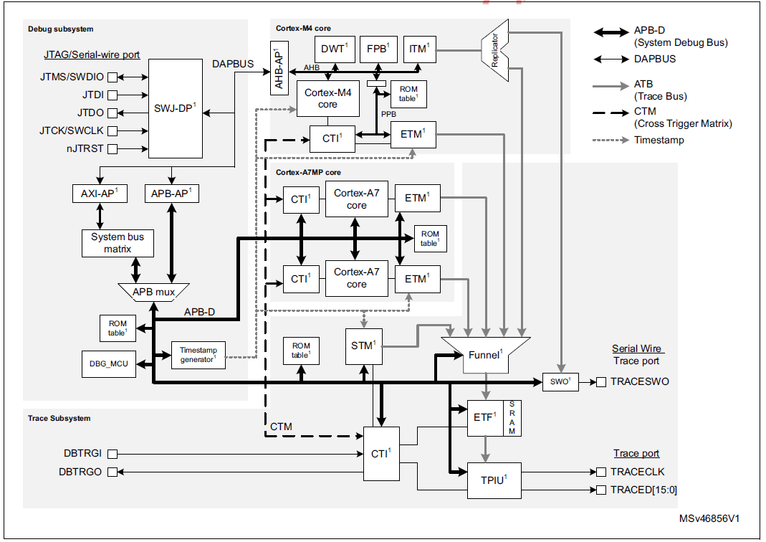
The debug features are based on Arm® CoreSight™ components:
• SWJ-DP: JTAG/Serial-wire debug port
• AXI-AP: AXI access port
• AHB-AP: AHB access port
• APB-AP: APB access port
• ITM: Instrumentation Trace Macrocell
• DWT: Data Watchpoint and Trace
• ETM: Embedded Trace Macrocell
• ETF: Embedded Trace FIFO
• TPIU: Trace Port Interface Unit
• SWO: Serial Wire Output
• CTI: Cross Trigger Interface
• CTM: Cross Trigger Matrix
• Timestamp Generator
• STM: System Trace Macrocell
More information about these components can be found in the Arm® documents referenced [1]
2.2. Features[edit source]
Refer to STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
3. Principle[edit source]
Internal peripheral generates a trace stream, namely instruction traces, depending on instructions and events happening when CPUs are executing a program. This encoded stream can be then stored in a dedicated SRAM via a buffer or extracted through an external JTAG port.
4. Configuration[edit source]
4.1. Kernel configuration[edit source]
Detailed procedure on how to activate the CoreSight subsystem :
4.2. Device tree configuration[edit source]
Detailed DT configuration for STM32 internal peripherals:
5. How to use the subsystem[edit source]
See examples in How to use CoreSight.
6. References[edit source]
- ↑ [1. IHI 0031C (ID080813) - Arm® Debug Interface Architecture Specification ADIv5.0 to
ADIv5.2, Issue C, 8th Aug 2013.
2. DDI 0480F (ID100313) - Arm® CoreSight™ SoC-400 r3p1 Technical Reference Manual, Issue F, 26th Sept 2013.
3. DDI 0461B (ID010111) - Arm® CoreSight™ Trace Memory Controller r0p1 Technical Reference Manual, Issue B, 10 Dec 2010
4. DDI 0314H - Arm® CoreSight™ Components Technical Reference Manual, Issue H, 10 July, 2009
5. DDI 0403D (ID100710) - Arm® v7-M Architecture Reference Manual, Issue Derrata2010_Q3, November 2010
6. DDI 0468A (ID101712) - Arm® CoreSight™ ETM™-A7 r0p0, Issue A, 12 Sept 2011
7. DDI 0440C (ID070610) - Arm® CoreSight™ ETM™-M4 r0p1 Technical Reference Manual, Issue C, 29 June 2012
8. DDI 0528B (ID062514) - Arm® CoreSight™ STM-500 System Trace Macrocell r0p1 Technical Reference Manual, Issue B, 11 March 2014
9. DDI 0464F (ID051113) - Arm® Cortex®-A7 MPCore™ r0p5 Technical Reference Manual, Issue F, 11 April 2013],Arm® documents referenced