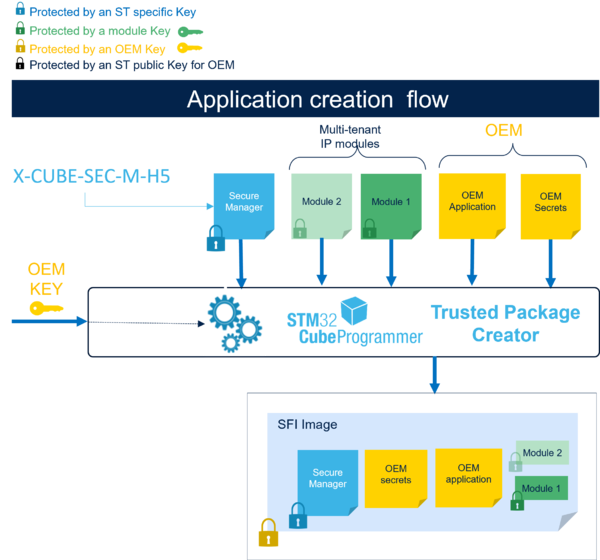
1. Applicable products
The following table shows the applicable products for SFI on STM32H5 with Secure Manager:
| Type | Products |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | STM32H573xx |
2. Environment setup
As explained in SFI Image generation, the secure firmware install (SFI) image generation and test rely on the Secure Manager Access Kit (SMAK).
Read SMAK prerequisites and SMAK package contents for the SFI environment setup and Script provisioning: Configuration to configure the Secure Manager installation, including the minimal and final product states.
In the rest of this wiki, the pathX-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM is referred to as SM.
3. Firmware development (on OEM premises)
The purpose of this SFI service is to securely install the OEM firmware developed with the Secure Manager.
To use this SFI service, the OEM must develop their nonsecure application during the SMAK development phase.
The OEM firmware file has a .hex extension. STMicroelectronics provides an application to build the X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\Applications\ROT\SMAK_Appli\Binary\appli_enc_sign.hex file.
4. SFI image generation and HSM provisioning (on secure OEM premises)
4.1. SFI with chip-specific license
To install an SFI with a chip-specific license, program an STM32HSM-V2 hardware security model (HSM). To do so, and configure the environment, follow the steps described in the How to start with Secure Manager customized config on STM32H5: SFI chip-specific license configuration wiki page.
After this first step, the configuration file SM\Config\sm.ini must look like this:
[sfi_generation]
license_key_encryption = ../Keys/SFI_Encryption_Key.bin
license_key_nonce = ../Keys/SFI_Encryption_Nonce.bin
[sfi_license]
# Type of license for the SFI: choose "global" for global license or "chip-specific" for chip-specific license
license_type = chip-specific
global_license_path = ../Keys/SFI_Global_License.bin
hsm_license_slot = 1
When the HSM has been programmed, it can be used with the SFI that is created during the SFI image generation and installation.
4.2. SFI with global license
To install an SFI with a global license, generate a new global license and configure the environment.
To generate a global license and configure the environment, follow the SFI license configuration step in the How to start with Secure Manager customized configuration on STM32H5 wiki page.
After this step, the configuration file SM\Config\sm.ini must look like this:
[sfi_generation]
license_key_encryption = ../Keys/SFI_Encryption_Key.bin
license_key_nonce = ../Keys/SFI_Encryption_Nonce.bin
[sfi_license]
# Type of license for the SFI: choose "global" for global license or "chip-specific" for chip-specific license
license_type = global
global_license_path = ../Keys/SFI_Global_License.bin
hsm_license_slot = 1
When the global license has been generated, it can be used with the SFI that is created during the SFI image generation and installation.
4.3. SFI image generation and installation
Once the OEM completes their nonsecure application development, they must prepare and test the final encrypted image (SFI image) to be used for OEM secure manufacturing with the SMAK production preparation phase.
The following sections provide step-by-step guidance through the SFI image generation and installation procedure.
4.3.1. Step 1: Profile selection
In the step described in the Security:How to start with Secure Manager customized config on STM32H5: Configuration Profile file: large.ini or ext_flash.ini wiki page, a profile is selected. In this next step, the configuration file varies based on the selected profile, as shown in the table below:
| Profile | Configuration file |
|---|---|
| Large | SM\Config\Profile_Large\large.ini
|
| External Flash | SM\Config\Profile_External_Flash\ext_flash.ini
|
In the following sections, these paths above are referred to as large.ini and ext_flash.ini.
4.3.2. Step 2: Configuration
In this step, JSON and .ini files are modified. These files can be customized, and all paths can be either absolute or relative to the file itself.
4.3.2.1. OEM Application
- Copy the signed and encrypted OEM application (named
oem_app.hexhereafter) to theBinaryfolder:
cp oem_app.hex X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary
- Copy the JSON template to the
Binaryfolder:
This JSON file specifies the path of the nonsecure application to be installed during the SFI procedure to thecp X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\Templates\ns_app_template.json X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\ns_app_oem.json
SM\provisioning.pyscript. - Modify the content of
ns_app_oem.jsonby replacing the existing path with the path to the OEM application, as shown in the code snippet below:{ '''"binary":"../../Binary/oem_app.hex"''', "active_slot":false }
- Depending on the selected profile, modify
large.iniorext_flash.ini. In this file, theimagesdictionary must contain an"ns_app"key and a corresponding path to a JSON file. In this case, the path corresponds to that of the previously modifiedns_app_oem.jsonfile:images = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json",
4.3.2.2. Factory internal trusted storage (FITS)
Follow the steps below to include a factory ITS in the SFI.
- Copy the default JSON to the
Binaryfolder:
This JSON file specifies the path of a factory ITS blob to be installed during the SFI procedure to thecp X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\fits_default.json X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\fits_oem.json
SM\provisioning.pyscript. - Prepare a custom FITS (named
oem_its_blob.binhereafter) with custom data and/or keys by following the steps on the Factory ITS blob preparation section of the linked wiki page. - Modify the content of
fits_oem.jsonby replacing the existing path with the path to the custom FITS, as shown in the code snippet below:
{ "binary":"../../Binary/oem_its_blob.bin", "xml":"../../Images/SM_ITS.xml", "auto_update":true }
- Finally, depending on the selected profile, modify
large.ini|ext_flash.ini.
In this file, theimagesdictionary must contain an"FITS"key and a corresponding path to a JSON file. In this case, the path corresponds to that of the previously modifiedfits_oem.jsonfile:
If no factory ITS is needed in the SFI, delete theimages = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json", "FITS" : "../../Binary/JSON/fits_oem.json"}
"FITS"key and its corresponding path in theimagesdictionary.
4.3.2.3. Secure module
The table below shows how to include the three types of modules in the SFI:
- Secure module without license
- Secure module with a global license
- Secure module with a chip-specific license
| Type of module | File(s) to copy to SM\Binary
|
Copy of the JSON template in SM\Binary\JSON
|
Content of the JSON file | Content of large.ini|ext_flash.ini
In this file, the a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Module without license | oem_module.hex
Note: Image already signed and encrypted |
Copy SM\Binary\JSON\Templates\module_template.json
to |
module_oem.json{
"license_type":"no_license",
"binary":"../../Binary/oem_module.hex"
}
|
images = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json",
"module_0" : "../../Binary/JSON/module_oem.json",
|
| Module with global license | 3rdPartyModule.smu
|
Copy SM\Binary\JSON\Templates\Profile_Large\module_with_global_license_Large_template.json
to Note: The selected profile does not affect the template mentioned above because the binary and license paths are updated afterwards. |
module_global_license.json{
"license_type":"global_license",
"binary":"../../Binary/3rdPartyModule.smu",
"license":"../../Binary/3rdPartyGlobalLicense.bin"
}
|
images = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json",
"module_0" : "../../Binary/JSON/module_global_license.json",
|
| Module with chip-specific license | 3rdPartyModule.smu
|
Copy SM\Binary\JSON\Templates\module_with_chip_specific_license_template.json
to |
module_chip_specific_license.json{
"license_type":"chip_specific_license",
"binary":"../../Binary/3rdPartyModule.smu"
}
|
images = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json",
"module_0" : "../../Binary/JSON/module_chip_specific_license.json",
|
4.3.2.4. External flash driver (External Flash profile only)
With the External Flash profile, an external flash driver must be included in the SFI procedure. STMicroelectronics provides an example of an external flash driver project compatible with the default external flash memory on the STM32H573I-DK board. This project is located at X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\Applications\ROT\External_Flash_Driver.
- Copy the external flash driver (named
Ext_Flash_Driver.binhereafter) to theBinaryfolder:
cp Ext_Flash_Driver.bin X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary
- Copy the default JSON file to the
Binaryfolder:
This JSON file specifies the path of an external flash driver to be installed during the SFI procedure to thecp X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\external_flash_driver_default.json X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\JSON\external_flash_driver_oem.json
SM\provisioning.pyscript. - Modify the content of
external_flash_driver_oem.jsonby replacing the existing path with the path to the external flash driver, as shown in the code snippet below:
{ "binary":"../../Binary/Ext_Flash_Driver.bin", "xml":"../../Images/SM_External_Flash_Driver_Image.xml", "auto_update":true }
- Finally, modify
ext_flash.ini.
In this file, theimagesdictionary must contain an"external_flash_driver"key and a corresponding path to a JSON file. In this case, the path is that of the previously modifiedexternal_flash_driver_oem.jsonfile:
images = {"ns_app" : "../../Binary/JSON/ns_app_oem.json", "module_0" : "../../Binary/JSON/module_oem.json", "external_flash_driver" : "../../Binary/JSON/external_flash_driver_oem.json"
4.3.3. Step 3: SFI image generation
Open a terminal in the Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM folder and execute the following command:
python provisioning.py --sfi-gen -a
This generates the SFI image. If the file is not renamed, the important files for the installation are listed in the table below:
| Files | Large profile | External Flash profile |
|---|---|---|
| License of the SFI |
The HSM card for the SFI must be retained | |
| SFI | SM\Binary\Output\Profile_Large\SecureManagerPackage.sfi
|
SM\Binary\Output\Profile_External_Flash\SecureManagerPackage.sfix
|
| If there is a secure module | SM\Binary\Output\Profile_Large\modules.mcsv
|
SM\Binary\Output\Profile_External_Flash\modules.ecsv
|
| ||
4.3.4. Step 4: SFI installation
To test the SFI before the programming phase at the OEM-CM manufacturer, make sure that all files generated during the previous step remain in the same location.
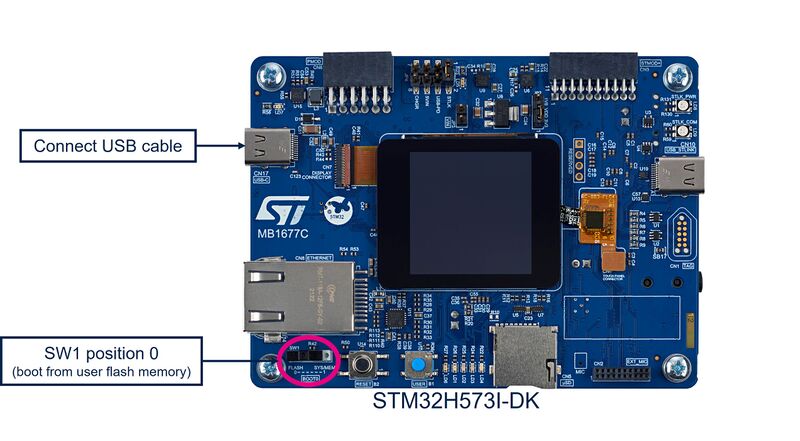
- Connect the STM32H573I-DK using the USB Type-C® cable.
- If a chip-specific license was selected for the installation of the SFI:
The HSM card for the SFI must be plugged in the smart-card reader slot defined in SFI with chip-specific license. - If a chip-specific license was selected for the installation of the module:
The HSM card for the module must be plugged into a different smart-card reader than the one used for the HSM, if applicable. - Open a terminal in the
SMfolder and execute the following command:
python provisioning.py --sfi-flash -a
The SFI image is now installed. The OEM application and secure module (if any) are running on the target device and are ready for testing.
If the installation fails:
- Check the
SM\provisioning.logfile. - Perform a regression by opening a terminal in the
X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\DA\folder and execute the command below:Then, repeat steps 3 and 4.python da.py --regression
5. Secure firmware installation (programmed during OEM-CM manufacturing)
In this step, the contract manufacturer (CM) receives the following from the OEM:
- The SFI image to be installed (
SecureManagerPackage.{sfi|sfix}) - The SFI global license (
SFI_Global_License.bin) or, in the case of an SFI chip-specific license, the HSM card provisioned with the OEM key and initialized with a maximum number of licenses - In the case of a secure module:
- The secure module information (
modules.{mcsv|ecsv}) - The global license file (
3rdPartyGlobalLicense.bin) or, in the case of a secure module chip-specific license, the HSM card provisioned with the secure module secret key and initialized with a maximum number of licenses
- The secure module information (
The SFI process can be performed through a regular JTAG/SWD interface or the system bootloader interface. Refer to the application note AN2606[1] for further details on the supported interface for each microcontroller).
5.1. Hardware
5.2. Target initial state
The target must be in "Open" product state. In the manufacturing use-case, this is the default product state.
If the target is not in an "Open" state, a full debug authentication (DA) regression must be performed by launching a terminal in X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\DA and executing the following command:
python da.py --regression
The device is now ready for the SFI process.
5.3. Secure firmware install
All commands below presume that the following files are in the same folder as STM32_Programmer_CLI.exe. If this is not the case, adapt the path accordingly:
SecureManagerPackage.sfi/SecureManagerPackage.sfixSFI_Global_License.binmodules.mcsv/modules.ecsv(making sure this file uses the correct paths)- RSSe:
X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\SM\Binary\RSSe_SFI_H56x_H573_v3.1.0.bin
The table below summarizes all possible commands for both profiles:
| Profile | Base | SFI | SFI license | External Loader | RSSe | Secure module (if any) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large profile | STM32_Programmer_CLI.exe -log sfi.log -c port=SWD mode=HotPlug -vb 1
|
-sfi SecureManagerPackage.sfi
|
Global license:hsm=0 SFI_Global_License.bin
hsm=1 slot=1
|
-rsse RSSe_SFI_H56x_H573_v3.1.0.bin
|
-mcsv modules.mcsv
| |
| External Flash profile | -sfi SecureManagerPackage.sfix
|
-el ./ExternalLoader/MX25LM51245G_STM32H573I-DK-RevB-SFIx.stldr
|
-ecsv modules.ecsv
|
Before running a command:
- If a chip-specific license was selected for the installation of the SFI:
The HSM card for the SFI must be plugged into the smart-card reader slot defined in the "SFI license" column of the table above. - If a chip-specific license was selected for the installation of the module:
The HSM card for the module must be plugged into a smart-card reader other than the one used for the SFI HSM, if applicable.
The extract below shows an example command for the Large profile with a global SFI license and a secure module.
STM32_Programmer_CLI.exe -log sfi.log -c port=SWD mode=HotPlug -vb 1 -sfi SecureManagerPackage.sfi hsm=0 SFI_Global_License.bin -rsse RSSe_SFI_H56x_H573_v3.1.0.bin -mcsv modules.mcsv
The extract below shows an example command for the External Flash profile, with a chip-specific SFI license and without a secure module.
STM32_Programmer_CLI.exe -log sfi.log -c port=SWD mode=HotPlug -vb 1 -sfi SecureManagerPackage.sfix hsm=1 slot=1 -el ./ExternalLoader/MX25LM51245G_STM32H573I-DK-RevB-SFIx.stldr -rsse RSSe_SFI_H56x_H573_v3.1.0.bin
The process log is stored in the sfi.log file.
The device is programmed with the Secure Manager, the secure module, the nonsecure OEM application, and the option bytes. The product state is now "Closed" or "Locked".
5.4. Troubleshooting
If an error eccors:
- Check
sfi.log. - If the device is not in the "Locked" state, open a terminal in the
X-CUBE-SEC-M-H5_VX.Y.Z\Projects\STM32H573I-DK\ROT_Provisioning\DAfolder and execute the command below to return to the "Open" state and relaunch the SFI procedure:python da.py --regression
6. Further reading
- Introduction to secure firmware install (SFI) for STM32 MCUs (AN4992, available from st.com)
- Third-party programmers guide for STM32H5 MCUs (AN6035, available upon request from an STMicroelectronics sales representative)
- Introduction to SFI tools, bootloader, and RSS interface for STM32 MCUs (AN5391, available upon request from an STMicroelectronics sales representative)
7. References