1. Human interface device over generic attribute profile
Human interface device over GATT profile (HOGP)[1] is a low-energy profile, based on the generic attribute profile (GATT) defined by the Bluetooth® special interest group (SIG)[2]
This profile is an adaptation of the USB human interface device (HID) specification[3] to operate over a Bluetooth® Low Energy wireless link. This profile operates on Bluetooth® Low Energy transport only.
The profile defines three roles:
- The human interface device (HID) is a GATT server.
- The boot host is a GATT client.
- The report host is a GATT client.
Bluetooth® Low Energy devices are not supported by PC BIOS, because the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack and drivers are not loaded yet at this point, so the boot host role cannot be used with clients like PCs, smartphones, or tablets.
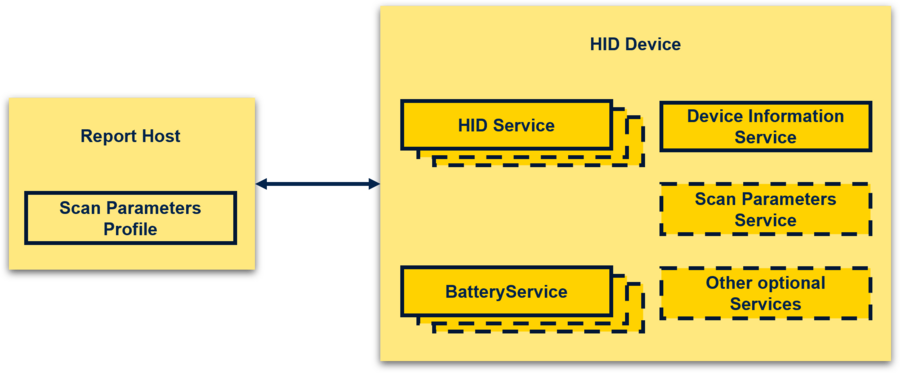
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP: report host and HID device |
|---|
The report host supports the scan client role of the scan parameters profile.
The HID device has:
- One or more instances of the HID service.
- One or more instances of the battery service.
- A single instance of the device information service.
- Optionally, one instance of the scan parameters service as part of the scan server role of the scan parameters profile.
- Optionally, a single or multiple instances of other services.
This wiki page describes the HID mouse project, provided with the STM32CubeWBA MCU Package[4]
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP mouse profile with STM32WBA |
|---|
The table below describes the structure of HOGP services:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP profile specification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The table below describes the HID report characteristic descriptors:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HID report characteristic descriptors specification | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The table below describes the battery level characteristic descriptor:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy battery level characteristic descriptor specification | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
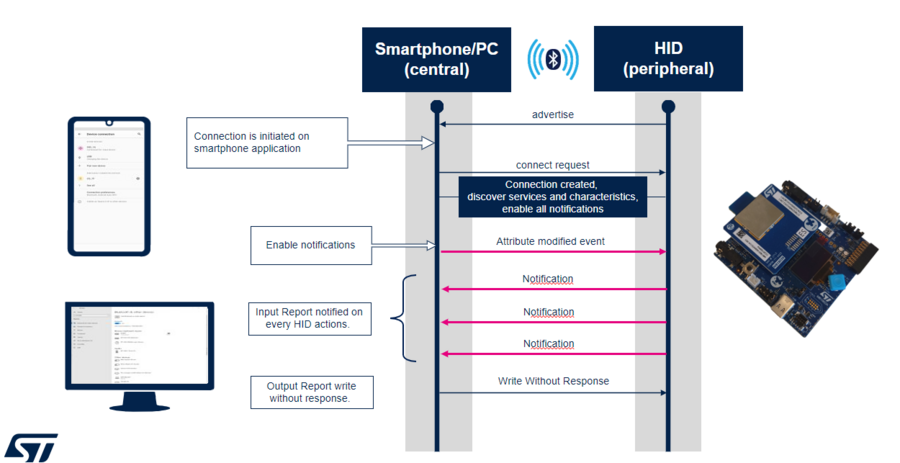
HOGP is a combination of a HID device and a report host to connect and exchange data in different applications.
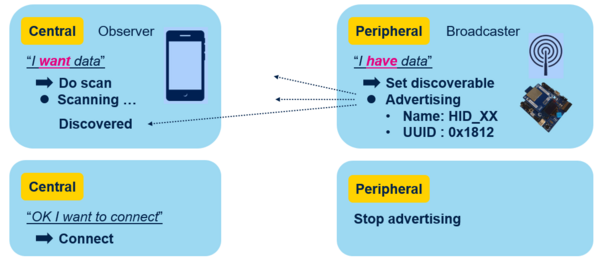
The generic access profile (GAP) defines and manages advertising and connection.
| Report host central device and HID peripheral device |
|---|
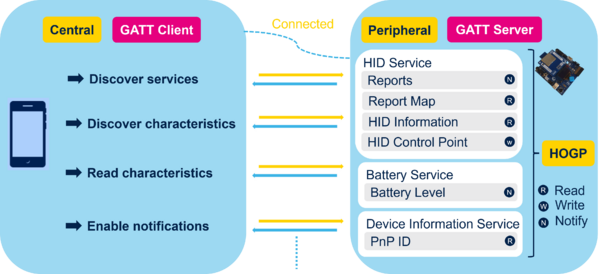
The generic attribute profile (GATT) defines and manages in/out data exchanges.
| Report host GATT client device and HID GATT service device |
|---|
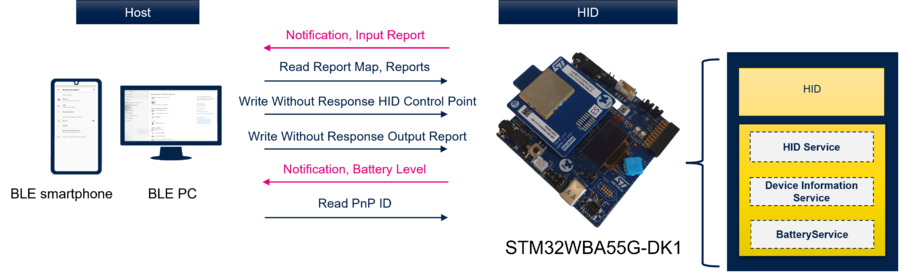
| Examples of an HID flow diagram between a STM32WBA55G-DK1 board and a Bluetooth® Low Energy PC or Bluetooth® Low Energy smartphone |
|---|
1.1. STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising data
At startup, HID device application starts fast advertising (80ms/100ms), including the STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising elements[5] described below:
| HID device STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Advertising is switched to low-power advertising (1s/2.5s) after 60 seconds.
2. Requirements
2.1. Software and Hardware requirements
For software and hardware requirements refer to STM32WBA Build BLE Project wiki page.
2.2. Collector applications compatible
The STM32CubeWBA HID device project is compatible with the following collectors:
3. STM32WBA55G-DK1 HID device example description
3.1. Project directory
The "BLE_HID_Mouse" application is available by downloading the STM32CubeWBA MCU Package[4], in the following folder:
STM32Cube_FW_WBA_Vx.y.z\Projects\STM32WBA55G-DK1\Applications\BLE\BLE_HID_Mouse
Refer to How to Build a Bluetooth® Low Energy project Wiki page for project directory information.
3.2. Project description
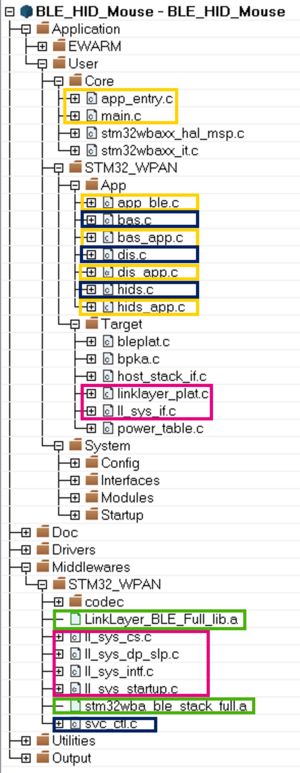
3.2.1. Structure
The figure below shows a software project structure, highlighting the most important parts:
| HID mouse project structure |
|---|
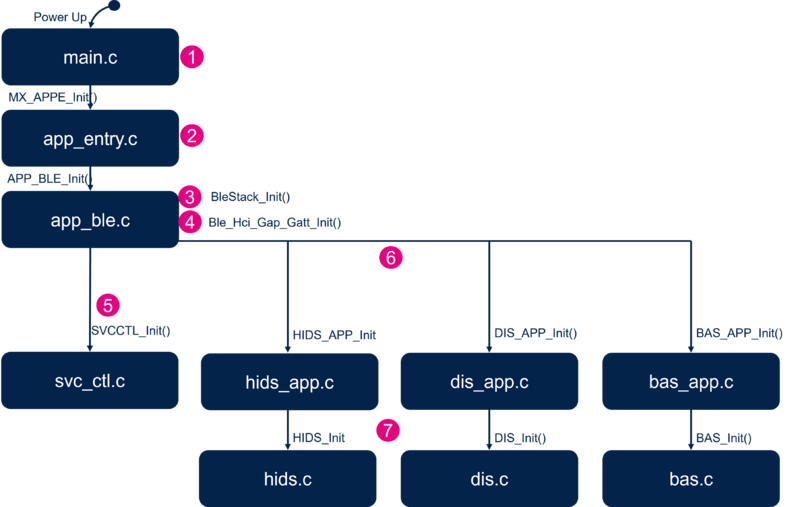
3.2.2. Application initialization
The figure below details the different steps of the application initialization.
| HID mouse project initialization |
|---|
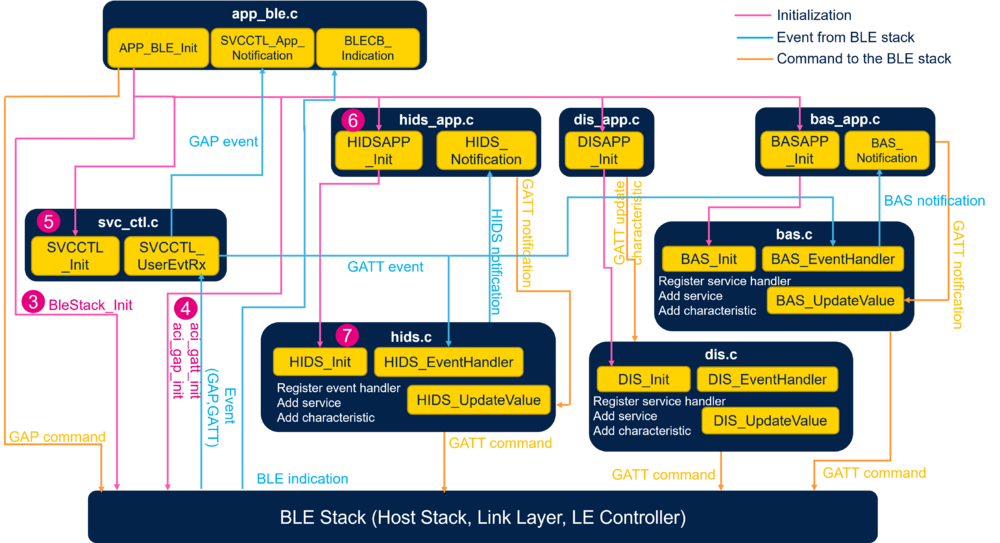
3.2.3. GAP and GATT initialization and interaction
| HID mouse device software module interaction |
|---|
and ![]() The Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse application initialization is done within app_ble.c.
The Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse application initialization is done within app_ble.c.
- Initialize the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack, initialize the device as a peripheral, and configure and start advertising: ADV parameters, local name, and UUID:
APP_BLE_init(). - Call the service controller initialization:
SVCCTL_Init()in svc_ctl.c. - Manage the GAP event:
SVCCTL_App_Notification().HCI_LE_CONNECTION_COMPLETEprovides information of the connection interval, slave latency, and supervision timeout.HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETEprovides the new information of the connection.HCI_DISCONNECTION_COMPLETEinforms the application about the link disconnection and the reason.
The service management is done by the service controller, svc_ctl.c.
- Initialize the number of registered handlers in
SVCCTL_Init(). - Manage events (
SVCCTL_UserEvtRx()) from the Bluetooth® Low Energy host stack and redirect them to the gap event handler (SVCCTL_App_Notification).
The application level of the HID mouse device is done with hids_app.c.
- Initialization of the services:
- HID Service:
HIDS_Init()in hids.c
- HID Service:
- Initialization of the context of the application:
- Report map
- HID information: BASE USB HID SPEC VERSION
- Receive notifications from the HID service:
HIDS_Notification(). - When the remote enables the input report characteristic, each update of the mouse position with the joystick (
HIDS_APP_UpdateReport) is transferred to the remote device (collector) (HIDS_UpdateValue()).
The HID service hids.c manages the specification of the service:
- Service init (
HIDS_Init()):- Registers the HID event handle to the service controller:
SVCCTL_RegisterSvcHandler(HIDS_EventHandler). - Initializes the service UUID and adds the HID service as a primary service.
- Initializes the report map characteristic.
- Initializes the HID information characteristic.
- Registers the HID event handle to the service controller:
- Manages the GATT event from the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack (
HIDS_EventHandler()).ACI_GATT_WRITE_PERMIT_REQ_VSEVT_CODE:- Reception of a write command: HID control point characteristic value.
- Sending of an
aci_gatt_write_response()with an OK or KO status. - Notification to the application to suspend or exit suspend (
HIDS_Notification(HIDS_HCP_WRITE_NO_RESP_EVT)).
- Sending of an
- Reception of a write command: HID control point characteristic value.
ACI_GATT_ATTRIBUTE_MODIFIED_VSEVT_CODE:- Reception of an attribute modification - input report characteristics description value: enable or disable notification.
- Notify application of the input report notification (
HIDS_Notification(HIDS_NOTIFICATION_ENABLED/DISABLED)).
- Notify application of the input report notification (
- Reception of an attribute modification - input report characteristics description value: enable or disable notification.
3.2.4. Report map and input report
HID report map characteristics should contain the USB HID descriptor, specified in the USB HID specification[3].
A USB HID descriptor is a hard-coded array of bytes describing the data packets of the device, including:
- The number of packets supported
- The packet size
- The purpose of each byte and bit in the packet
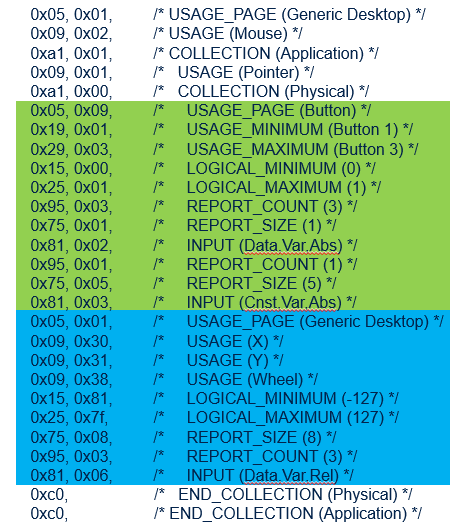
The figures below show an example of a USB mouse HID descriptor for a three-button mouse with X and Y axes and a wheel.
| USB mouse HID descriptor |
|---|
| Three-button mouse with X and Y axes and a wheel |
|---|
All hard-coded bytes are described in the USB HID usage tables document[6]. This USB HID descriptor also defines the data structure sent in the associated reports (input, output, or feature).
In this USB mouse HID descriptor example, you can find:
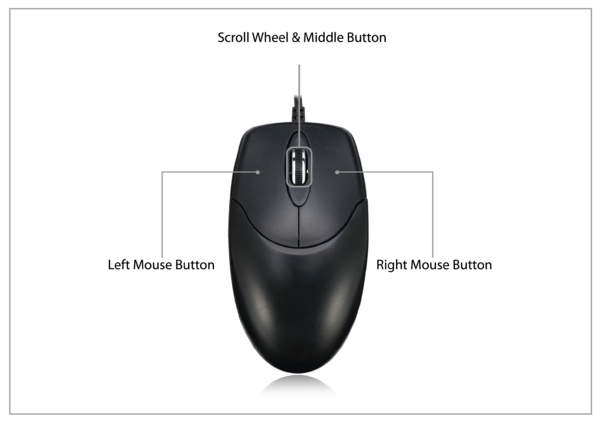
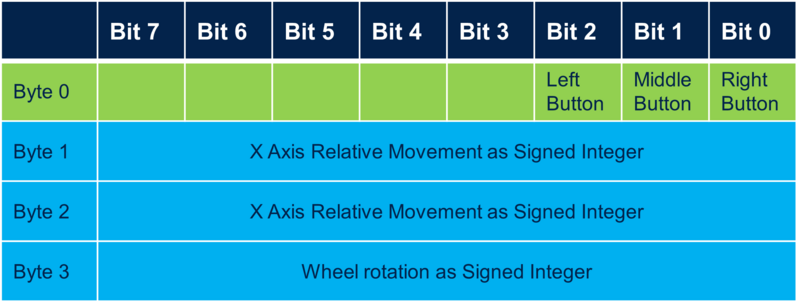
- Highlighted in green, the definition of three buttons represented by the first three bits of a byte that can have the boolean state 0 or 1. Bits 0, 1, and 2 represent the states of respectively the left, middle, and right buttons of the mouse. The remaining bits of the byte are unused.
- Highlighted in blue, the definition of three bytes for the X and Y axes for relative movement and wheel rotation. Each byte represents a signed integer that can take a value comprised between -127 to 127.
The figure below shows an example of the input report associated with the USB mouse HID descriptor.
| Data structure for a three-button mouse with X and Y axes and a wheel |
|---|
3.3. How to use the Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse application
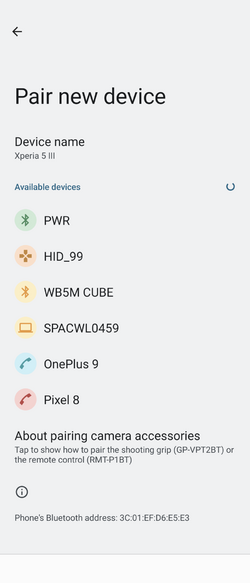
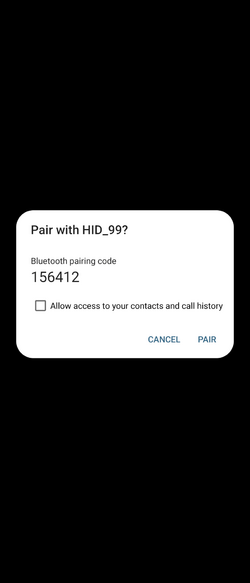
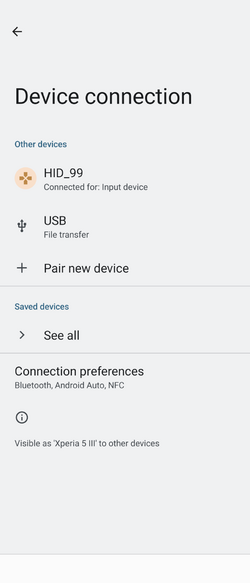
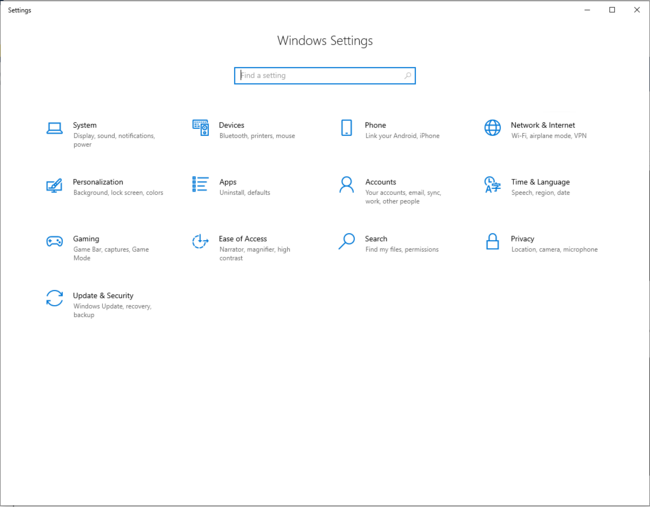
Once the Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse application is installed on the STM32WBA55G-DK1 platform, launch a Bluetooth® Low Energy connection on a smartphone or a PC. Then, scan and connect the device called HIDS_XX (where XX is replaced by the last byte of the BD address) to the application.
3.3.1. Android Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse
| Android Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse connection – How to | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
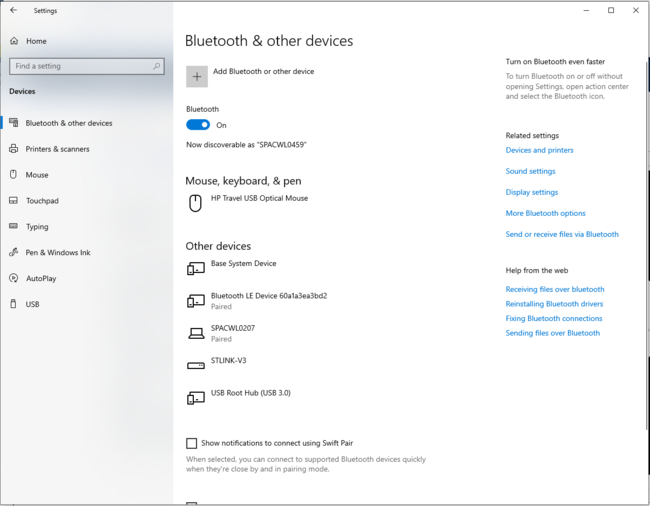
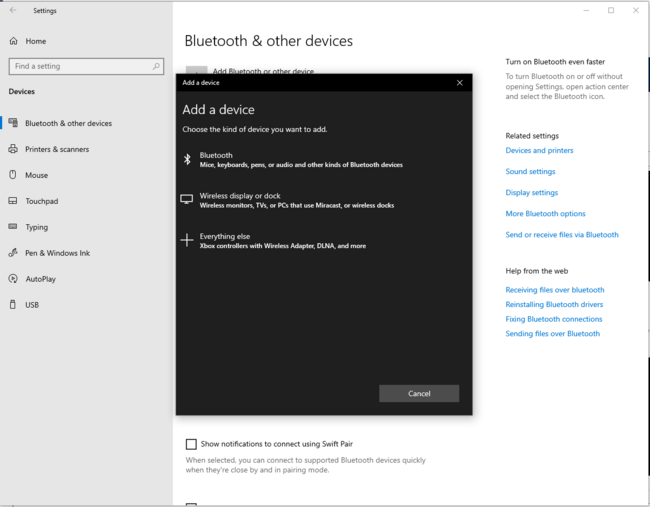
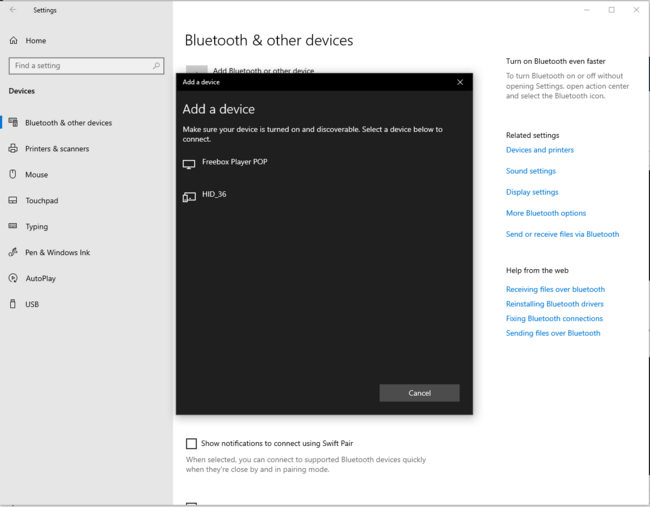
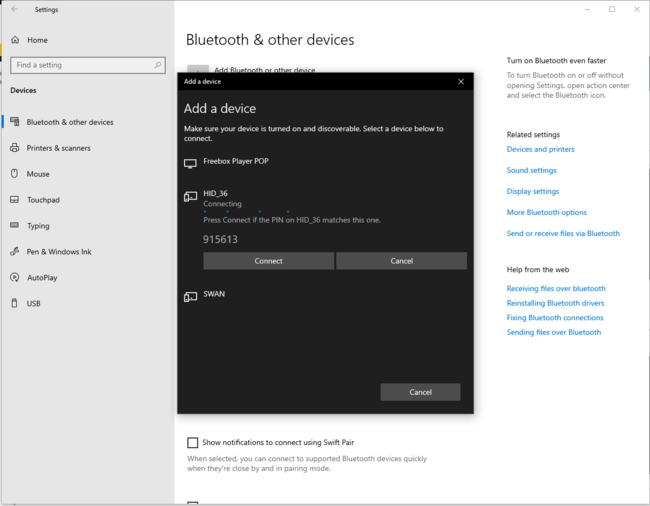
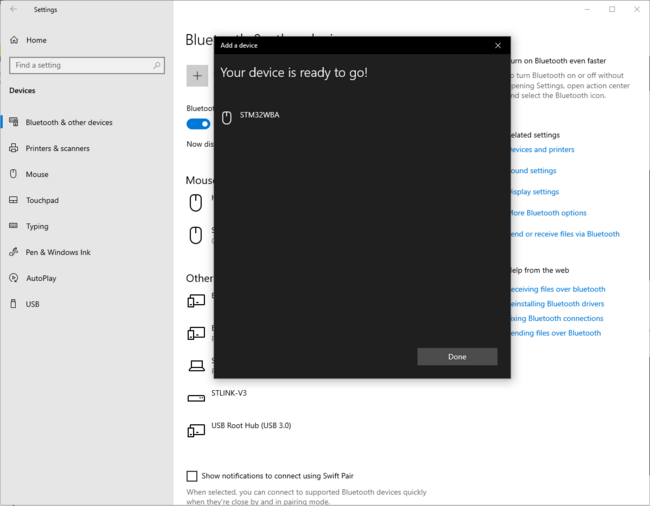
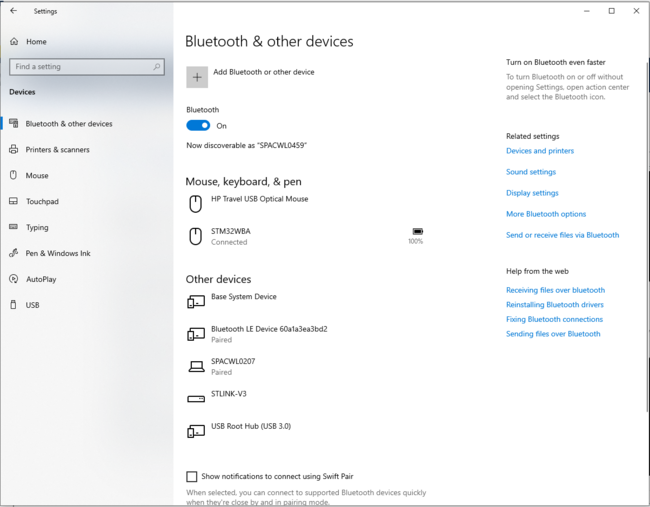
3.3.2. PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
3.3.3. Bluetooth® Low Energy HID mouse how to
Once the Bluetooth® Low Energy connection is established and the notification enabled by the smartphone or the PC, the HID input report is sent each time an action is performed on the STM32WBA55G-DK1 joystick.
| STM32WBA55G-DK1 joystick |
|---|
- Action on up, down, left, and right direction sends an input report containing a relative position.
- Pressing on the joystick in neutral position sends an input report containing the state of the left button.
3.4. Low-power optimization
The project is delivered with the full system low-power feature disabled:
- Debug trace enabled
- Debugger enabled, even in Low-power mode
It is possible to enable/disable the low-power feature within app_conf.h:
/******************************************************************************
* Low Power
*
* When CFG_LPM_LEVEL is set to:
* - 0 : Low Power Mode is not activated, RUN mode will be used.
* - 1 : Low power active, the one selected with CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED
* - 2 : In addition, force to disable modules to reach lowest power figures.
*
* When CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED is set to:
* - 1 : Standby is used as low power mode.
* - 0 : Standby is not used, so stop mode 1 is used as low power mode.
*
******************************************************************************/
#define CFG_LPM_LEVEL (0)
#define CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED (0)
3.5. UART debug trace
With the debug log via UART interface it is possible to trace the application project.
To enable the traces within the project, enable them in app_conf.h as described below:
/*****************************************************************************
* Logs
*
* Applications must call LOG_INFO_APP for logs.
* By default, CFG_LOG_INSERT_TIME_STAMP_INSIDE_THE_TRACE is set to 0.
* As a result, there is no time stamp insertion inside the logs.
*
* For advanced log use cases, see the log_module.h file.
* This file is customizable, you can create new verbose levels and log regions.
*****************************************************************************/
/**
* Enable or disable LOG over UART in the application.
* Low power level(CFG_LPM_LEVEL) above 1 will disable LOG.
* Standby low power mode(CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED) will disable LOG.
*/
#define CFG_LOG_SUPPORTED (1U)
/* Configure Log display settings */
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_COLOR_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_TIME_STAMP_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_EOL_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
/* macro ensuring retrocompatibility with old applications */
#define APP_DBG LOG_INFO_APP
#define APP_DBG_MSG LOG_INFO_APP
A debugger can also be supported by enabling it in app_conf.h, as described below:
/******************************************************************************
* Debugger
*
* When CFG_DEBUGGER_LEVEL is set to:
* - 0 : No Debugger available, SWD/JTAG pins are disabled.
* - 1 : Debugger available in RUN mode only.
* - 2 : Debugger available in low power mode.
*
******************************************************************************/
#define CFG_DEBUGGER_LEVEL (2)
| HID mouse - initialization phase | HID mouse - connected phase |
|---|---|
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 26349
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 26349==>> Start Ble_Hci_Gap_Gatt_Init function
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_PUBADDR_OFFSET
Public Bluetooth Address: 00:80:e1:2a:ff:36
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_IR_OFFSET
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_ER_OFFSET
Success: aci_hal_set_tx_power_level command
Success: aci_gatt_init command
Success: aci_gap_init command
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value - Device Name
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value - Appearance
Success: hci_le_set_default_phy command
Success: aci_gap_set_io_capability command
Success: aci_gap_set_authentication_requirement command
Success: aci_gap_configure_whitelist command
==>> End Ble_Hci_Gap_Gatt_Init function
Services and Characteristics creation
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: HIDS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : INPUTREP
Success: aci_gatt_add_char_desc command : INPUT REP REF DESC on handle 0x10
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : REM
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : HII
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : HCP
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value REM command
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value HII command
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: DIS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : PNI
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value PNI command
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: BAS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : BAL
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value BAL command
End of Services and Characteristics creation
==>> aci_gap_set_discoverable - Success
==>> Success: Start Advertising
|
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE - Connection handle: 0x0001
- Connection established with @:65:92:b8:52:36:4b
- Connection Interval: 45.00 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
>>== ACI_GAP_NUMERIC_COMPARISON_VALUE_VSEVT_CODE
- numeric_value = 447414
- Hex_value = 6d3b6
==>> aci_gap_numeric_comparison_value_confirm_yesno : Success
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
SNVMA_Write - Flash operation started (Header write request) : 16
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
>>== ACI_GAP_PAIRING_COMPLETE_VSEVT_CODE
- Pairing Success
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_HEADER_WRITE
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_BUFFER_WRITE
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 48382
FM_Erase - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Erase operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Erase operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_RETRY_WRITE
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE
- Connection Interval: 7.50 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE
- Connection Interval: 45.00 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
HIDS_REP_NOTIFY_ENABLED_EVT
|
4. References