1. What is NanoEdge AI Library for anomaly detection?
NanoEdge™ AI Library is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) static library for embedded C software running on Arm® Cortex® microcontrollers.
A NanoEdge AI Library is compiled in the last step of any NanoEdge AI Studio project.
The goal of Anomaly detection libraries is to distinguish normal and abnormal behavior defined during its training in NanoEdge AI Studio. A library contains everything needed to be embedded on a microcontroller:
- The AI model and its hyperparameters
- The preprocessing of the signals
Few files are given to make a use of it:
- libneai.a contains the ML model as an obfuscated static library
- NanoEdgeAI.h contains the variables and functions declaration
1.1. Embedded learning
Anomaly detection libraries have the particularity to be retrainable directly on a microcontroller. It is the only kind of library able to do so in NanoEdge AI Studio.
Compared to other kinds of libraries, Anomaly detection libraries need to be retrained before being used. You can do it in three different ways:
- Deploy the model and initialize without pretrained knowledge (
neai_anomalydetection_init(false)), then collect and learn new signals directly on the microcontroller before doing detection. - Deploy the model and initialize with pretrained knowledge (
neai_anomalydetection_init(true)). Use the pretrained benchmark knowledge and then do detection. - Deploy the model and initialize with pretrained knowledge (
neai_anomalydetection_init(true)), but also collect new signals and callneai_anomalydetection_learn()to enrich the knowledge before doing detection.
If you use the pretrained knowledge from the benchmark, you don't exploit the advantages of anomaly detection. If you decide to retrain the model with new signals, you should get a model that is more specifically made for its final environment and thus should give better results.
2. Install / Getting started
The main functions available via the library are:
init()
|
run first before learning/detecting, or to reset the knowledge of the library/emulator |
learn()
|
start a number of learning iterations (to establish an initial knowledge, or enrich an existing one) |
detect()
|
start a number of detection iterations (inference), once a minimum knowledge base has been established |
2.1. How to get an AI library
- In NanoEdge AI Studio, after obtaining a library, click Compile (on the "Deployment" screen, which follows the "Benchmark" and "Validation" screens)
The .zip file obtained contains:
- the static precompiled NanoEdge AI library file
libneai.a - the NanoEdge AI header file
NanoEdgeAI.h - the NanoEdge AI Emulators (both Windows® and Linux® versions)
- some library metadata information in
metadata.json
To use it, simply add libneai.a and NanoEdgeAI.h to your project. Then, link the library for the compilation in your IDE. For example in STM32CubeIDE, go to Project -> Properties -> C/C++ Build -> Settings -> MCU GCC Linker -> Libraries. Add "neai" in the Libraries section and the libneai.a' path in the Library search path section. Click Apply and Close.
2.2. NanoEdge AI Library functions
Most NanoEdge AI function return the status of the library in the following enum, neai_state:
enum neai_state {
NEAI_OK = 0,
NEAI_ERROR = 1,
NEAI_NOT_INITIALIZED = 2,
NEAI_INVALID_PARAM = 3,
NEAI_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4,
NEAI_LEARNING_DONE = 5,
NEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS = 6
};
Here are the possible statuses:
NEAI_OK: library working as expectedNEAI_ERROR: internal error with the libraryNEAI_NOT_INITIALIZED: learn or detect functions were called without running the init function first; initialize your library.NEAI_INVALID_PARAM: neai function was called with one or more incorrect or missing parameters.NEAI_NOT_SUPPORTED: board not supportedNEAI_LEARNING_DONE: minimum number of learning iterations reachedNEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS: fail-safe to prevent insufficient number of learning iterations; run more iterations.
2.2.1. Initialization
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_init(bool use_pretrained);
Initialization can be run at the beginning to initialize the model and/or later to initialize a new model and reset all knowledge.
Specify at initialization whether to use a pretrained model or perform on-device learning:
neai_anomalydetection_init(true)- Use embedded pretrained model (see below, no learning phase required)neai_anomalydetection_init(false)- Perform on-device learning using neai_anomalydetection_learn()
Returns the neai_state enum (NEAI_OK == 0, in case of success).
2.2.2. Using embedded pretrained model
The main advantage of anomaly detection libraries is that they can be re-trained directly on the edge. By default, if you use the library on a microcontroller, the model must be retrained to better fit the data in its real environment. The training knowledge acquired during the benchmark (corresponding to the training data of the project) is automatically embedded in the library. It is up to you to either included it, or start from scratch; use the boolean argument use_pretrained to do so.
2.2.3. Learning
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_learn(float data_input[]);
This function is used to learn patterns in your data. It can be used at any time, in the beginning to build the original knowledge base of the AI model, but also later, as an additional learning phase to complement the existing knowledge.
- Input:
float data_input[], the length of the data isNEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER.
- Output:
- the
neai_stateenum (NEAI_LEARNING_DONE or NEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS).
- the
2.2.4. Detection
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_detect(float data_input[], uint8_t *similarity);
This function returns returns a similarity percentage, measure of the mathematical distance between the incoming signal and the existing knowledge, learned by the library.
- Input:
float data_input[], the length of the data isNEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER.uint8_t *similarity, the variable that contains the similarity score returned by the function.
- Output:
- The percentage of similarity [0-100] between the new signal and learned patterns ("100" means completely similar, and "0" completely dissimilar).
- The
neai_stateenum.
2.3. Backing up and restoring the library knowledge
2.3.1. Creating backups
When using NanoEdge AI Library, knowledge is created on the go. It means that after each learning iteration, the Machine Learning model is incrementally getting richer and richer.
For performance reasons, this knowledge is saved into the microcontroller RAM. Since RAM is volatile, better copy this knowledge into non-volatile memory and prevent its loss (for example, in case of power failure).
NanoEdge AI Library attributes a specific memory section called .neai for the knowledge variables (model hyperparameters). To use it, you need to create a memory section in your linker script according to your microcontroller architecture.
The idea is to create a section called .neai (for NanoEdge AI) in your RAM, using the linker script that is specific to the board / MCU that you use (it is a .ld file).
For example, using a STM32F401RE:
- First of all, modify your linker script "STM32F401RETX_FLASH.ld":
At the end of file, just after ._user_heap_stack section, add .neai section :
.neai :
{
_sneai_knowledge = .; /* Start address of .neai section */
KEEP(*(.neai)) /* Keep my variable even if not referenced */
_eneai_knowledge = .; /* End address of .neai section */
} >RAM
- Once the linker script has been edited, we've to declare our "_neai_knowledge" variable in main.c :
extern void *_sneai_knowledge;
extern void *_eneai_knowledge;
- Now, we've to define .neai size and address in Flash where we want to store the knowledge. In your main.c defines section, add :
#define NEAI_KNOWLEDGE_SIZE ((unsigned int)&_eneai_knowledge - (unsigned int)&_sneai_knowledge) /* To determine .neai section size */
[...]
#define FLASH_USER_START_ADDR ADDR_FLASH_SECTOR_4 /* Start @ of user Flash area */
#define FLASH_USER_END_ADDR FLASH_USER_START_ADDR + NEAI_KNOWLEDGE_SIZE /* End @ of user Flash area */
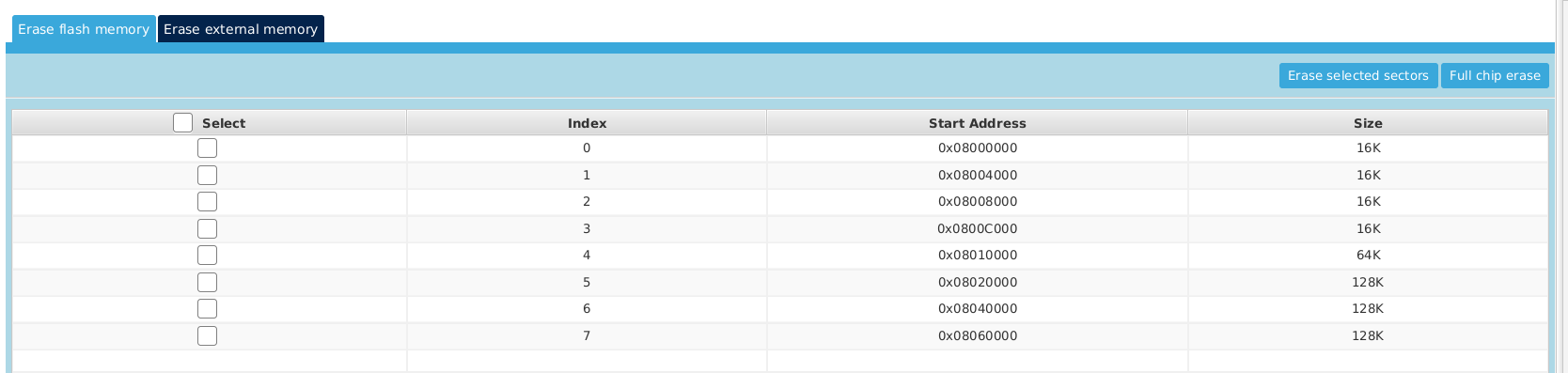
Make attention to not overwrite .data section in Flash memory. In my case, the start address is at 0x08010000 which works fine. Overwriting .data section could lead to hardfault. The available sectors on NUCLEO-F401RE dev board are:
2.3.1.1. Save knowledge
Saving knowledge consists to write _neai_knowledge in Flash memory. To perform this operation, you've to erase the sector(s) you want to write then, write in :
erase_flash_memory();
write_flash_memory(_neai_knowledge);
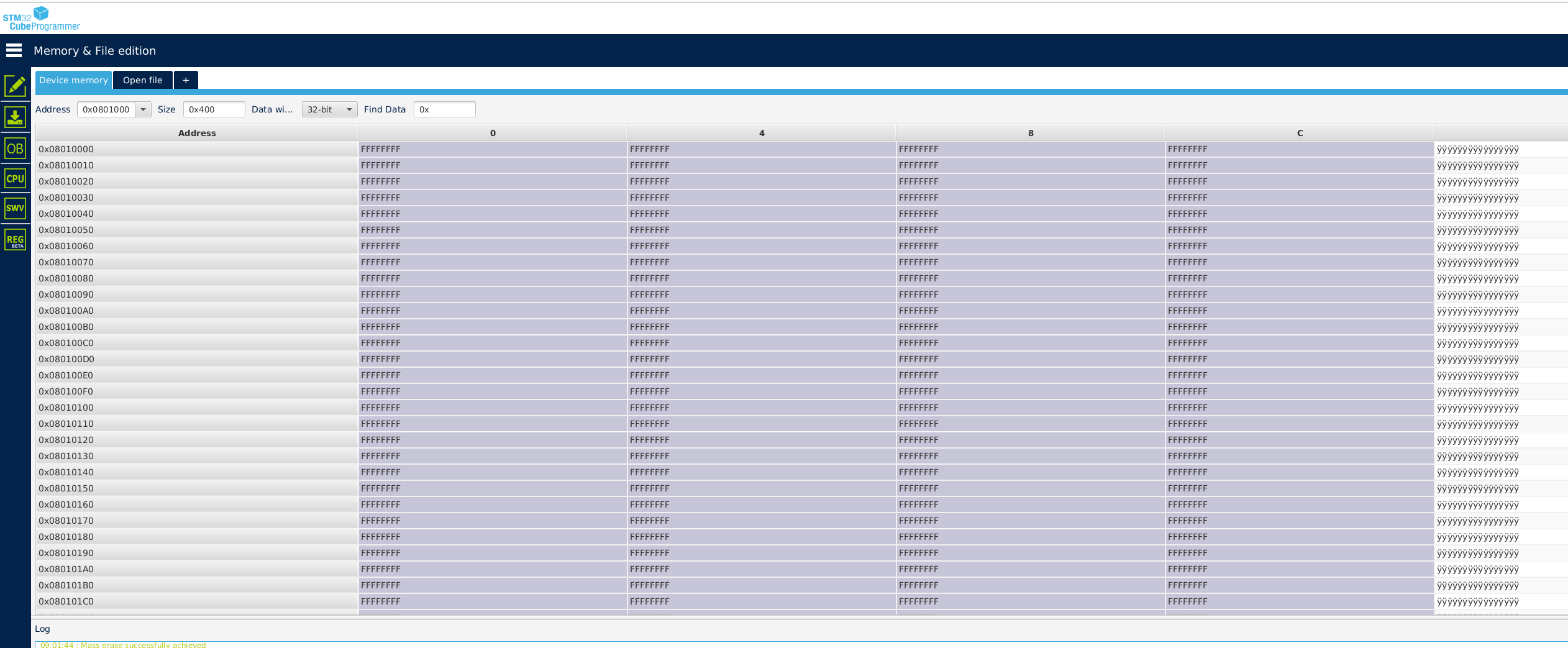
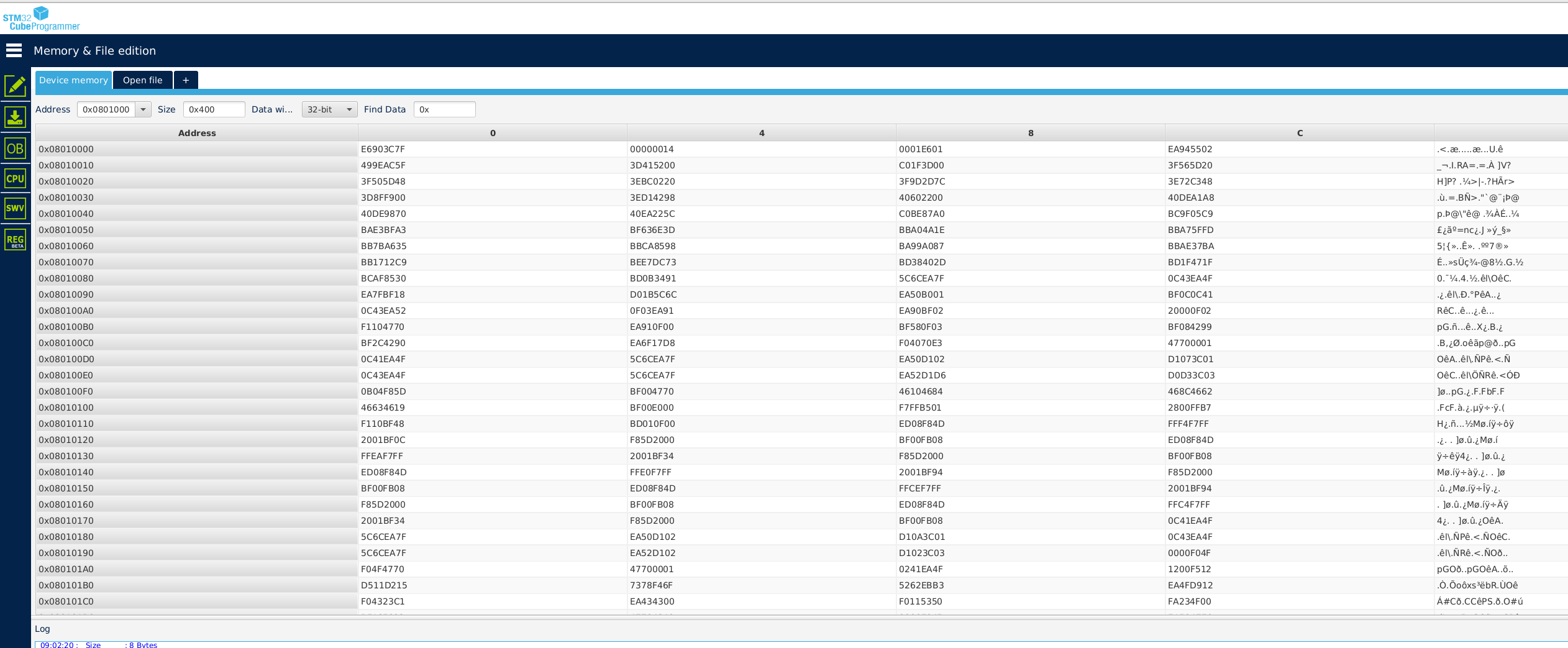
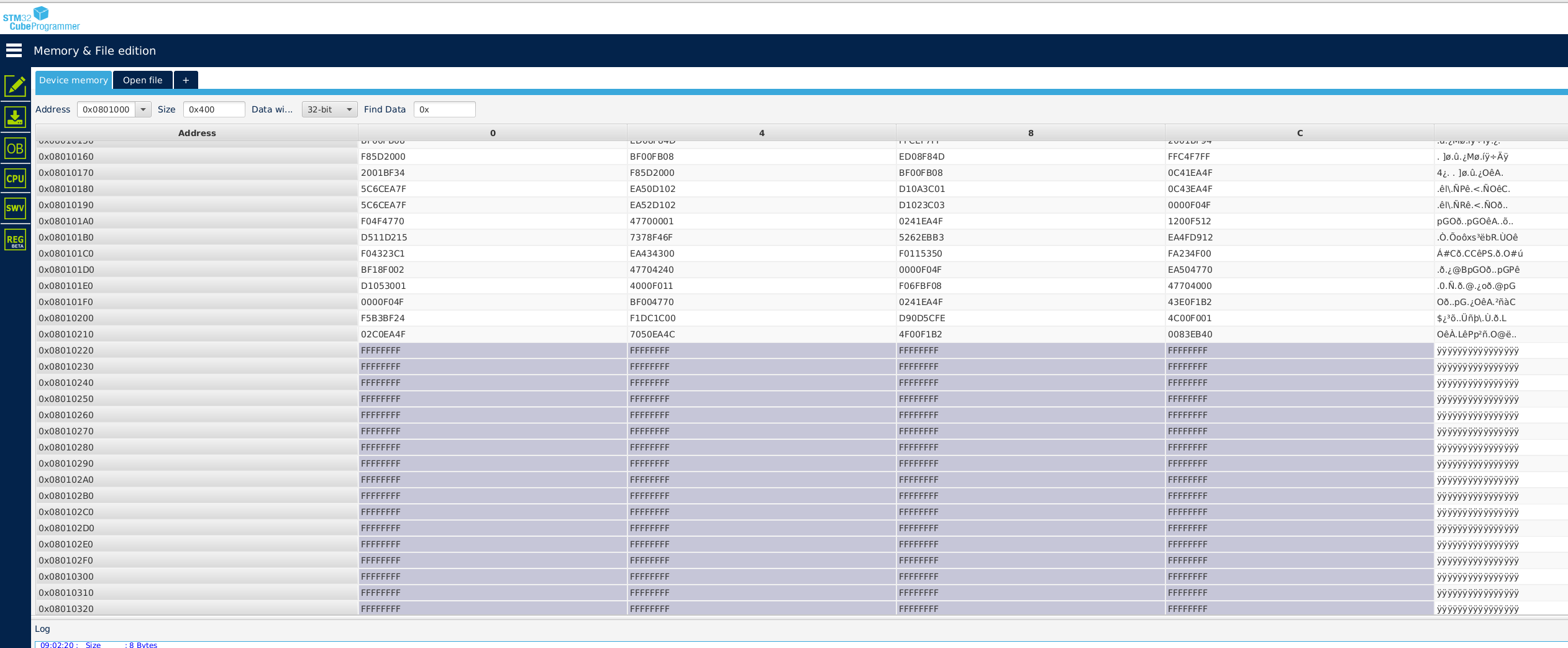
You can have a look to these two functions in the main.c. Check (optionnal) If you want to check the write operation in Flash, you can use STM32CubeProgrammer. Before write, you should see something like :
After:
Data is written until address 0x08010220 which is normal because : 0x08010000 (start address) + 4 (word size) * 136 (my .neai section size) = 0x08010220.
2.3.1.2. Restore knowledge
After a reboot or a reset, in order to get back the knowledge into RAM, you just have to do :
memcpy((uint32_t *) &_sneai_knowledge, (uint32_t *) FLASH_USER_START_ADDR, NEAI_KNOWLEDGE_SIZE);
With this operation, you copy data from FLASH_USER_START_ADDR in Flash to _sneai_knowledge in RAM. After performing this operation, you can pass in detect mode without doing a new learning phase.
2.4. Example "Hello World!"
Header file: NanoEdgeAI.h
Example of NanoEdge AI Library header file:
/* =============
Copyright (c) 2026, STMicroelectronics
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted
provided that the following conditions are met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions
and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
with the distribution.
* Neither the name of the copyright holders nor the names of its contributors may be used to
endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written
permission.
*THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER /
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.*
*/
#ifndef NANOEDGEAI_H
#define NANOEDGEAI_H
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
/* NEAI ID */
#define NEAI_ID "None"
/* Input signal configuration */
#define NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH 256
#define NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER 3
/* NEAI State Enum */
enum neai_state {
NEAI_OK = 0,
NEAI_ERROR = 1,
NEAI_NOT_INITIALIZED = 2,
NEAI_INVALID_PARAM = 3,
NEAI_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4,
NEAI_LEARNING_DONE = 5,
NEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS = 6
};
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* ===== Anomaly Detection API ===== */
/**
* @brief Must be called at the beginning to initialize the anomaly detection model.
* @param use_pretrained [in] Set to true to use a pretrained model, false to start learning
* from scratch (pretrained model comes from NanoEdge AI Studio
* and is embedded in the library).
* @return NEAI_OK on success, error code otherwise.
*/
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_init(bool use_pretrained);
/**
* @brief Learn patterns from a new input sample.
* It can be called at any time after initialization.
* At the beginning, multiple calls to build the knowledge base of the model.
* Later as an additional learning step to complement the knowledge base.
* @param in [in] Pointer to the input signal array
* (size NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER).
* @return NEAI_LEARNING_DONE when minimum learning calls are reached.
* NEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS if more learning calls are needed.
* Error code otherwise.
*/
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_learn(float *in);
/**
* @brief Perform anomaly detection on a new input sample by returning a similarity percentage.
* The mathematical distance between the incoming sample and the learned patterns.
* @param in [in] Pointer to the input signal array
* (size NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER).
* @param similarity [out] Pointer to the similarity percentage [0-100]
* (100 means completely similar, 0 means completely different).
* @return NEAI_OK on success.
* NEAI_LEARNING_IN_PROGRESS if the model needs more learning calls (minimum learning
* calls not reached).
* Error code otherwise.
*/
enum neai_state neai_anomalydetection_detect(float *in, uint8_t *similarity);
/* ===== Common getter functions ===== */
/**
* @brief Get the NEAI identifier.
* @return Pointer to a string containing the NEAI ID.
*/
char* neai_get_id(void);
/**
* @brief Get the input signal size (number of samples per axis).
* @return Input signal size.
*/
int neai_get_input_signal_size(void);
/**
* @brief Get the number of input axes/channels.
* @return Number of input axes.
*/
int neai_get_axis_number(void);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* NANOEDGEAI_H */
/* =============
Declarations to add to your main program to use the NanoEdge AI library.
You may copy-paste them directly or rename variables as needed.
WARNING: Respect the structures, types, and buffer sizes; only variable names may be changed.
enum neai_state state; // Captures return states from NEAI functions
bool use_pretrained = false; // Init function parameter: true = use pretrained model, false = learn from scratch
uint8_t similarity; // Similarity percentage returned by detect function
float input_signal[NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER]; // Input signal buffer
============= */
Main program: main.c
This program must be completed by the user (depending for instance on the applications or the desired features).
/**
**************************************************************************
* Demo: NanoEdge AI process to include in main program body
*
* @note This program must be completed and customized by the user
**************************************************************************
*/
/* Includes --------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "NanoEdgeAI.h"
#include <stdbool.h>
/* Number of samples for learning: set by user ---------------------------------*/
#define LEARNING_ITERATIONS replace_learning_samples
float input_signal[NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH * NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER]; // Buffer of input values
/* Private function prototypes defined by user ---------------------------------*/
/*
* @brief Collect data process
*
* This function is defined by user, depends on applications and sensors
*
* @param input_signal: [in, out] buffer of sample values
* @retval None
* @note If NEAI_INPUT_AXIS_NUMBER = 3 (cf NanoEdgeAI.h), the buffer must be
* ordered as follow:
* [x0 y0 z0 x1 y1 z1 ... xn yn zn], where xi, yi and zi
* are the values for x, y and z axes, n is equal to
* NEAI_INPUT_SIGNAL_LENGTH (cf NanoEdgeAI.h)
*/
void fill_buffer(float *input_signal)
{
/* USER BEGIN */
/* USER END */
}
/* -----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int main(void)
{
/* Initialization ------------------------------------------------------------*/
bool use_pretrained = false; // true to use the pretrained model, false to start learning from scratch
enum neai_state error_code = neai_anomalydetection_init(use_pretrained);
uint8_t similarity = 0;
if (error_code != NEAI_OK) {
/* Check the returned error code (cf NanoEdgeAI.h). */
}
/* Learning process ----------------------------------------------------------*/
for (uint16_t iteration = 0 ; iteration < LEARNING_ITERATIONS ; iteration++) {
fill_buffer(input_signal);
neai_anomalydetection_learn(input_signal);
}
/* Detection process ---------------------------------------------------------*/
while (1) {
fill_buffer(input_signal);
neai_anomalydetection_detect(input_signal, &similarity);
/* USER BEGIN */
/*
* e.g.: Trigger functions depending on similarity
* (blink LED, ring alarm, etc.).
*/
/* USER END */
}
}
3. Resources
Documentation
All NanoEdge AI Studio documentation is available here.
Tutorials
Step-by-step tutorials to use NanoEdge AI Studio to build a smart device from A to Z.