1. Article purpose
Unlike a camera module that embeds the lens, the image sensor, and the image signal processor (ISP), the RAW sensor module only embeds the lens and the image sensor.

For camera modules, the ISP is tuned by the camera module provider.
For sensor modules, the ISP needs to be tuned by the application provider.
The purpose of this article is to provide step-by-step guidance to tune the DCMIPP ISP pipeline for a given RAW sensor and its associated lens.
2. Overview of DCMIPP ISP block diagram

The DCMIPP ISP (instantiated only once) is shared by both pipe1 and pipe2. It includes capabilities such as:
- Statistic removal: Eliminates unnecessary metadata, such as statistics, from the images received.
- Bad pixel: Detects and corrects artifacts generated by a bad pixel on the sensor array.
- Decimation: Downsizes the frame by selecting one pixel out of every 1, 2, 4, or 8. It ensures that the RAW frame size does not exceed 2688 pixels in width before demosaicing.
- Black level: Suppresses a potential sensor positive black offset by adjusting the black level for each pixel in the red, green, and blue components.
- ISP gain control: Sets the gains applied to the R, G, and B components.
- Demosaicing: Transforms the RAW Bayer format to RGB.
- Statistics extraction: Computes, from a statistic area, the average values for red, green, and blue components or histograms. Statistics are used by the software image quality algorithms.
- Color correction: Corrects the color with a fully programmable 3x3 coefficients matrix.
- Contrast: Enhances contrast through luminance adjustment.
- Gamma conversion: Implements a gamma compression on each R, G, and B component, using a static gamma exponent of 2.
Refer to the STM32 reference manuals for the complete list of features.
3. Why tune the ISP for a RAW sensor?
Different light sources, also called illuminants, have different spectral distributions and color temperatures, measured in Kelvin, that can affect how the colors are captured by the camera sensor. The white balance adjustment (ISP gain) ensures that the whites appear white, and the color adjustment (color correction matrix) ensures that the colors in the captured image closely match the actual scene.
Tuning ISP parameters for different illuminants is a mandatory step in the camera application development process. It ensures that the sensor and lens connected to the device can produce good image quality in terms of white balance and color accuracy under different lighting conditions, meeting user application needs. The results of the tuning procedure are a set of parameters that are programmed in the ISP and controlled by ISP algorithms.
4. Tuning procedure
4.1. Prerequisite
The STM32 ISP IQTune application must be installed.
4.2. Needed materials
- X-Rite ColorChecker® chart
- Spectrometer
- Light box
4.3. Tuning step by step
To execute the tuning procedure, start from a blank page:
- Click on the "Start tuning from scratch" button to begin with a blank configuration of the ISP.
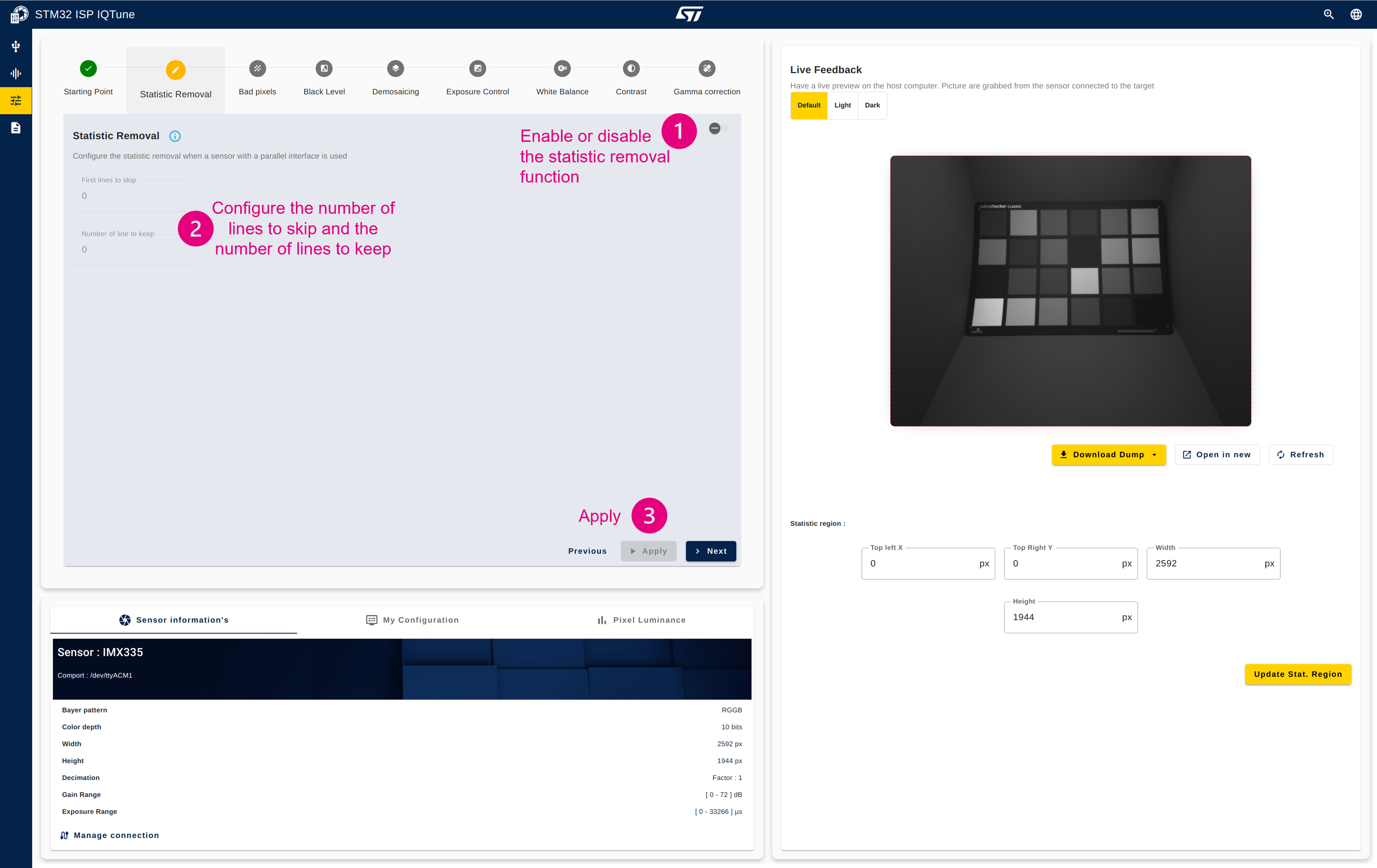
4.3.1. Step 1: Configure the statistics removal
Description:
This module removes potential statistical data inserted by a sensor before starting the demosaicing conversion, which could be impacted by remaining statistics. It is typically used by sensors with a parallel interface, which cannot distinguish between statistics and pixel data. CSI-2 sensors typically split these flows using different virtual channel IDs.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable or disable the statistic removal module.
- When enabled, you can configure the number of first lines to skip and the number of lines to keep. These parameters depend on the sensor datasheet.
- Apply the configuration.
4.3.2. Step 2: Configure the bad pixel
Description:
This module aims to detect and correct artifacts generated by a bad pixel on the sensor array. It is based on correlation extraction, not fixed locations.
It works for RAW Bayer flows only, as RGB flows are assumed to be already cleaned.
All arriving components are scanned, and the horizontal continuity correlation versus the two left and two right neighbors, on both the local component and the adjacent RAW Bayer component, is extracted:
- If a component is considered too light, it is declared as bad.
- Components that are too dark are not extracted to avoid false positives.
If a component is assumed to be bad, it is replaced by the horizontal average of its two neighbors (with the same component).
When the module is enabled, the user can configure the strength from 0 (high tolerance) to 7 (aggressive detection). In return, the 12-bit counter reports the number of bad components corrected. The counter resets every frame.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable the bad pixel module.
- Once enabled, enable or disable the bad pixel software algorithm.
- If the bad pixel algorithm is enabled, you can configure the threshold and in return be informed of the strength selected by the algorithm and the number of bad pixels detected. If the bad pixel algorithm is disabled, you can choose a fixed strength and in return be informed of the number of bad pixels detected.
- Apply the configuration.
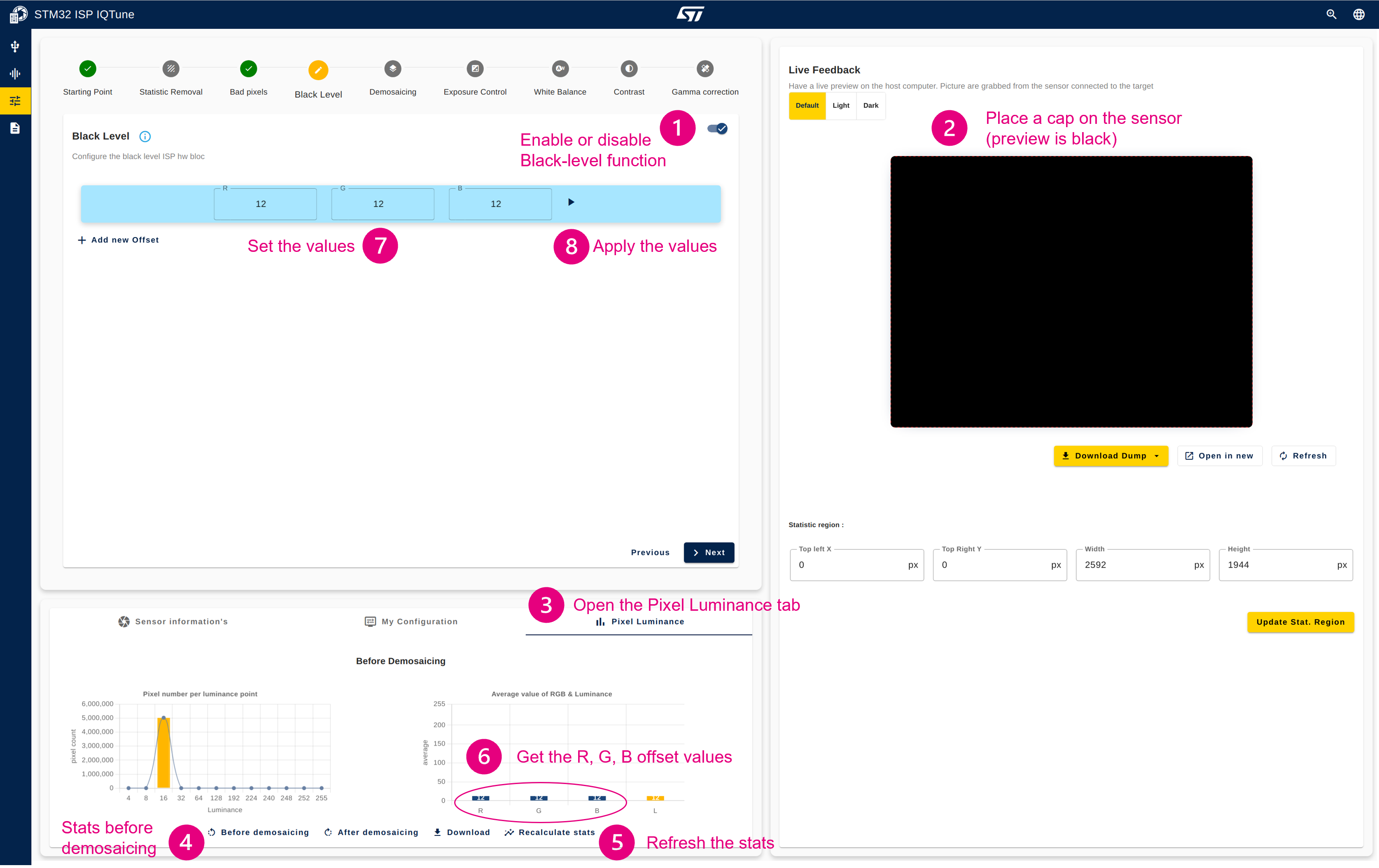
4.3.3. Step 3: Configure the black level
Description:
This module suppresses a potential positive black-level offset, which occurs when the sensor sends non-null pixels while capturing a black picture. R, G, and B component offsets are subtracted from the R, G, and B Bayer components to achieve a black picture: R = G = B = 0.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable the black level module
- Place a cap on the sensor (the preview frame is now black)
- Open in the "Pixel Luminance" panel
- Click on "Before demosaicing" to get the statistics before the demosaicing (in the RAW world)
- Click on "Recalculate stats"
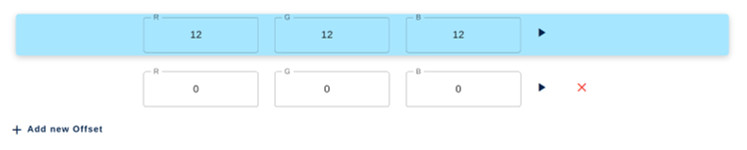
- The "Average value of RGB & Luminance" graph is updated with the R, G, and B component averages that correspond to the black offset to be applied for each R, G, and B component. In this example, with the IMX335, we obtain R=12, G=12, and B=12.
- Set the R, G, and B offset values
- Apply the values by clicking the play button
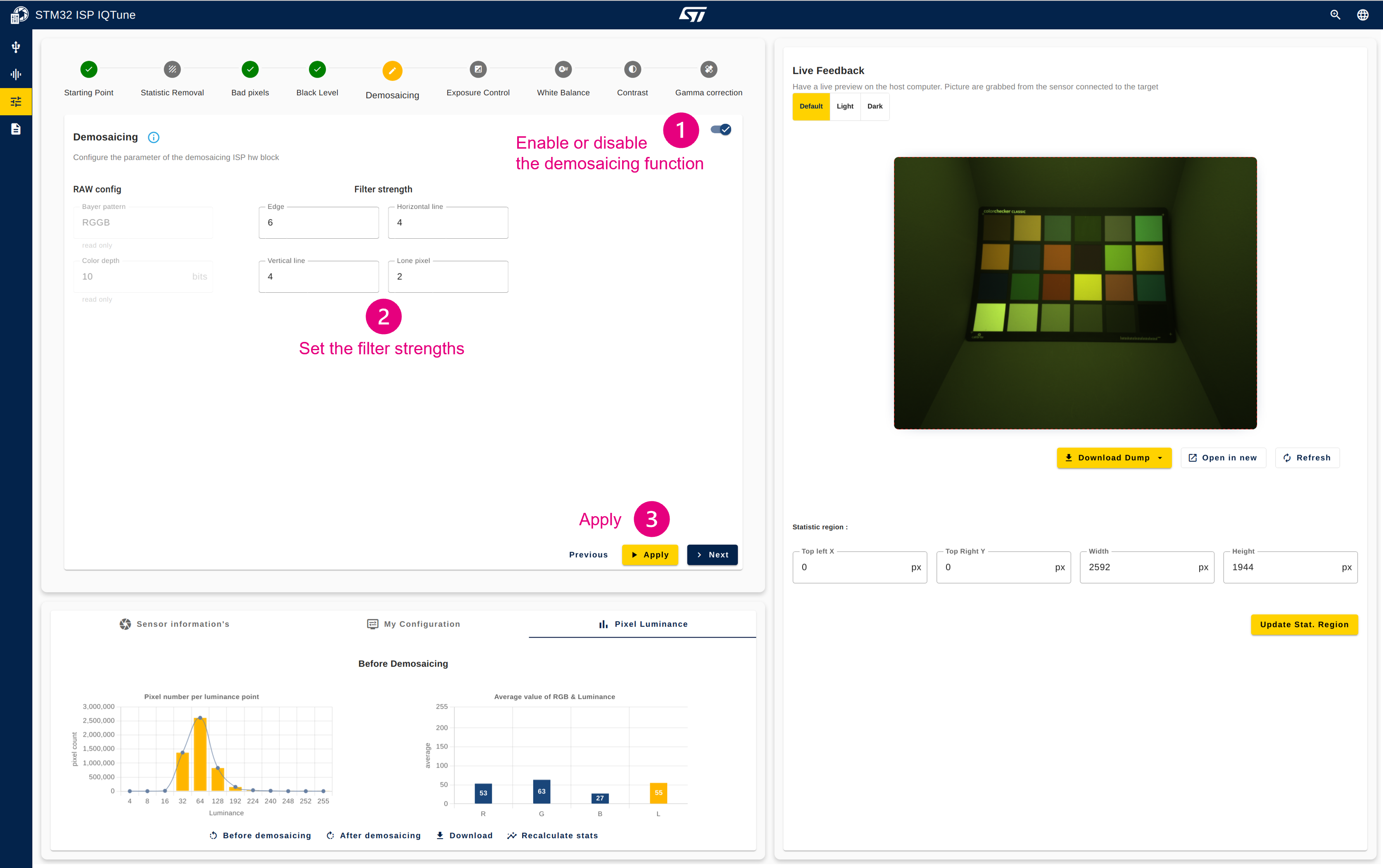
4.3.4. Step 4: Configure the demosaicing
Description:
The module operates on the pixel pipes. It implements a medium-quality conversion from RAW Bayer 8 bpp to RGB 24 bpp. The output RGB pixel rate matches the input component rate.
The demosaicing process takes the surrounding 3x3 components as input, applies linear heuristics to determine the most likely missing components, and generates an output RGB888 pixel. The underlying heuristic filters try to extract and adapt to edges, horizontal and vertical lines, and lone pixels (0: no detection, pure linear interpolation; 1 to 7: relative detection strength).
Configuration procedure:
- Enable the demosaicing module.
- Once enabled, you can update the strength of the filters used to detect edges, horizontal and vertical lines, and lone pixels. The default values provide good results.
- Apply the configuration.
4.3.5. Step 5: Configure the gamma correction
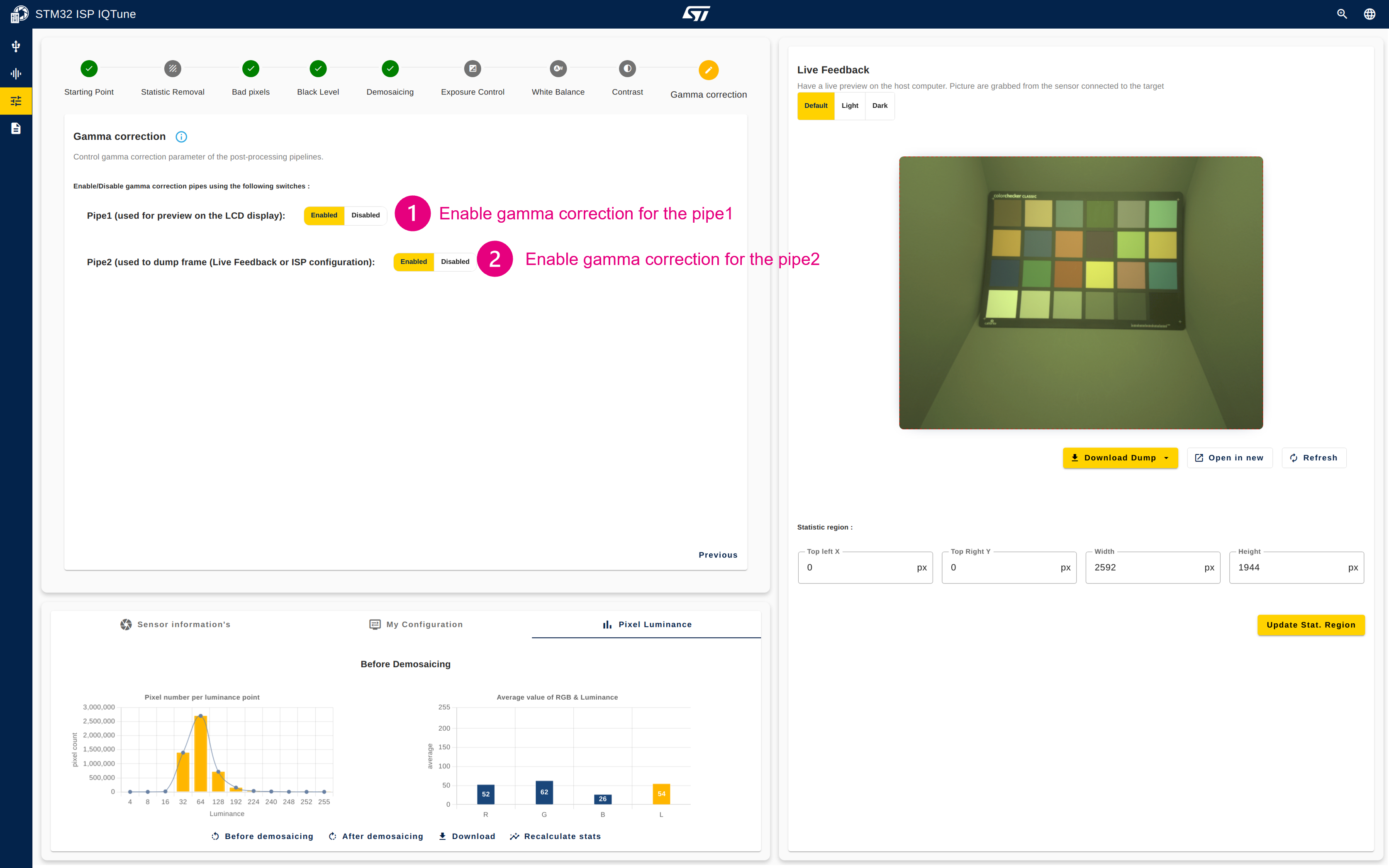
Description:
This module implements a gamma compression on each R, G, and B component using a static gamma exponent of 2.2 to store gamma-compressed pictures, as defined in the sRGB standard.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable gamma correction for the pipe1
- Enable gamma correction for the pipe2
4.3.6. Step 6: Configure auto white balance (AWB) profiles
Description:
This module interacts with the ISP gains and the color correction matrix block:
- The ISP gain equalizes the R, G, and B components by applying independent gains to each R, G, and B component to ensure white appears white. The G gain is the reference and is always 1. The R and B gains are updated using the G gain as reference.
- The color correction matrix converts the frame from the sensor RGB space to the sRGB space to achieve good color rendering.
Configuration procedure:
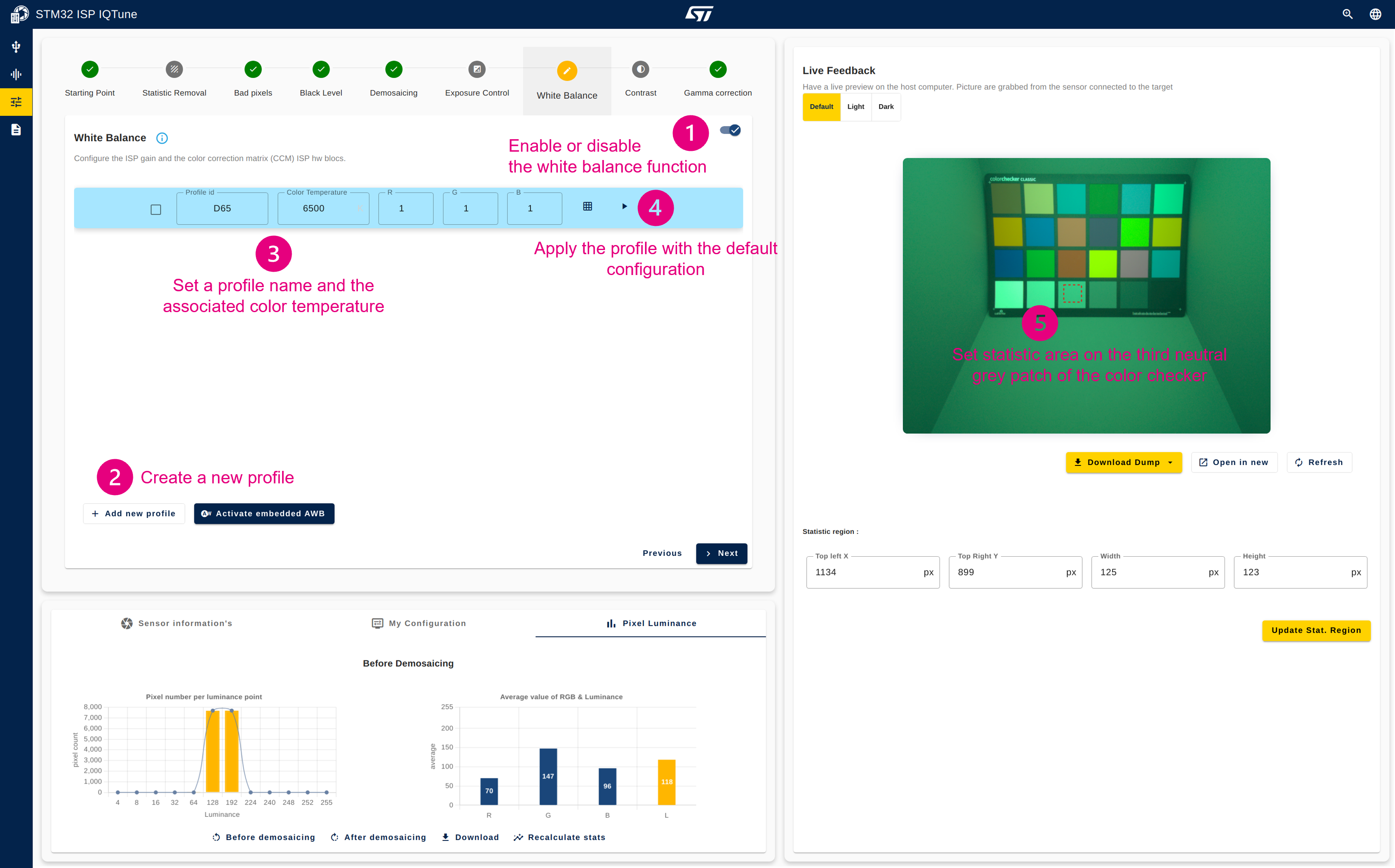
4.3.6.1. Prepare your white balance profile
- Enable the white balance correction module.
- Ensure that the AWB algorithm is disabled.
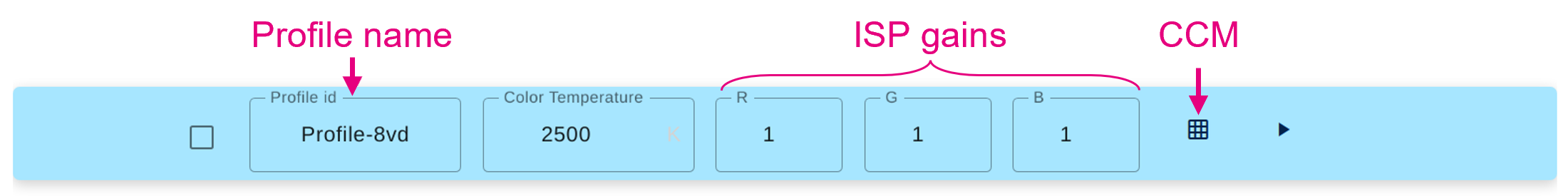
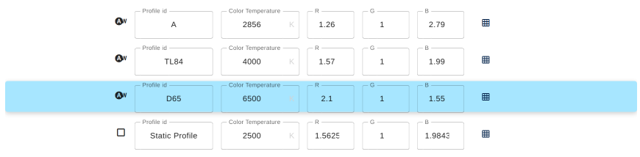
- Create a new white balance profile. Newly created profiles always have all gains set to 1 and a CCM set with an identity matrix.
- Name your profile and set the color temperature information box with the value retrieved using the spectrometer.
- Apply the white balance profile.
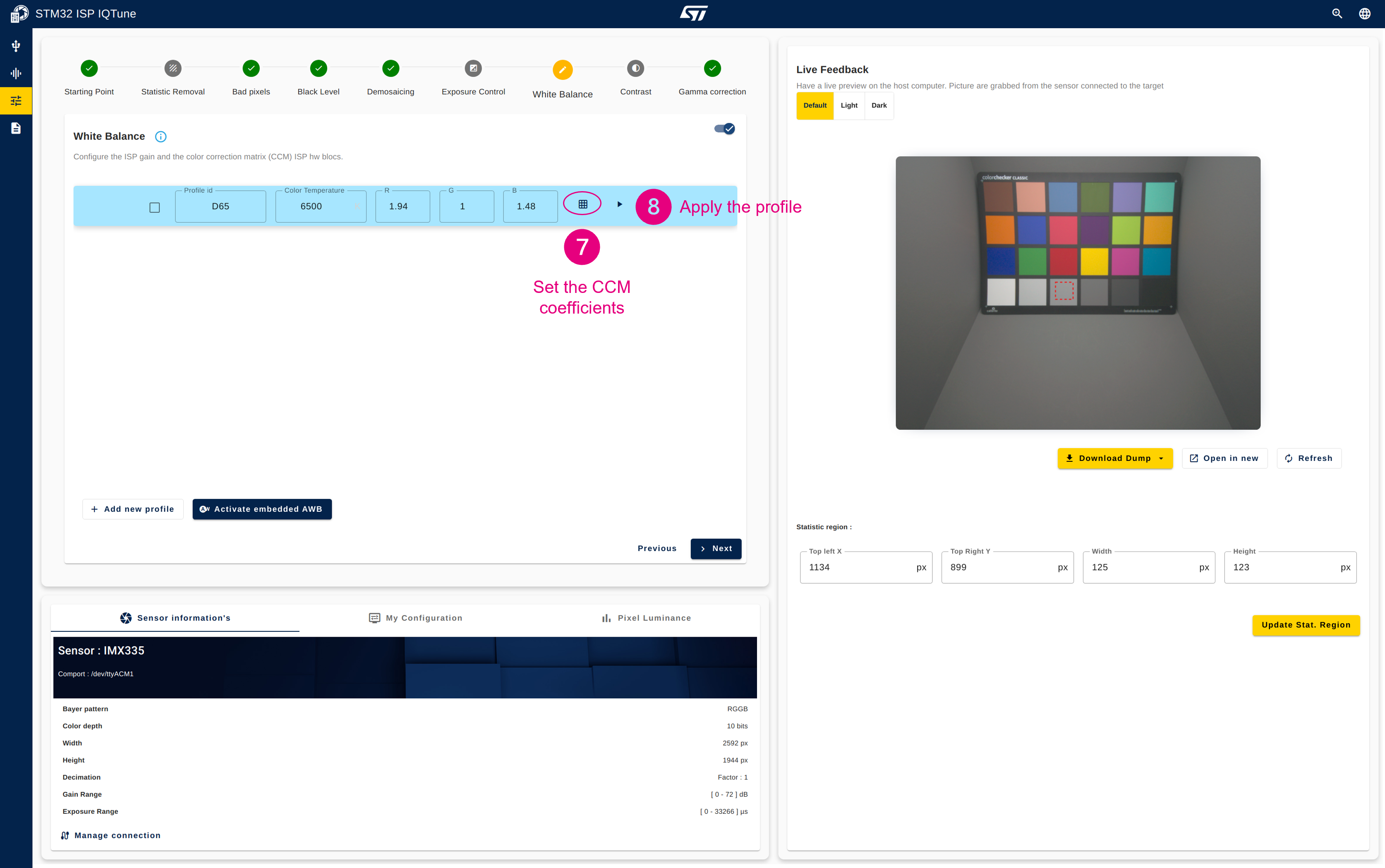
- Set the statistics area on the third neutral gray patch of the color checker.
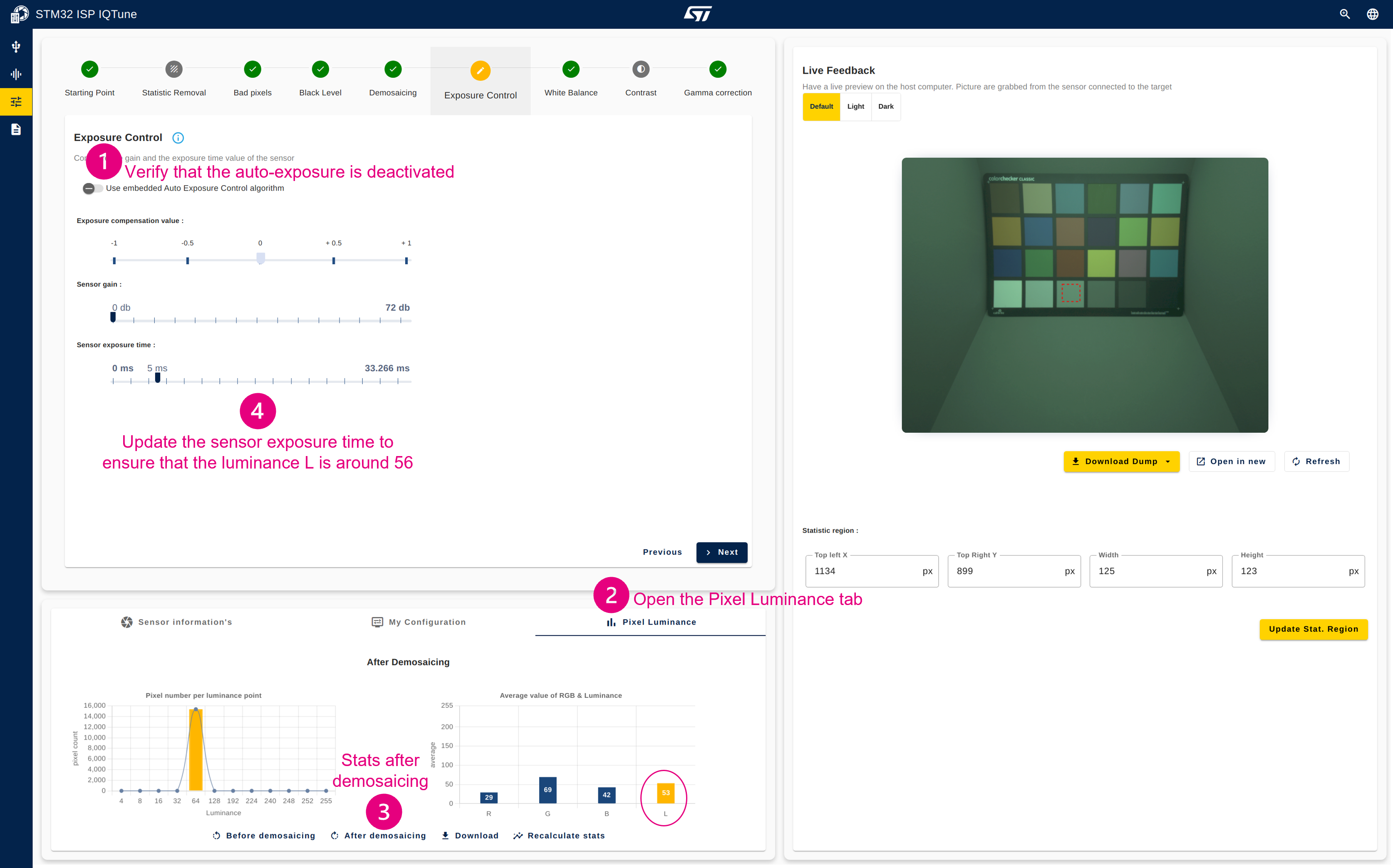
4.3.6.2. Ensure the color checker is well exposed using the exposure control panel
- Verify that the auto exposure algorithm is deactivated.
- Open the "Pixel Luminance" panel.
- Click "After demosaicing" to get the statistics after the demosaicing process (in the RGB world)
- Update the "Sensor exposure time" to ensure that the luminance L (displayed in the "Average value of RGB & Luminance" graph) is around 56. The sensor gain must be as low as possible.
4.3.6.3. Configure the ISP gain to ensure white appears white
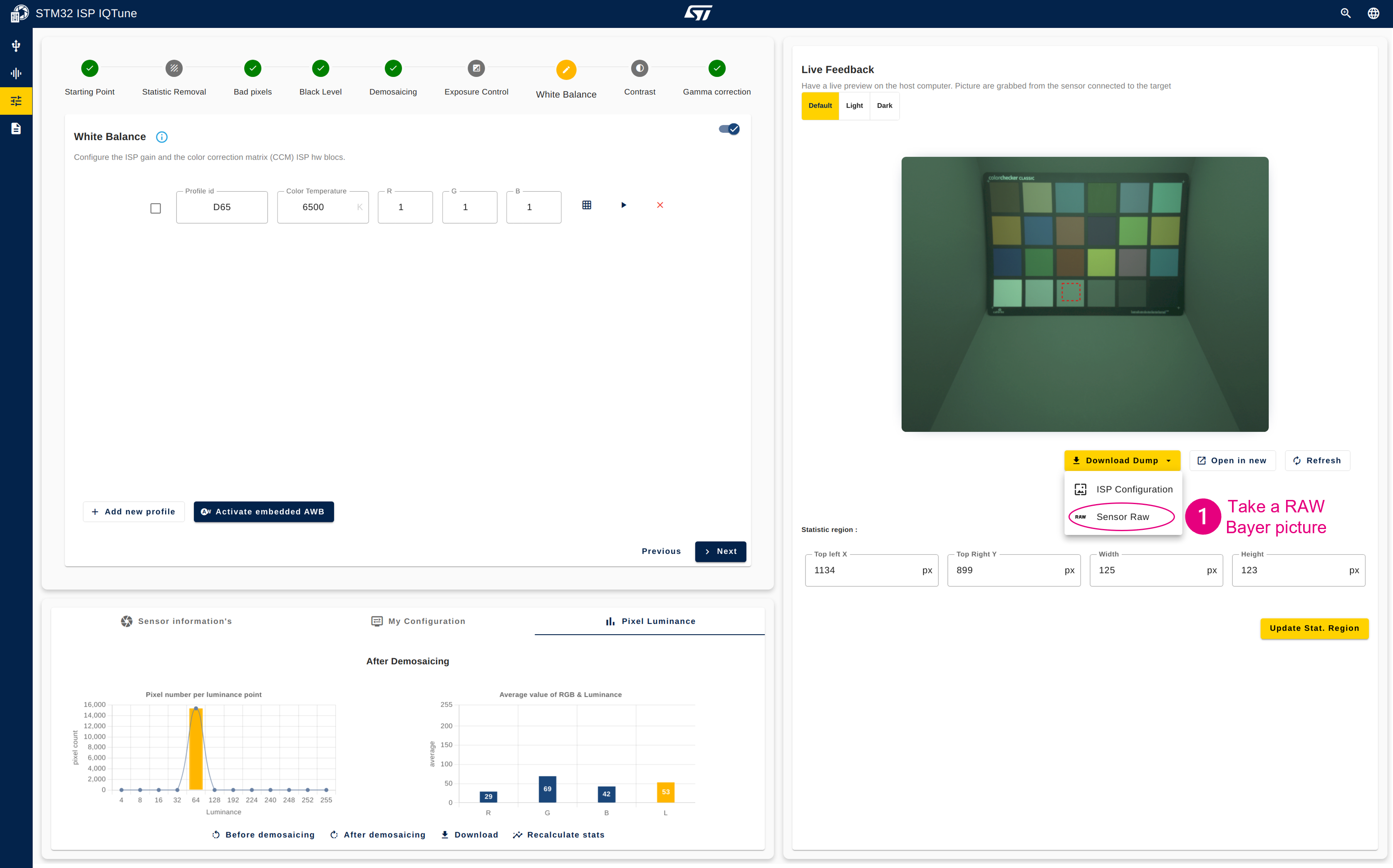
- Take a RAW Bayer picture of the color checker (picture is saved as a .pgm file).
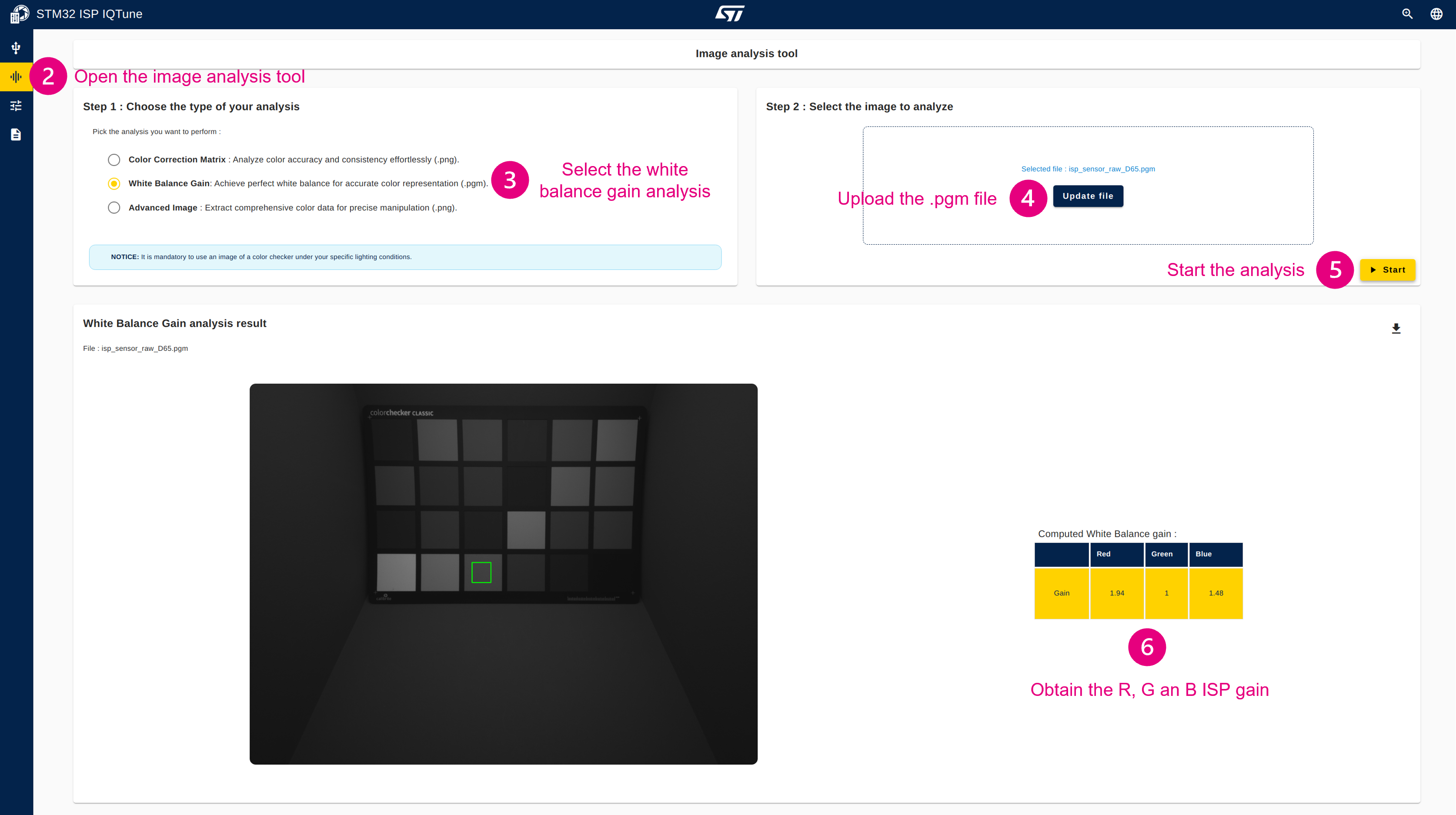
- Open the "Analysis" panel.
- Select "White Balance Gain" analysis.
- Upload the RAW Bayer picture (.pgm file).
- Start the white balance gain analysis. If the analysis fails, it is likely that the color checker is not detected because it is underexposed. In that case, slightly update the sensor exposure time and perform the steps again from step 1.
- Get the R, G, and B ISP gains computed by the analysis tool.
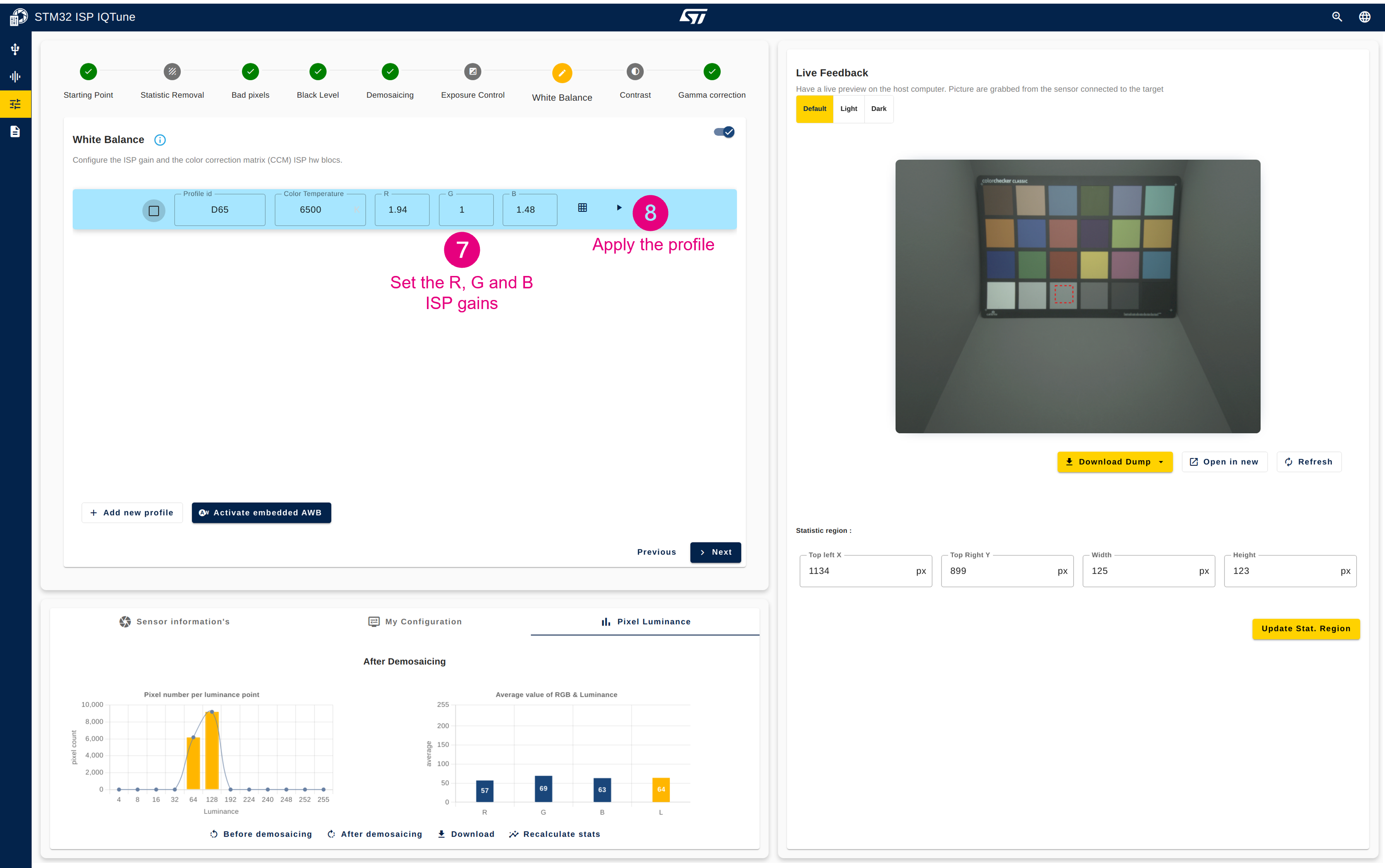
- Go back to the "White Balance" panel and set the R, G, and B gains of your white balance profile.
- Apply the white balance profile.
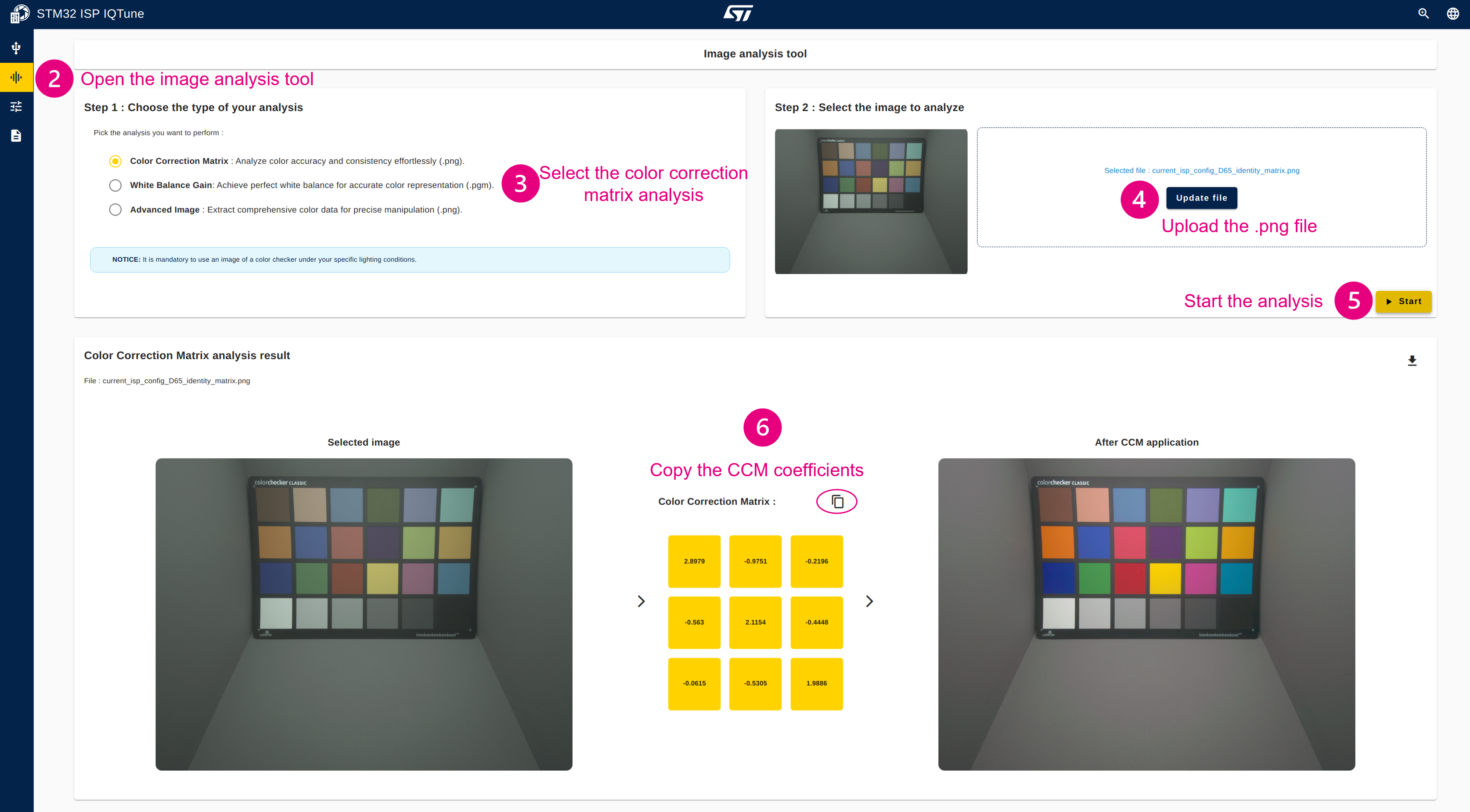
4.3.6.4. Configure the color correction matrix for optimal color rendering
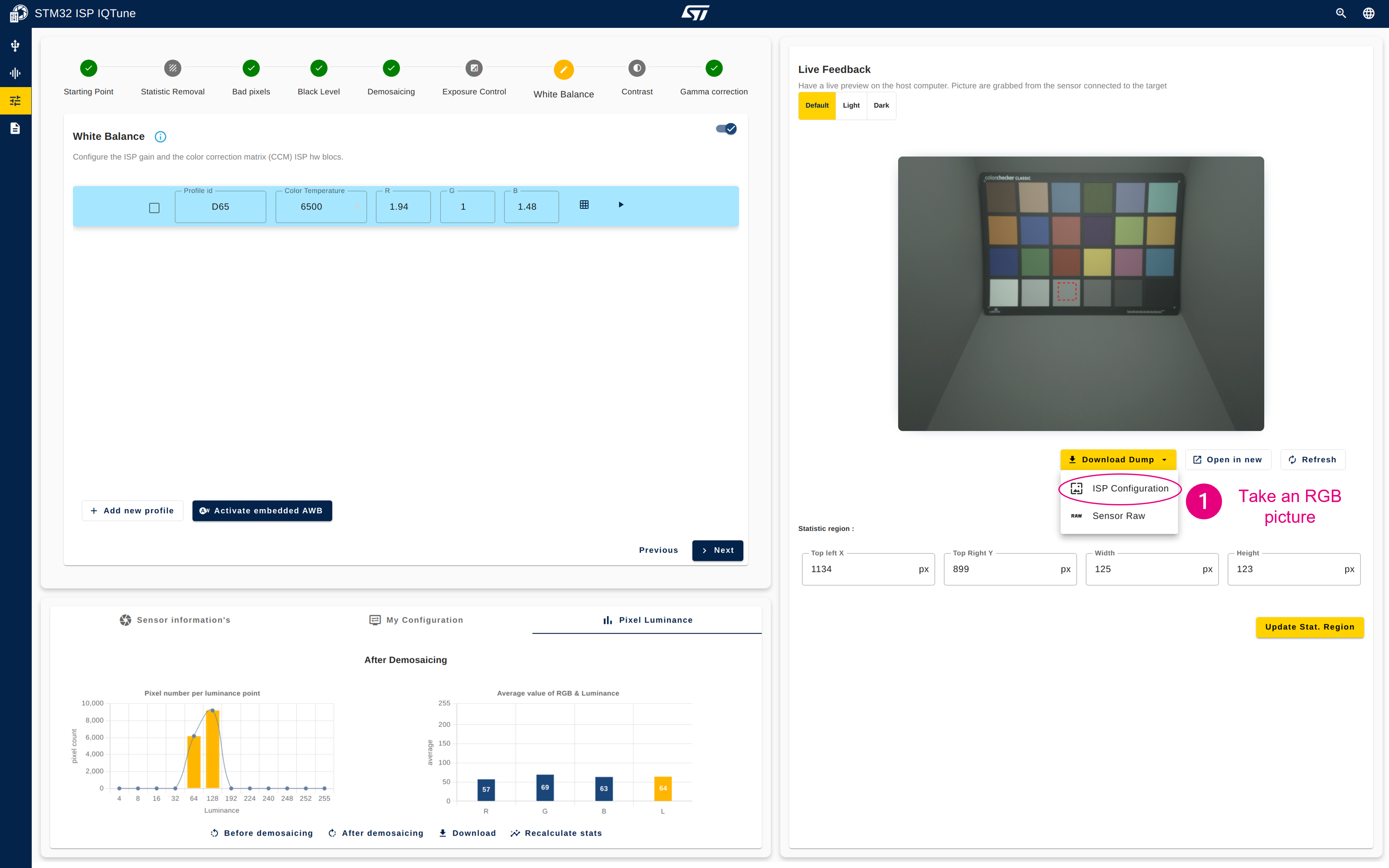
- Take an RGB picture of the color checker with ISP gain applied (frame is saved as a .png file).
- Open the "Analysis" panel.
- Select "Color Correction Matrix" analysis.
- Upload the RGB picture (.png file)
- Start the CCM analysis.
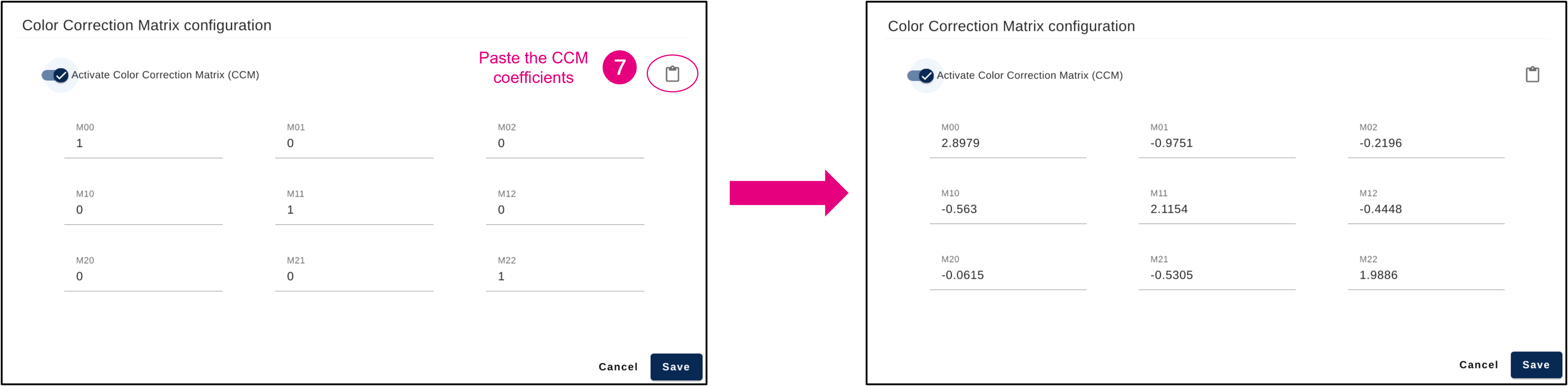
- Get the CCM coefficient that have been computed (you can use the copy button to save those values).
- Go back to the "White Balance" panel and set the CCM coefficients (you can paste the coefficient values that have been copied)
- Apply the white balance profile.
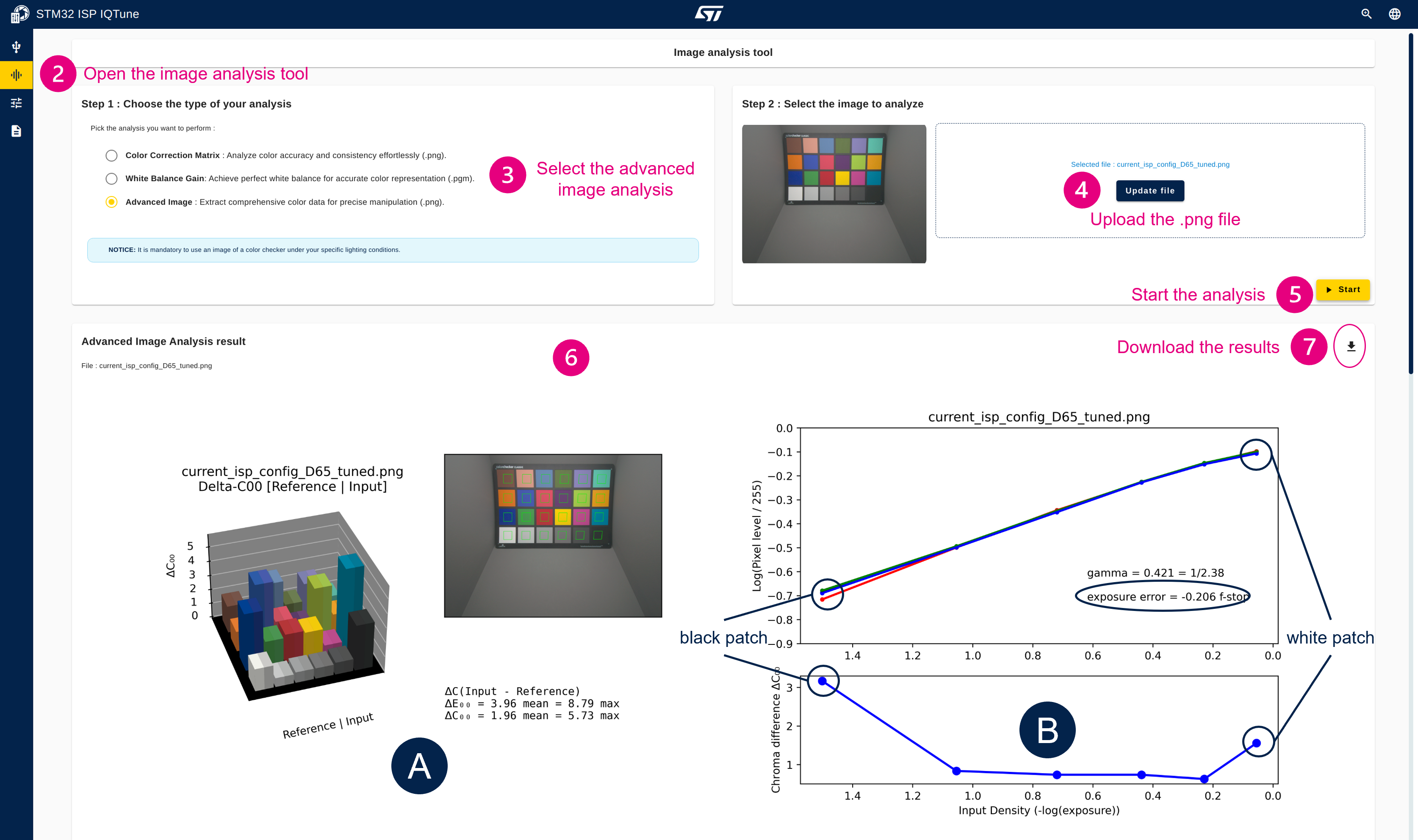
4.3.6.5. Analyze the final ISP configuration to check color accuracy versus the reference colors
- Take an RGB picture of the color checker with ISP gain and CCM applied (frame is saved as a .png file).
- Open the "Analysis" panel.
- Select "Advanced Image" analysis.
- Upload the RGB picture (.png file).
- Start the advanced image analysis.
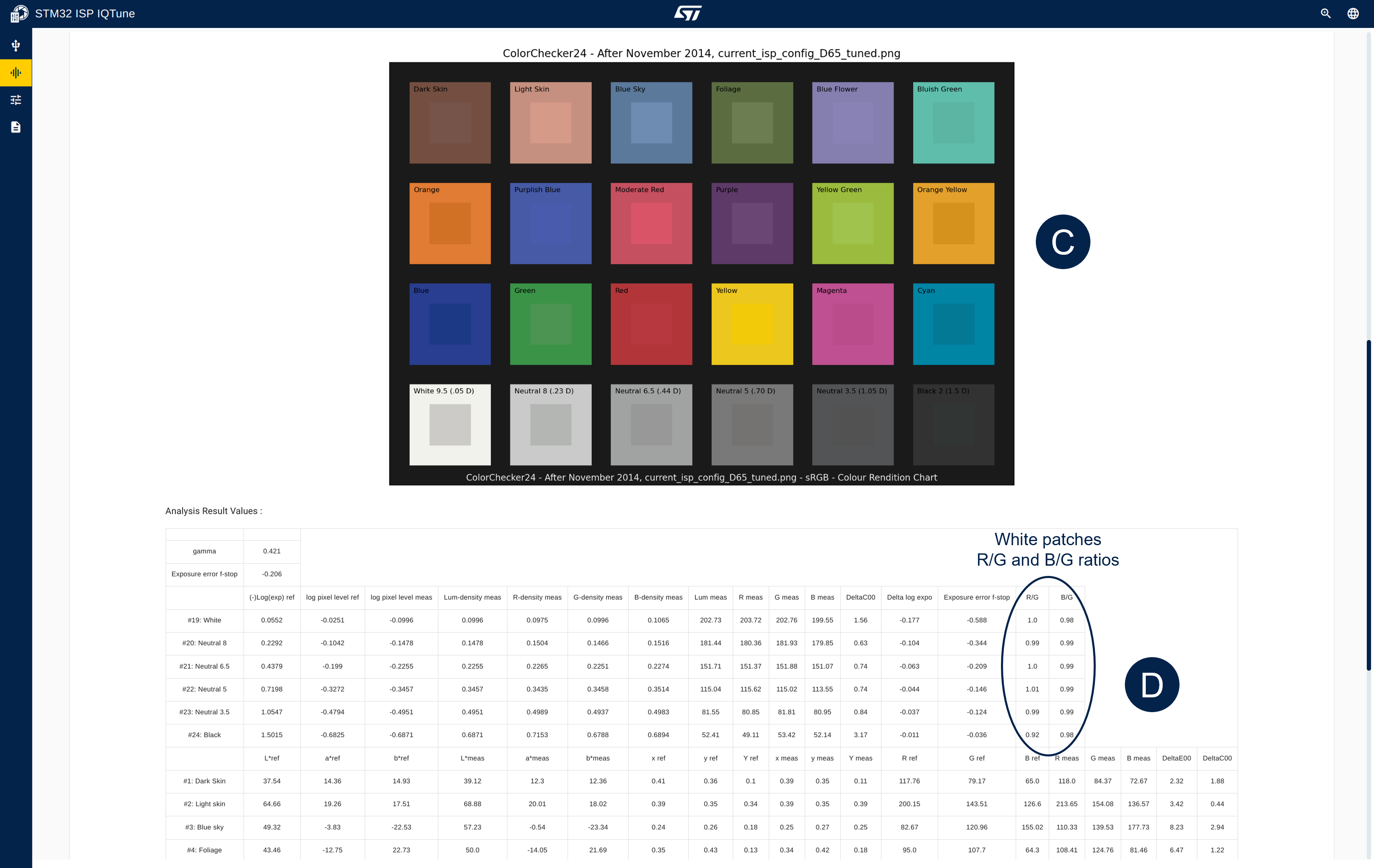
- The color analysis is complete, and you can verify the color accuracy with the different graph and information provided.
- Optionally, you can download the analysis results as a zip file containing the graphs and .csv file.
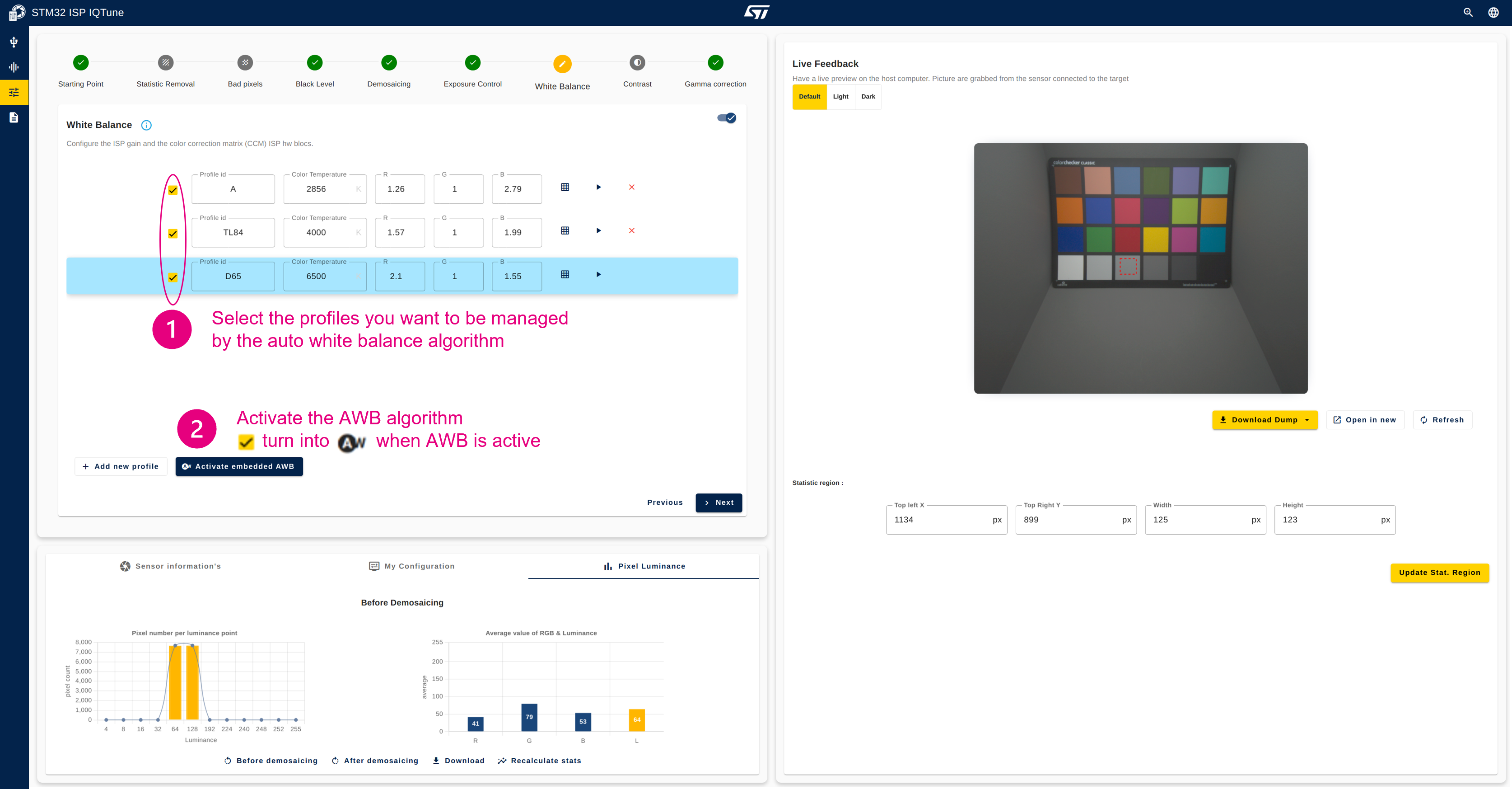
4.3.6.6. Enable the AWB algorithm
- Select the white balance profile to be managed by the AWB algorithm.
- Activate the AWB algorithm.
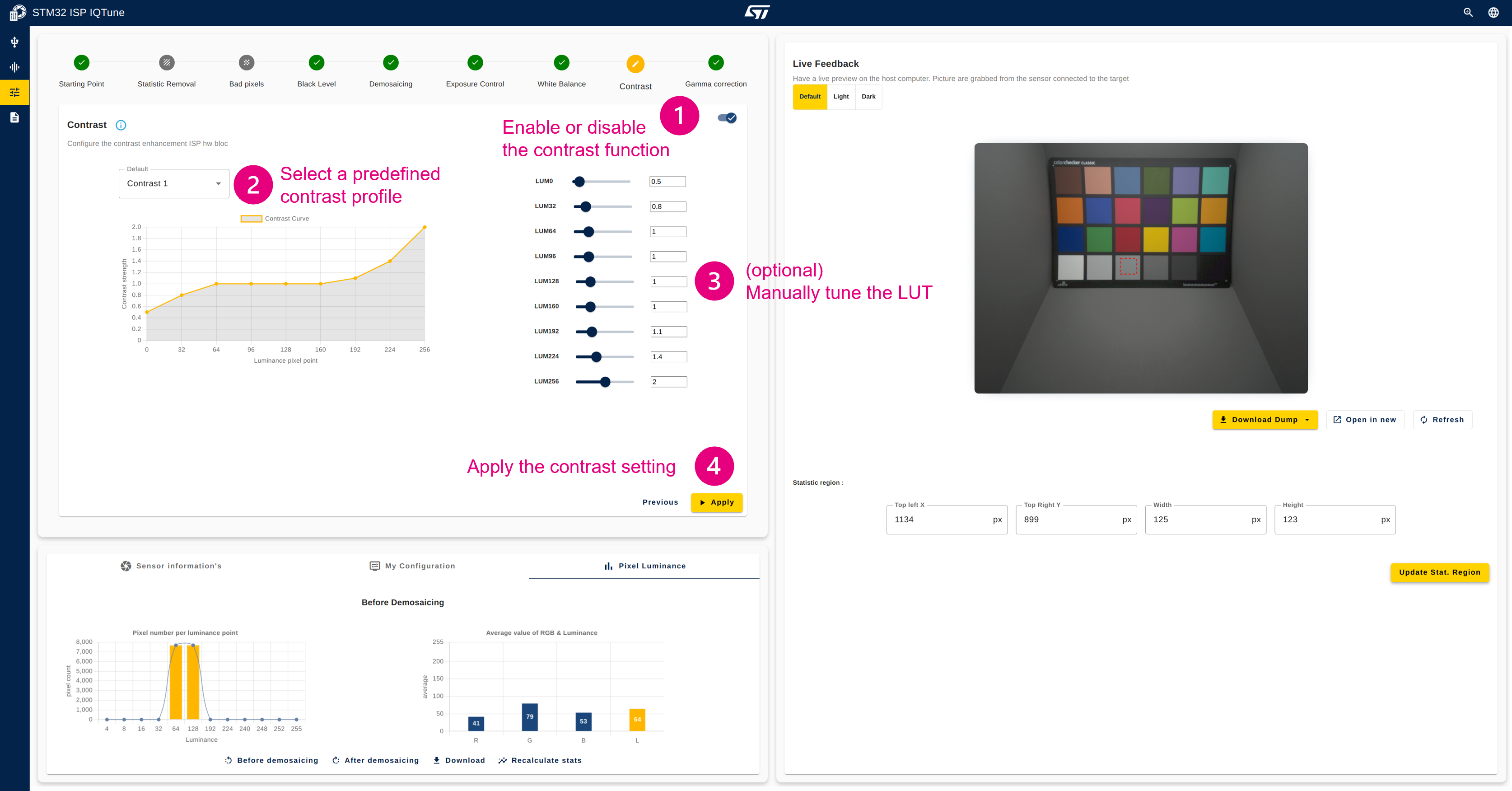
4.3.7. Step 7: Configure the contrast (optional)
Description:
This module concludes the image processing pipeline. It enhances the contrast of the frame by non-linear emphasis of pixel luminance. It takes the RGB values from the pipeline, computes the luminance of the local pixel, and determines the desired luminance adjustment factor based on the input luminance using a lookup table. The output RGB components are clamped to 8 bits.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable the contrast module
- Select a predefined contrast profile
- Optionally tune the LUT
- Apply the contrast settings
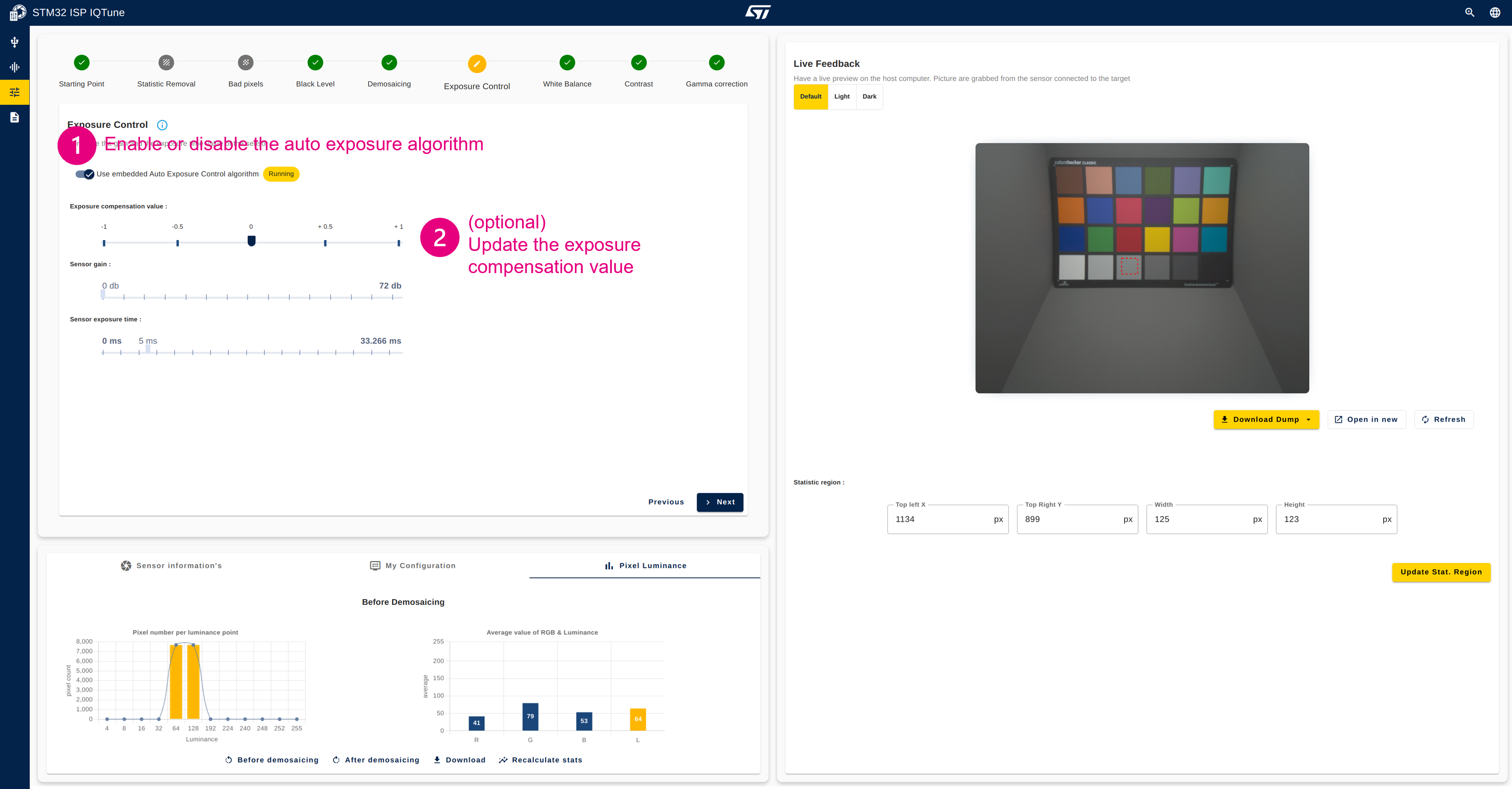
4.3.8. Step 8: Configure the exposure control
Description:
This module aims to configure the sensor exposure to ensure the frame is well-exposed (neither too dark nor too bright). The exposure is not controlled by a parameter inside the ISP but by the sensor itself by updating the exposure time or the sensor gain, or both.
The user has the possibility to:
- Control the exposure manually by updating the gain or the exposure time, or both
- Enable the auto exposure algorithm
- The algorithm automatically sets the appropriate sensor gain and exposure time based on statistics retrieved by the ISP and the ideal exposure target.
- In this configuration, the user can control only the exposure compensation to shift the exposure target value.
Configuration procedure:
- Enable the auto exposure algorithm
- Optionally change the exposure compensation value
4.3.9. Step 9: Export the ISP configuration
Description:
Once the ISP tuning is finalized, the ISP configuration needs to be exported so that the ISP settings and behaviors are reflected in the final application.
Configuration procedure:
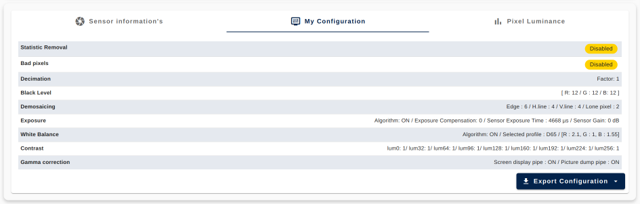
- Open the "My Configuration" panel
- Click on "Export Configuration" and chose the .h code file format.
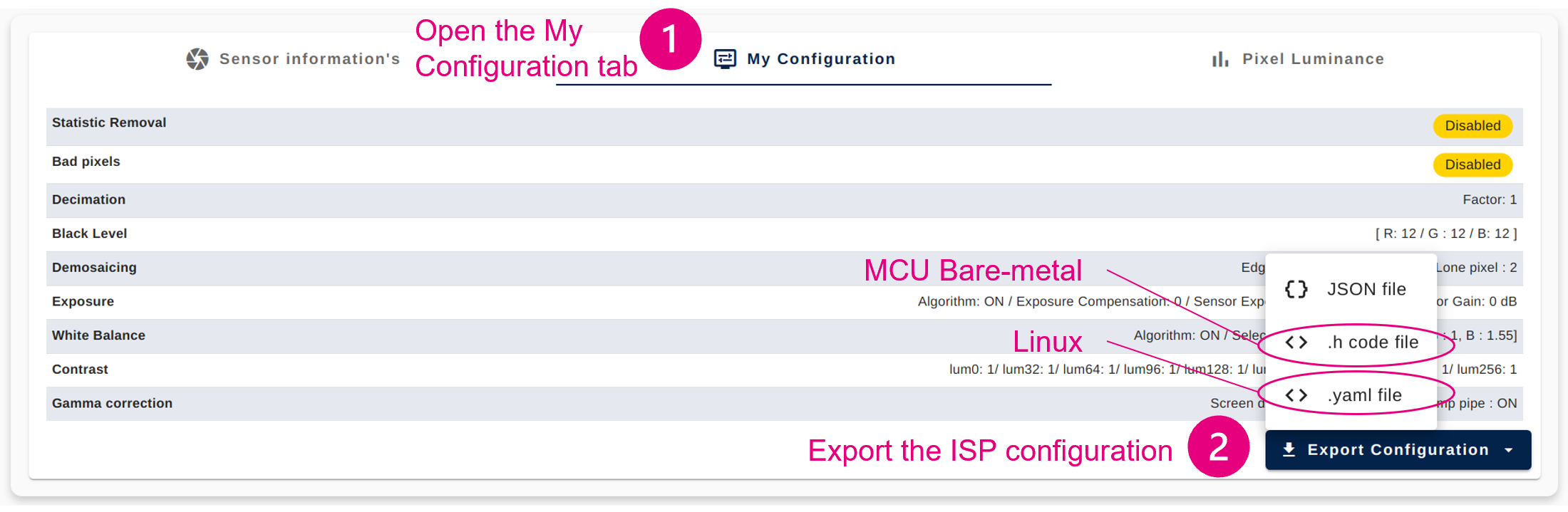
4.4. Tips
4.4.1. Save and load your current work
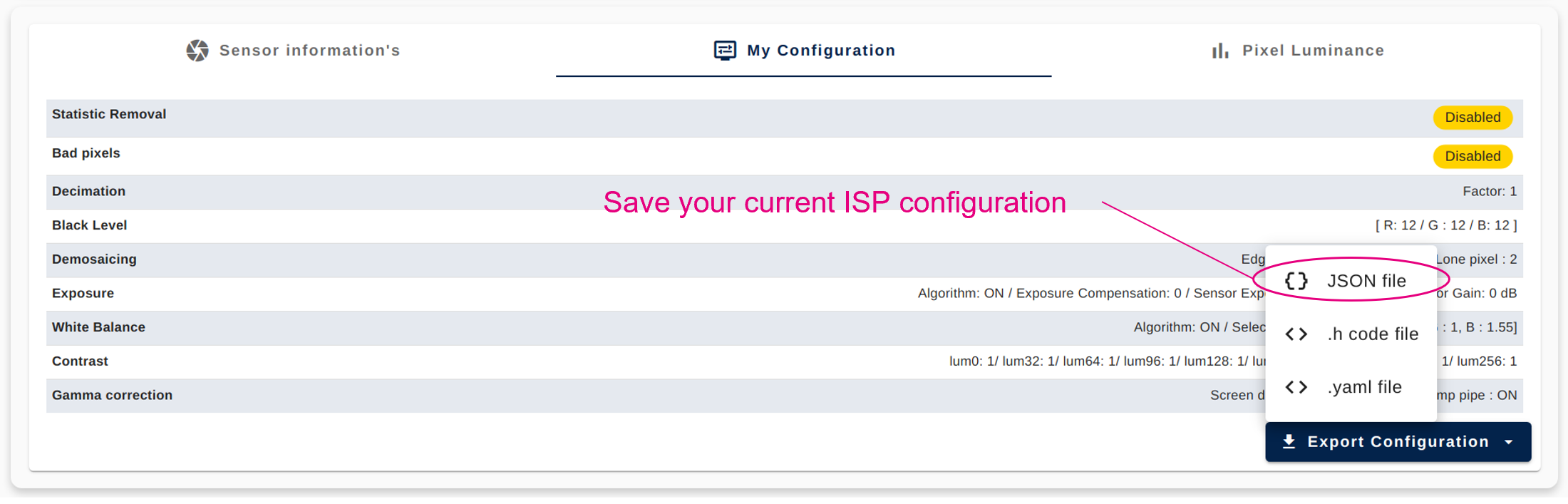
4.4.2. Load a saved work
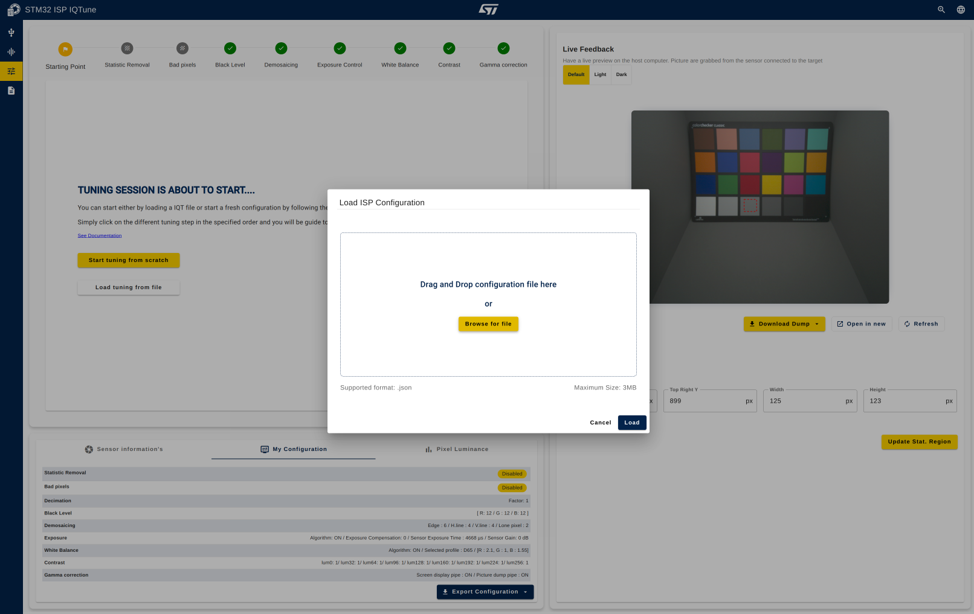
4.4.3. Sensor information at a glance
All the sensor information is summarized in the "Sensor Information" panel.
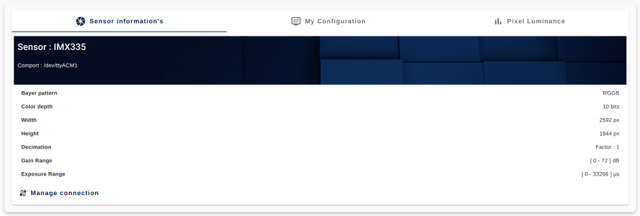
4.4.4. Current configuration at a glance
All ISP module status is summarized in the "My Configuration" panel.