STiRoT stands for ST immutable (unchangeable) Root Of Trust. The STiRoT is embedded in all STM32H7S devices.
1. Introduction
The purpose of this article is to provide the necessary background to understand and execute the related How to start with STiRoT on STM32H7S wiki article.
This article describes STiRoT process steps developed in STM32CubeH7RS firmware provided by ST.
For more information about STiRoT please refer to STiRoT for STM32H7S
2. STiRoT services
The two STiRoT services that are provided are used in the How to start with STiRoT on STM32H7S.
- 1) The Secure Boot (Root of Trust services):
- It is an immutable code that runs after every system reset. It activates STM32 runtime protections and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- Integrity: to ensure that no corrupted or maliciously modified firmware is about to run.
- Authenticity: to verify that firmware comes from a trusted and known source to prevent unauthorized entities from installing and executing code.
- Integrity: to ensure that no corrupted or maliciously modified firmware is about to run.
- It is an immutable code that runs after every system reset. It activates STM32 runtime protections and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- 2) The Secure Firmware Update:
- It is an immutable code that detects if a new firmware image is available, checks its authenticity and verifies the integrity of the code before installing it after decryption.
3. STiRoT use cases and processes
STiRoT can be used in two configurations :
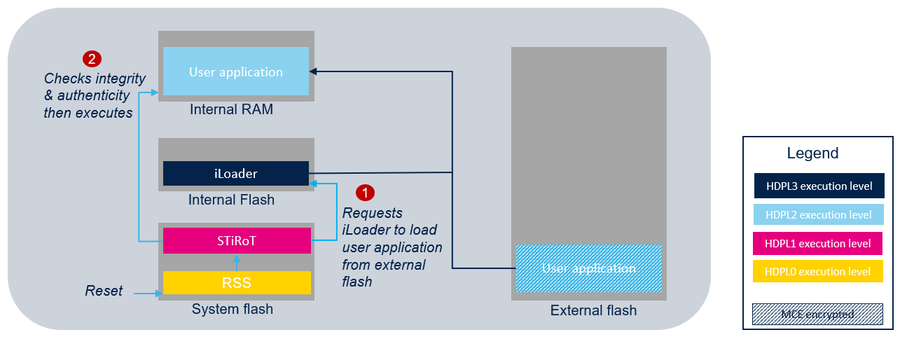
- One boot stage : STiRoT directly manages the user application. At reset, STiRoT first requests iLoader to load the user application from external flash to internal RAM. Then after a successful verification of the authenticity and the integrity of the user application, STiRoT executes it.
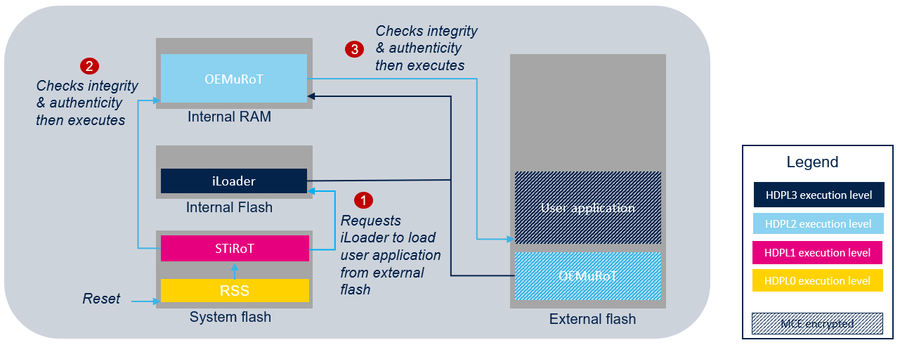
- Two boot stages: STiRoT manages an updatable boot stage (OEMuRoT) which manages the user application. The updatable boot stage can be customized to fit the customer needs.
4. STiRoT configuration preliminary stage
4.1. Product state definition
The product states define the security level of the product. Four levels are available :
- Open:
- Debug entirely open.
- Bootloader available.
- State mainly used during development.
- Provisioning:
- Debug access only available if DA-Config is previously provisioned. Full-Regression and Intrusive Debug are the only allowed regressions.
- Bootloader available.
- Secure Firmware Install (SFI) can be initiated. It is not possible in Closed and Locked states.
- State defined during the product provisioning and is therefore not a selectable state.
- Closed:
- Debug closed but can be still opened through Debug Authentication.
- State defined when the product is entirely provisioned.
- Locked:
- Final and immutable product state.
- Debug definitively closed even through Debug Authentication.
- Regression is not possible anymore.
- State used for the fully provisioned product.
The product state must be chosen depending on the user application development phase and the security level needed.
In the STM32CubeH7RS firmware the script provisioning.bat allows the user to select a product state and sets it by modifying the right option bytes.
4.2. Debug Authentication configuration
The Debug Authentication allows the user to securely re-open the debug access or perform regressions. Two methods are available to use the Debug Authentication :
- Password authentication allows only full regression to OPEN state.
- Certificate authentication allows regression and debug opening.
For more details about debug authentication mechanism please refer to Debug Authentication for STM32H7RS.
4.3. iLoader compilation
The STiRoT never accesses the external flash memory and relies on an immutable loader installed in the user flash to handle the transfers between internal RAM and the external flash memory.
The iLoader is an example of an immutable loader application provided in the STM32Cube_FW_H7RS including functions to manage the iLoader features.