1. Human interface device over generic attribute profile (GATT)
Human interface device over GATT profile (HOGP)[1] is a low-energy, generic-attribute-profile-based profile defined by the Bluetooth® special interest group (SIG)[2]
This profile is an adaptation of the USB human interface device (HID) specification[3] to operate over a Bluetooth® Low Energy wireless link. This profile operates on Bluetooth® Low Energy transport only.
The profile defines three roles:
- The human interface device (HID) is a GATT server.
- The boot host is a GATT client.
- The report host is a GATT client.
Bluetooth® Low Energy devices are not supported by PC BIOS, because the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack and drivers are not loaded yet at this point, so the boot host role cannot be used with clients like PCs, smartphones, or tablets.
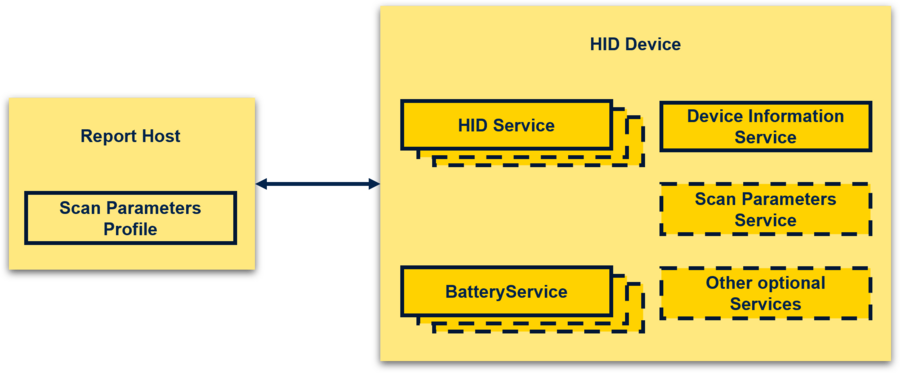
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP: report host and HID device |
|---|
The report host supports the scan client role of the scan parameters profile.
The HID device has:
- One or more instances of the HID service.
- One or more instances of the battery service.
- A single instance of the device information service.
- Optionally, one instance of the scan parameters service as part of the scan server role of the scan parameters profile.
- Optionally, a single or multiple instances of other services.
This wiki page describes the HID mouse project, provided with the STM32CubeWBA MCU Package[4]
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP mouse profile with STM32WBA |
|---|
The table below describes the structure of HOGP services:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HOGP profile specification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The table below describes the HID report characteristic descriptors:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy HID report characteristic descriptors specification | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The table below describes the battery level characteristic descriptor:
| Bluetooth® Low Energy battery level characteristic descriptor specification | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
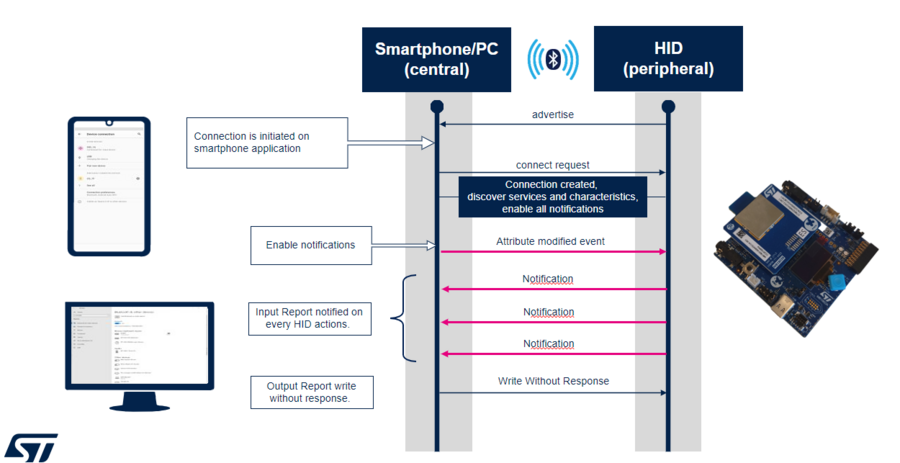
HOGP is a combination of a HID device and a report host to connect and exchange data in different applications.
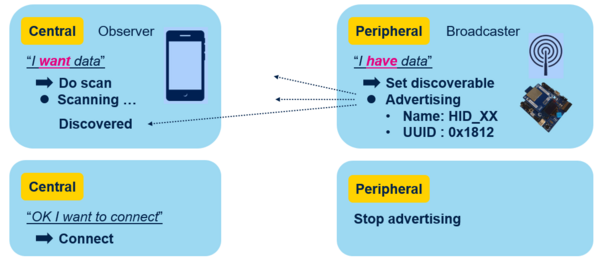
The generic access profile (GAP) defines and manages advertising and connection.
| Report host central device and HID peripheral device |
|---|
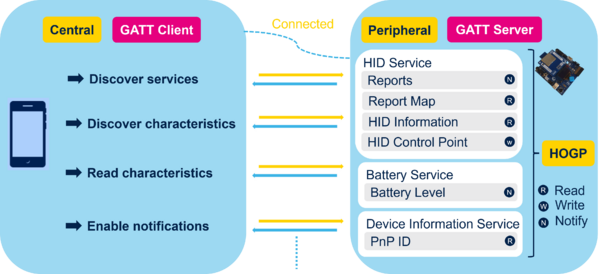
The generic attribute profile (GATT) defines and manages in/out data exchanges.
| Report host GATT client device and HID GATT service device |
|---|
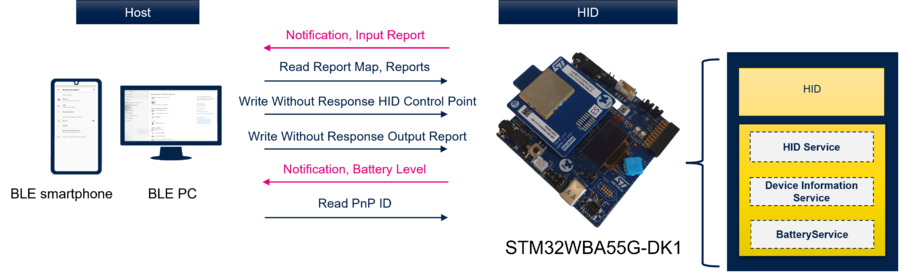
| Examples of an HID flow diagram between a STM32WBA55G-DK1 board and a Bluetooth® Low Energy PC or Bluetooth® Low Energy smartphone |
|---|
1.1. STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising data
At startup, HID device application starts fast advertising (80ms/100ms), including the STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising elements[5] described below:
| HID device STMicroelectronics manufacturer advertising data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Advertising is switched to Low-power advertising (1s/2.5s) after 60 seconds.
2. Requirements
2.1. Software and system requirements
The following list contains the required software and minimum IDE versions:
- IAR Embedded Workbench for ARM (EWARM) toolchain V9.20.1, with a patch available in the STM32WBA firmware package: STM32Cube_FW_WBA_Vx.x.x/Utilities/PC_Software/EWARMv8_STM32WBAx_V1.3.zip
- RealView Microcontroller Development Kit (MDK-ARM) toolchain V5.38, plus a patch available in the STM32WBA firmware package: STM32Cube_FW_WBA_Vx.x.x/Utilities/PC_Software/Keil.STM32WBAx_DFP.1.3.0.zip
- STM32CubeIDE toolchain V1.14.0[6]
The following programmer software is required to program the board with a pregenerated binary:
- STM32CubeProgrammer[7]
2.2. Hardware requirements
This application requires an STM32WBA55G-DK1 (Discovery Kit) board.
| STM32WBA55G-DK1 board |
|---|
2.3. Collector applications compatible
The STM32CubeWBA HID device project is compatible with the following collectors:
3. STM32WBA55G-DK1 HID Device example description
3.1. Project directory
Refer to STM32CubeWBA Bluetooth® LE MCU Package Wiki page for project directory information and how to download the "BLE_HID_Mouse" application.
3.2. Project description
3.2.1. Structure
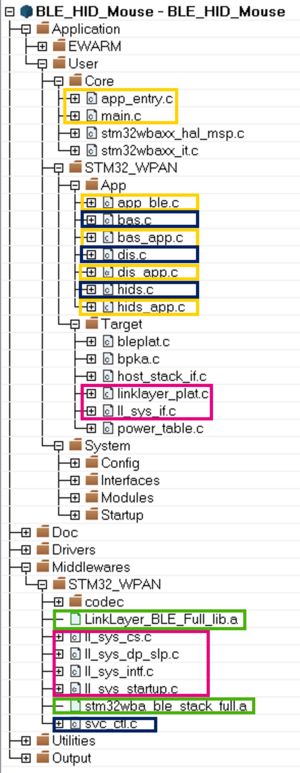
Below, a software project structure with the most important parts:
| HID Mouse project structure |
|---|
|
WARNING: Do not modify the files in Middleware folder |
3.2.2. Application initialization
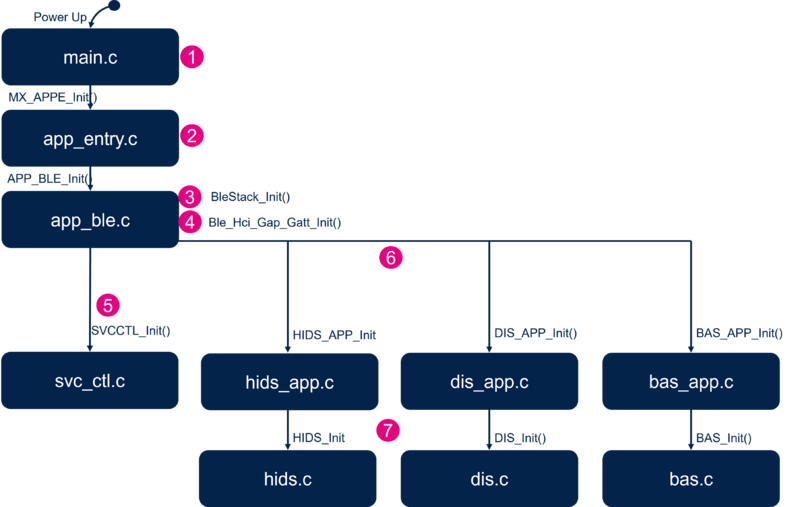
The different steps of the application initialization are described below:
| HID Mouse project initialization |
|---|
3.2.3. GAP and GATT initialization and interaction
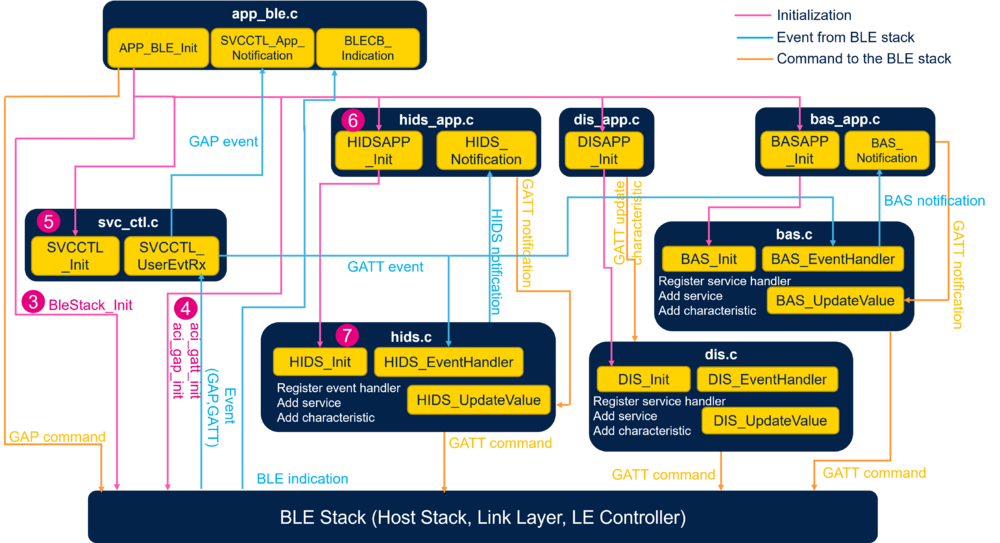
| HID Mouse Device software module interaction |
|---|
and ![]() The Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse application initialization is done within app_ble.c
The Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse application initialization is done within app_ble.c
- Initialize the Bluetooth® Low Energy stack - initialize the device as peripheral - configure and start advertising: ADV parameters, local name, UUID - APP_BLE_init().
- Call the services controller initialization SVCCTL_Init() - svc_ctl.c.
- Manage the GAP event - SVCCTL_App_Notification().
- HCI_LE_CONNECTION_COMPLETE - provides information of the connection interval, slave latency, supervision timeout.
- HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETE- provides the new information of the connection.
- HCI_DISCONNECTION_COMPLETE - informs the application about the link disconnection and the reason.
The Services management is done by the service controller, svc_ctl.c
- Initialize the number of registered handlers - SVCCTL_Init().
- Manage events - SVCCTL_UserEvtRx()- from the Bluetooth® Low Energy Host Stack and redirect them to the gap event handler - SVCCTL_App_Notification.
The application level of the HID Mouse Device is done with hids_app.c:
- Initialization of the services:
- HID Service - HIDS_Init() - hids.c
- Initialization of the context of the application
- Report Map
- HID Information - BASE USB HID SPEC VERSION
- Receive notification from the HID Service - HIDS_Notification()
- When Input Report characteristic is enabled by the remote, each update of the mouse position with the joystick (HIDS_APP_UpdateReport) is transfered to the remote device (collector) - HIDS_UpdateValue().
The HID Service hids.c manages the specification of the service:
- Service Init - HIDS_Init()
- Registers HID Event Handle to Service Controller - SVCCTL_RegisterSvcHandler(HIDS_EventHandler).
- Initializes Service UUID – add HID service as Primary services.
- Initializes Report Map characteristic.
- Initializes HID Information characteristic.
- Manages the GATT event from the Bluetooth® Low Energy Stack - HIDS_EventHandler().
- ACI_GATT_WRITE_PERMIT_REQ_VSEVT_CODE
- Reception of a Write Command: HID Control Point Characteristic Value
- Sending of an aci_gatt_write_response() with an OK or KO status
- Notification to the application to Suspend or Exit Suspend - HIDS_Notification(HIDS_HCP_WRITE_NO_RESP_EVT)
- Reception of a Write Command: HID Control Point Characteristic Value
- ACI_GATT_ATTRIBUTE_MODIFIED_VSEVT_CODE
- Reception of an attribute modification - Input Report Characteristics Description Value : ENABLE or DISABLE Notification
- Notify application of the Input Report Notification - HIDS_Notification(HIDS_NOTIFICATION_ENABLED/DISABLED)
- Reception of an attribute modification - Input Report Characteristics Description Value : ENABLE or DISABLE Notification
- ACI_GATT_WRITE_PERMIT_REQ_VSEVT_CODE
3.2.4. Report Map and Input Report
HID Report Map characteristics should contain the USB HID descriptor specified in the USB HID specification [3].
An USB HID descriptor is a hard coded array of bytes describing the device’s data packets, including:
- Number of packets supported,
- Packets size,
- Purpose of each byte and bit in the packet.
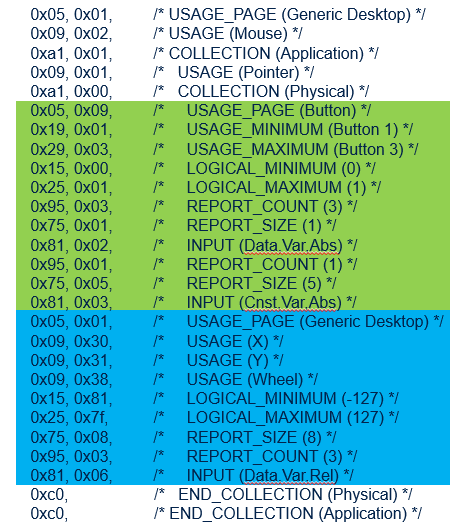
Example of USB Mouse HID descriptor for a 3 buttons Mouse with X, Y axis and a wheel:
| USB Mouse HID descriptor |
|---|
| 3 buttons Mouse with X, Y axis and a wheel |
|---|
All the hard coded bytes are described in the USB HID Usage Tables [8] document. This USB HID descriptor also defines the data structure sent in the associated Reports (Input, Output or Feature).
In this USB Mouse HID descriptor example, you can find:
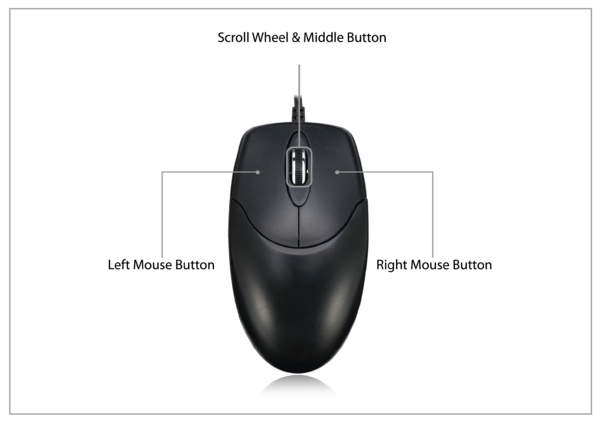
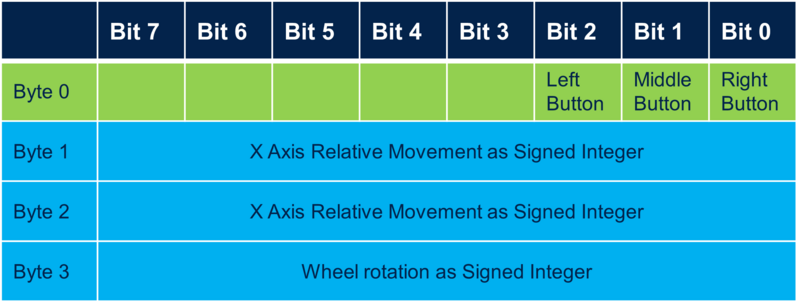
- Highlighted in green, the definition of 3 buttons represented by the 3 first bits of a byte that can have the boolean state 0 or 1.Bits 0, 1 and 2 represents the states of respectively the left, the middle and the right buttons of the mouse.The remained bits of the byte are unused.
- Highlighted in blue, the definition of 3 bytes for the X, Y axes relative movement and wheel rotation. Each byte represents a signed integer that can take a value comprised between -127 to 127.
Example of the Input Report associated to USB Mouse HID descriptor:
| 3 buttons Mouse with X, Y axis and a wheel data structure |
|---|
3.3. How to use the Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse application
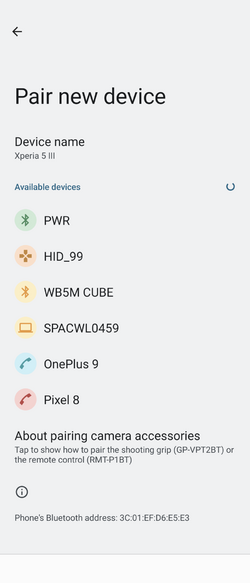
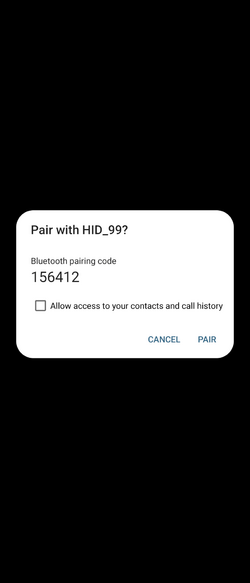
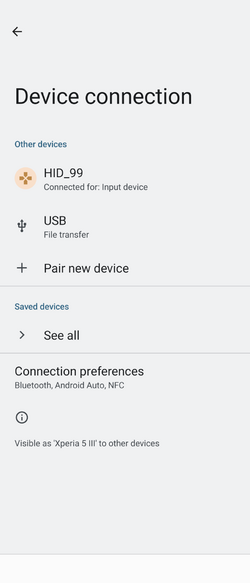
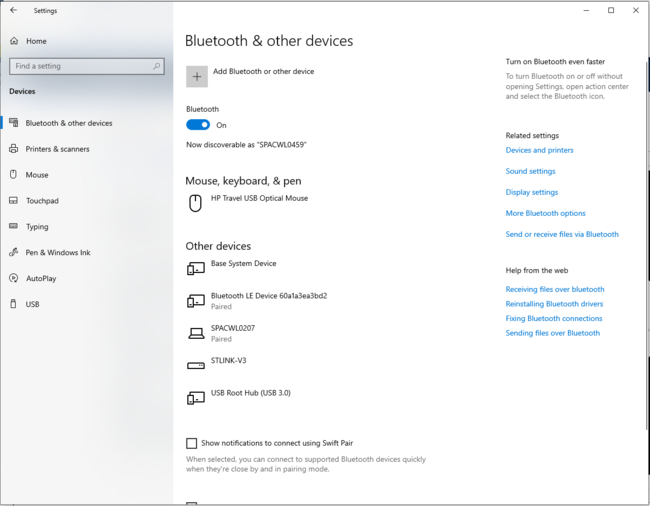
Once the Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse application is installed on the STM32WBA55G-DK1 platform, launch a Bluetooth® Low Energy connection on a smartphone or a PC. Then, scan and connect the device called HIDS_XX (where XX is replaced by the last byte of the BD address) to the application.
As shown in the following screenshots for a ANDROID smartphone connection:
| Android Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse – How to | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
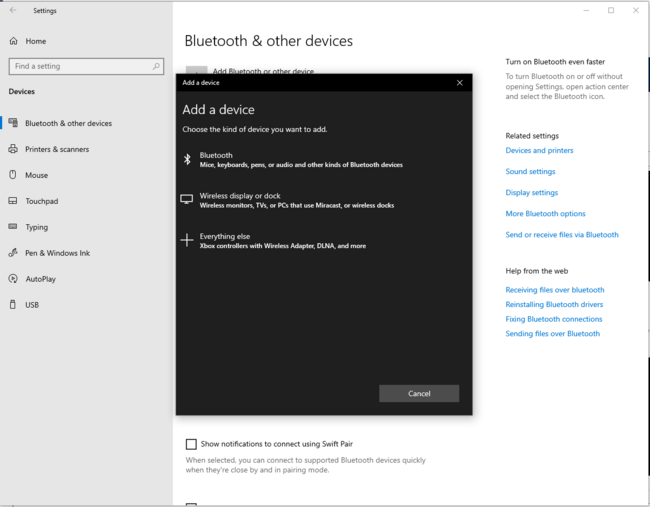
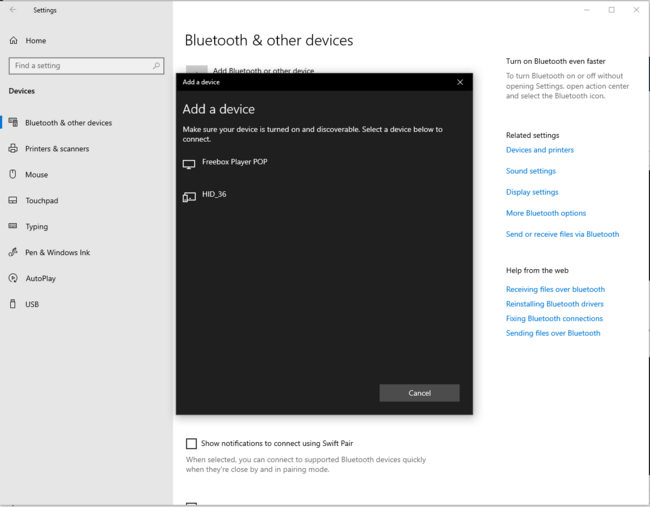
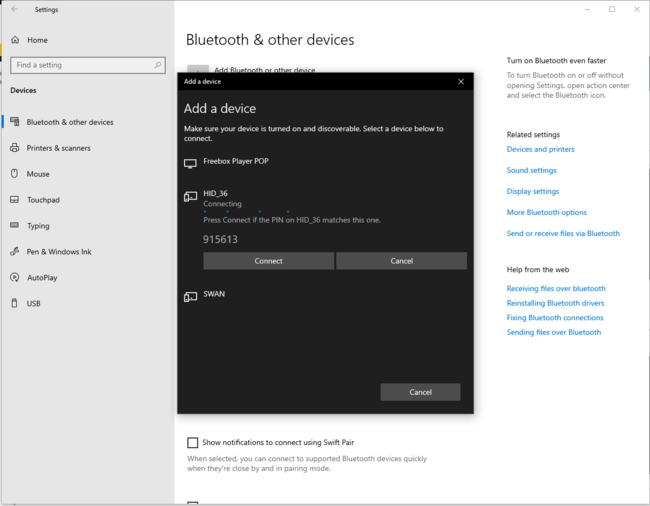
Or for a PC connection:
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
| PC Bluetooth® Low Energy HID Mouse – How to | |
|---|---|
Once the Bluetooth® Low Energy connection is established and the notification enabled by the smartphone or the PC, HID Input Report is sent each time an action is performed on the STM32WBA55G-DK1 joystick .
| STM32WBA55G-DK1 joystick |
|---|
- Action on Up, down, left and right direction sends an Input report containing a relative position.
- Press on the joystick on neutral position sends an input report containing the state of the left button.
3.4. Low-power optimization
The project is delivered with the full system low-power disabled:
- debug trace enabled
- debugger enabled even in Low Power Mode
It is possible to enable/disable the low-power feature within app_conf.h.
/******************************************************************************
* Low Power
*
* When CFG_LPM_LEVEL is set to:
* - 0 : Low Power Mode is not activated, RUN mode will be used.
* - 1 : Low power active, the one selected with CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED
* - 2 : In addition, force to disable modules to reach lowest power figures.
*
* When CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED is set to:
* - 1 : Standby is used as low power mode.
* - 0 : Standby is not used, so stop mode 1 is used as low power mode.
*
******************************************************************************/
#define CFG_LPM_LEVEL (0)
#define CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED (0)
3.5. UART debug trace
Thanks to the debug log via UART interface , it is possible to trace the application project.
To enable the traces within the project, enable them within app_conf.h as described below:
/*****************************************************************************
* Logs
*
* Applications must call LOG_INFO_APP for logs.
* By default, CFG_LOG_INSERT_TIME_STAMP_INSIDE_THE_TRACE is set to 0.
* As a result, there is no time stamp insertion inside the logs.
*
* For advanced log use cases, see the log_module.h file.
* This file is customizable, you can create new verbose levels and log regions.
*****************************************************************************/
/**
* Enable or disable LOG over UART in the application.
* Low power level(CFG_LPM_LEVEL) above 1 will disable LOG.
* Standby low power mode(CFG_LPM_STDBY_SUPPORTED) will disable LOG.
*/
#define CFG_LOG_SUPPORTED (1U)
/* Configure Log display settings */
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_COLOR_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_TIME_STAMP_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
#define CFG_LOG_INSERT_EOL_INSIDE_THE_TRACE (0U)
/* macro ensuring retrocompatibility with old applications */
#define APP_DBG LOG_INFO_APP
#define APP_DBG_MSG LOG_INFO_APP
A debugger can also be supported by enabling it within app_conf.h as described below:
/******************************************************************************
* Debugger
*
* When CFG_DEBUGGER_LEVEL is set to:
* - 0 : No Debugger available, SWD/JTAG pins are disabled.
* - 1 : Debugger available in RUN mode only.
* - 2 : Debugger available in low power mode.
*
******************************************************************************/
#define CFG_DEBUGGER_LEVEL (2)
| HID Mouse - Initialization phase | Connected Phase |
|---|---|
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 26349
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 26349==>> Start Ble_Hci_Gap_Gatt_Init function
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_PUBADDR_OFFSET
Public Bluetooth Address: 00:80:e1:2a:ff:36
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_IR_OFFSET
Success: aci_hal_write_config_data command - CONFIG_DATA_ER_OFFSET
Success: aci_hal_set_tx_power_level command
Success: aci_gatt_init command
Success: aci_gap_init command
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value - Device Name
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value - Appearance
Success: hci_le_set_default_phy command
Success: aci_gap_set_io_capability command
Success: aci_gap_set_authentication_requirement command
Success: aci_gap_configure_whitelist command
==>> End Ble_Hci_Gap_Gatt_Init function
Services and Characteristics creation
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: HIDS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : INPUTREP
Success: aci_gatt_add_char_desc command : INPUT REP REF DESC on handle 0x10
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : REM
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : HII
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : HCP
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value REM command
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value HII command
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: DIS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : PNI
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value PNI command
Success: aci_gatt_add_service command: BAS
Success: aci_gatt_add_char command : BAL
Success: aci_gatt_update_char_value BAL command
End of Services and Characteristics creation
==>> aci_gap_set_discoverable - Success
==>> Success: Start Advertising
|
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE - Connection handle: 0x0001
- Connection established with @:65:92:b8:52:36:4b
- Connection Interval: 45.00 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
>>== ACI_GAP_NUMERIC_COMPARISON_VALUE_VSEVT_CODE
- numeric_value = 447414
- Hex_value = 6d3b6
==>> aci_gap_numeric_comparison_value_confirm_yesno : Success
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
SNVMA_Write - Flash operation started (Header write request) : 16
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
SNVMA_Write - Impacted NVM : 1
SNVMA_Write - Pending buffer : 1
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
>>== ACI_GAP_PAIRING_COMPLETE_VSEVT_CODE
- Pairing Success
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_HEADER_WRITE
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Write operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_BUFFER_WRITE
Start of CRC computation
End of CRC computation, value : 48382
FM_Erase - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Erase operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
FM_WindowAllowed_Callback
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Time window granted
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_WINDOWED_FLASHOP - Erase operation
SNVMA_FlashManagerCallback - Flash operation state : SNVMA_RETRY_WRITE
FM_Write - Returned value : 0
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP
FM_BackgroundProcess - Case FM_BKGND_NOWINDOW_FLASHOP - Write operation
FM_BackgroundProcess - Flash operation not complete yet, request a new time window
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE
- Connection Interval: 7.50 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
>>== HCI_LE_CONNECTION_UPDATE_COMPLETE_SUBEVT_CODE
- Connection Interval: 45.00 ms
- Connection latency: 0
- Supervision Timeout: 5000 ms
HIDS_REP_NOTIFY_ENABLED_EVT
|
4. References
- ↑ Human interface device over GATT profile specification
- ↑ Bluetooth® SIG
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 USB Device class definition for human interface devices (USB HID specification), version 1.11
- ↑ STM32CubeWBA MCU Package
- ↑ STMicroelectronics Manufacturer Advertising Data
- ↑ STM32CubeIDE
- ↑ STM32CubeProgrammer software
- ↑ USB HID Usage Tables