OEM-iROT stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer immutable Root of Trust. The users can develop OEM-iROT on all the STM32H5xx devices.
1. Introduction
This wiki article describes the OEMiROT process developped for STM32H5 MCUs. For practical examples please refer to OEMiROT STM32H5 How to Introduction which introduce the many steps to use OEMiROT.
2. OEM-iROT services
- 1) The secure boot (Root of Trust services):
- It is an immutable code that is always executed after a system reset. It activates STM32 runtime protections, and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- Integrity: to ensure that a firmware about to be executed has not been corrupted or maliciously modified.
- Authenticity: to verify that a firmware is coming from a trusted and known source in order to prevent unauthorized entities to install and execute code.
- Integrity: to ensure that a firmware about to be executed has not been corrupted or maliciously modified.
- It is an immutable code that is always executed after a system reset. It activates STM32 runtime protections, and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- 2) The Secure Firmware Update:
- It is an immutable code that detects if a new firmware image is available, checks its authenticity and verifies the integrity of the code before installing it after decryption.
3. OEM-iROT use cases
There are two possible cases explained below:
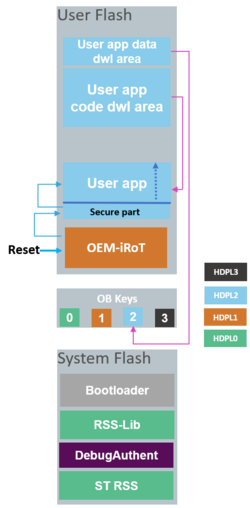
3.1. Case 1: The user application is executed after OEM-iROT
At each Reset, the OEM-iROT firmware located in User Flash is first executed in HDPL1. It is the user's responsibility to develop a root of trust firmware that:
- First checks authenticity and integrity of user application
- Secondly jumps to the user application or bootloader depending on the authenticity and integrity checks.
After a successful check of authenticity and integrity of the user application, OEM-iROT can jump directly in HDPL2 or HDPL3 (user application can be installed in HDPL2 or HDPL3). User Application can be a fully secure application, a full nonsecure application, or a combined secure/ nonsecure application. If parameters configured in User Root of Trust are not respected or if Authenticity and integrity checks fail, OEM-iROT executes bootloader to download new user application and user data. It is the user’s responsibility to activate all the required security protections during the User Application execution.
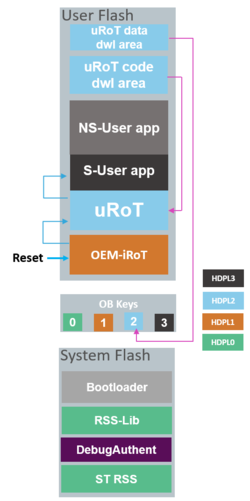
3.2. Case 2: Two boot stage: The updatable Root of Trust (uROT) is executed after the OEM-iROT
The uROT is in the user flash and acts as a second boot stage adapted to customer requirements. The following figure shows the entry point after reset and the OEM-iROT controlling the step to uROT.
OEM-iROT is the entry point executed after any reset.
After a successful verification of the uRoT by the OEM-iROT, the uROT is executed in HDPL2 and verifies the secure and nonsecure applications before jumping to secure, and switching to HDPL3.
In the provided example from STM32CubeH5 FW, if there is a verification failure of the uROT, OEM-iROT executes the bootloader to download a new uRoT code and/or data. By default the bootloader is used in this example to get new firmware but the user can develop other connections like OTA.
4. OEM-iROT provisioning steps
OEMiROT provisioning can be divided in 3 steps :
- Step 1 – OEM-iROT and Debug Authentication configuration
This step configures the keys used to encrypt/ decrypt the datas, ans sign / check signature of th user application
- Step 2 – Code and data image generation
All the firmware are compiled and the images generated thanks tools and IDE.
- Step 3 – Product state setting
The final product state can be chosen by the user.
These steps are detailed in which is the introduction article to the How to articles. Many use cases are given as example in STM32CubeH5 firmware that you can use with the help of the How to articles to start a new project.
5. How to start with STM32 and OEM-iROT
You can refer to the following pages for getting started examples of OEM-iROT.