OEMiROT states for Original Equipment Manufacturer immutable Root of Trust. OEM-iROT can be developed by users in all STM32H5xx devices.
1. OEM-iROT services
- 1) The Secure Boot (Root of Trust Services):
- It is an immutable code, always executed after a system reset, that activates STM32 runtime protections and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- Integrity: to ensure that a firmware that is going to be executed has not been corrupted or maliciously modified.
- Authenticity: to verify that a firmware is coming from a trusted and known source in order to prevent unauthorized entities to install and execute code.
- Integrity: to ensure that a firmware that is going to be executed has not been corrupted or maliciously modified.
- It is an immutable code, always executed after a system reset, that activates STM32 runtime protections and verifies the authenticity and integrity of the application code before every execution.
- 2) The Secure Firmware Update:
- It is an immutable code that detects if a new firmware image is available, checks its authenticity and verifies the integrity of the code before installing it after decryption.
2. OEM-iROT use cases
There are two possible cases explained below.
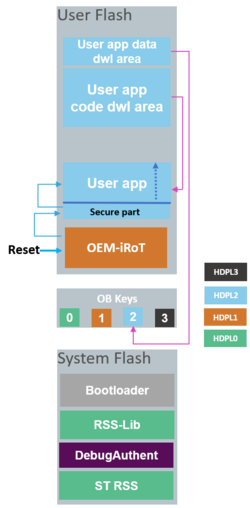
2.1. Case 1: The user application is executed after OEM-iROT
At each Reset the OEM-iROT firmware located in User Flash is first executed in HDPL1. It is the user responsibility to develop a root of trust firmware that
- First checks authenticity and integrity of user application
- Secondly jumps to the user application or Bootloader depending on the authenticity and integrity checks.
After a successful check of authenticity and integrity of user application, OEM-iROT can jump directly in HDPL2 or HDPL3 (user application can be installed in HDPL2 or HDPL3). User Application can be a fully secure application, a full non secure application, or a combined secure/ non secure application. If parameters configured in User Root of Trust are not respected or if Authenticity and integrity checks fail, OEM-iROT executes Bootloader to download new user application and user data. It is the user’s responsibility to activate all the required security protections during the User Application execution.
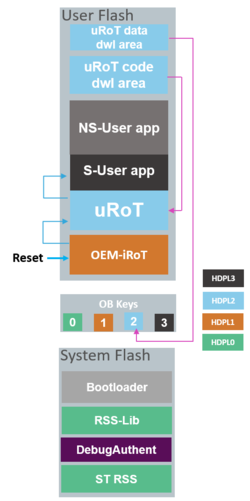
2.2. Case 2: Two boot stage : The updatable Root of Trust (uROT) is executed after the OEM-iROT
The uROT is in the user flash and will act as a second boot stage adapted to customer requirements. The following figure shows the entry point after reset and the OEM-iROT controlling the step to uROT.
OEM-iROT is the entry point executed after any reset.
After a successful verification of the uRoT by the OEM-iROT, the uROT is executed in HDPL2 and verifies the secure and non secure applications before jumping to secure, and switching to HDPL3.
In case there is a verification failure of the uROT, OEM-iROT will execute the Bootloader to download a new uRoT code and/or data.
3. OEM-iROT provisioning steps
3.1. Step 1 - OEM-iROT and Debug Authentication configuration
3.1.1. OEM-iROT configuration
STM32TrustedPackageCreator tool is used to generate OEM-iROT configuration file (.obk) based on template provided in STM32CubeH5 Software package. This configuration file generates keys that will be used to
- Encrypt the User application and data
- Check the authenticity of the user application and data
All other parameters are configured directly by the User in his Root of Trust firmware located in HDPL1 in User Flash. This code must be able to perform authenticity and integrity checks of the User application and data images. It also configures the number of User application and images:
- Number of data image secure (0 or 1)
- Number of data image non-secure (0 or 1)
- Number of code image secure (0 or 1)
- Number of code image non-secure (0 or 1)
An example of user Root of trust firmware called OEMiROT_Boot is delivered in STM32CubeH5 firmware: Projects\STM32H573I-DK\Applications\ROT\OEMiROT_Boot. During the OEMiROT execution if the number of images is wrong Bootloader is launched to load new code and/or data images. In the OEMiROT_Boot application given as example in STM32CubeH5 FW package, the application code download area and execution area offsets are configured. It’s mandatory to compile the OEMiROT_Boot code to generate the correct related user application code binary which will be the input to generate the signed and encrypted image using STM32TrustedPackageCreator.
3.1.2. DA configuration
STM32TrustedPackageCreator is also used to generate the Debug Authentication configuration file (.obk) based on template provided in STM32CubeH5 Software package. This file is used to configure the conditions to reopen a protected device and the debugger. Depending on the User application additional configuration files could be generated.
3.2. Step 2 – Code and data image generation
The signed and encrypted user application code image and user data image are generated with STM32TrustedPackageCreator. The user data are optional and chosen during the OEMiROT configuration. These images are downloaded in the user flash download area. Area location and size that are defined in the OEM-iROT code (called OEM-iROT_Boot code in STM32H5Cube FW package). After authenticity verification, the OEM-iROT decrypts the firmware code and data and will copy it in the execution slot. Execution slot location and size are defined in the OEM-iROT code.
3.2.1. User application code image generation
The user application code binary file can be generated by any IDE.
STM32TrustedPackageCreator can be launched separately to generate the encrypted and signed image file using the same encryption and authenticity keys provisioned during the OEM-iROT configuration. The image creation can also be done automatically during the user application compilation. STM32TrustedPackageCreator is using a configuration file to generate images. Files examples are available in the STM32Cube_FW (OEMiRoT_S_Code_Image.xml and OEMiRoT_NS_Code_Image.xml )and can be edited using STM32TrustedPackageCreator.
3.2.2. User Data Image generation
STM32TrustedPackageCreator needs to be launched separately to generate the encrypted and signed image file using the same encryption and authenticity keys provisioned during the OEMiROT configuration. These keys are also used for the user application code image generation.
STM32TrustedPackageCreator is using a configuration file (OEMiRoT_S_Data_Image.xml and OEMiRoT_NS_Data_Image.xml are configuration files examples available in the STM32Cube_FW that can be edited using STM32TrustedPackageCreator) .
3.3. Step 3 – Product state setting
The following figure shows the possible product state.
(for more details refer to product lifecycle and Debug Authentication articles).
The provided script Provisioning.bat given as example in STM32CubeH5 firmware is guiding the user during this phase.
At the end of the provisioning script execution, the product state can be chosen, and the related option byte will be automatically set.
The product state is chosen depending on the user application development phase and the wanted security level.
- Open:
- This state is mainly used during development phase since the device is fully open.
- Debug is fully open.
- The Trust Zone can be disabled or enabled (TZEN option byte programming).
- Bootloader can be used.
- This state is mainly used during development phase since the device is fully open.
- Provisioning:
- This state is used during the provisioning.
- It is the device state during the provisioning script execution (Provisioning.bat).
- So this state will not be part of the proposed state that can be chosen at the end of the script execution.
- The debug is only available when non secure user application is executed.
- The Trust Zone can be disabled or enabled (TZEN option byte programming).
- Bootloader can be used.
- Secure Firmware install can be launched in this state (not anymore possible in following states).
- This state is used during the provisioning.
- Provisioned:
- In this state the OEM-iROT setup is done.
- Debug is available only when non secure user application is executed.
- Debug access for secure application can be available by launching the Debug Authentication (see Debug Authentication setting).
- The OEM-iROT can launch the bootloader if the verification of the code located in the next isolation level is failing (authentication, integrity or missing code)
- In this state the OEM-iROT setup is done.
- TZ-Closed:
- The Trust Zone closed state is used when the OEM-iROT is provisioned and the secure user application (case 1) or the uROT+Secure user application (case2) (see section 5.1.2).
- For case 2, the uROT is allowing the update of the next isolation level (Code and Data).
- uROT can launch the bootloader if the verification of the code located in the next isolation level is failing (authentication, integrity or missing code).
- uROT can launch the bootloader if the verification of the code located in the next isolation level is failing (authentication, integrity or missing code).
- The debug is only available when non secure user application is executed.
- Debug access for secure application can be available by launching the Debug Authentication (see Debug Authentication setting).
- The Trust Zone closed state is used when the OEM-iROT is provisioned and the secure user application (case 1) or the uROT+Secure user application (case2) (see section 5.1.2).
- Closed:
- This state is used when the product is fully provisioned.
- The debug is fully closed but can be open by launching the Debug Authentication (see Debug Authentication setting) .
- This state is used when the product is fully provisioned.
- Locked:
- This state is used when the product is fully provisioned, and no changes are done anymore.
- Locked is definitive product state that can’t be changed anymore, the embedded FW and product configuration can’t be modified by any method.
- The debug is definitively closed and can’t be reopen through debug authentication.
- No regression is possible anymore
- This state is used when the product is fully provisioned, and no changes are done anymore.
- Open:
4. How to start with STM32 and OEM-iROT
You can refer to the following pages for getting started examples of OEM-iROT.