Based on STM32 MC Motor Pilot 5.Y.2 V0.9.7 (included in STM32 MC-SDK 5.Y.2).
1. Overview of the STM32 MC motor-pilot tool
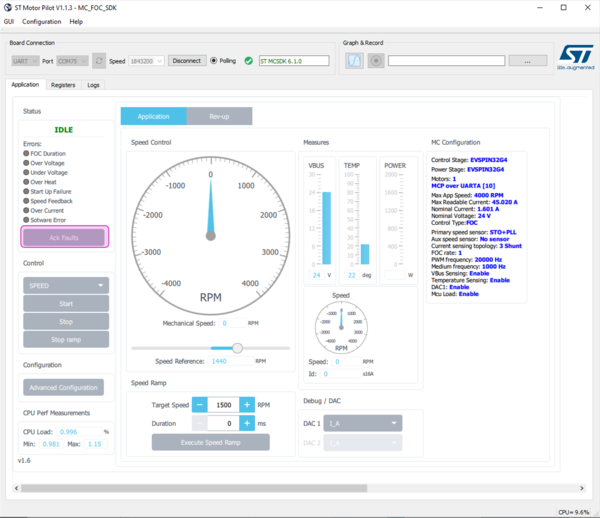
STM32 MC Motor Pilot is a monitoring tool for STM32 motor-control applications that:
- connects to MC applications built with the UI module through the serial port
- uses the same protocol as the current monitor
- allows for controlling, monitoring, and tuning MC applications
- replaces in the future the monitor part of STM32 MC workbench
- current available version is an already usable preview
STM32 MC Motor Pilot added values are:
- enhanced plotting feature: the user can now plot most registers
- the user can easily customize GUI at run time
- to fit specific needs or to experiment with new firmware features
- solid foundation to support future firmware features
- ACIM, 6-Step, sensor-less zero speed, enhanced debug features
- runs on all three MCD target platforms: Windows, Mac, and Linux
2. STM32 MC motor-pilot quick guide
2.1. Installation and run
STM32 MC Motor Pilot is now automatically installed with STM32 MC SDK.
A shortcut is now created in Windows menus to run it.
2.2. Quick start-up
2.2.1. Quick step 1
- MotorPilot:
- starts unconnected
- lists available serial ports
- displays the default UI
- Connect a Motor Pilot board to the PC.
- Click on Connect.
2.2.2. Quick step 2
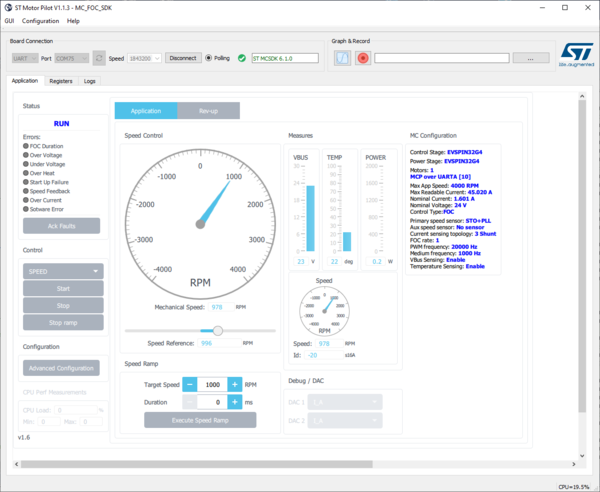
- When MotorPilot is connected, it:
- displays version of embedded firmware [[file:STM32_
MC_MotorPilot_slide7_1.png|200px|center]]
- retrieves importants parameters for motor control form the board and adjust the GUI with theses informations
- starts to monitor parameters needed by the GUI
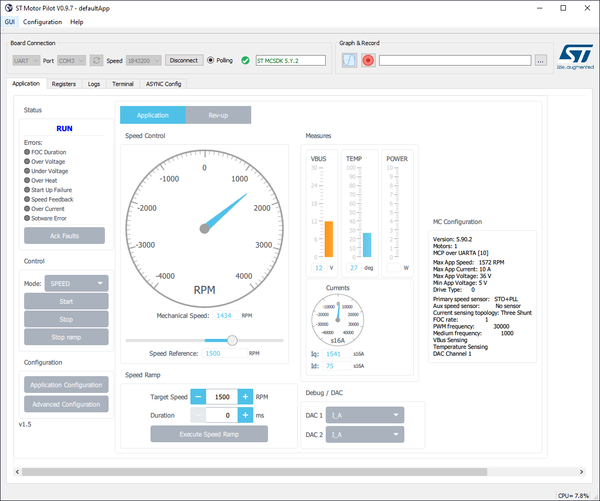
- Spin the motor:
- Click on the Start button.
- Motors starts and the pilot updates the GUI.
2.2.3. Quick step 3
- Control the motor:
- Slide the knob to set the speed
- Set Target Speed, Duration and click to apply a ramp
- Click Stop Ramp to stop it before end
- Click Stop to stop spinning the motor
3. MC application parameters
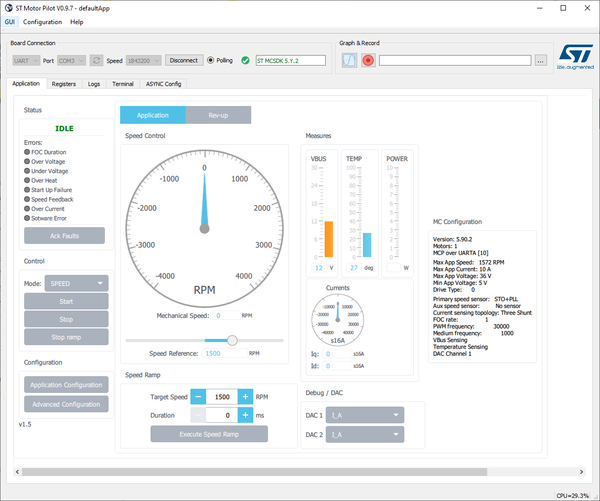
STM32 MC Motor Pilot gets MC application parameters from the board and adapts widgets to them.
4. MC application advanced settings
4.1. Speed PID, Toque PID, Flux PID and Flux reference
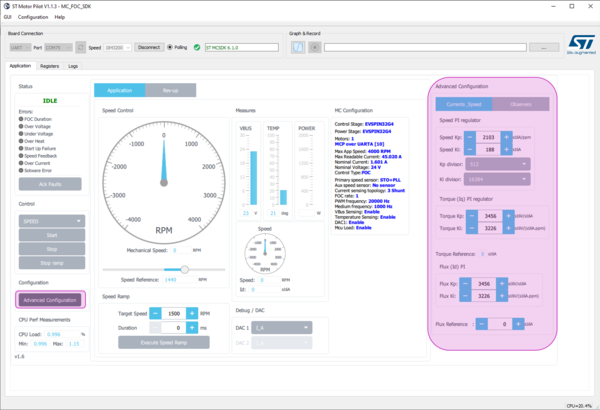
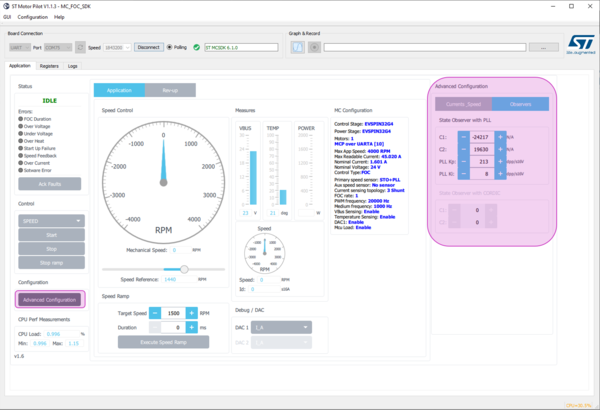
- Click Advanced Configuration:
- displays additional panel with more settings
- As in the current monitor, customizes:
- Speed PID
- Toque PID
- Flux PID
- Set Flux reference
4.2. State Observer, PLL parameters, CORDIC parameters and DAC settings
- Click Advanced Configuration
- Displays additional panel with more settings
- As in the current monitor, customizes:
- State Observer + PLL parameters
- State Observer + CORDIC parameters
- if DAC is available on your board you can select which register you want to output on it
4.3. Handling errors
4.3.1. Control Board disconnection
Board freeze due to firmware critical error or breakpoint trigger:
- Resume execution or reset the board, and the connection resumes.
4.3.2. Firmware errors
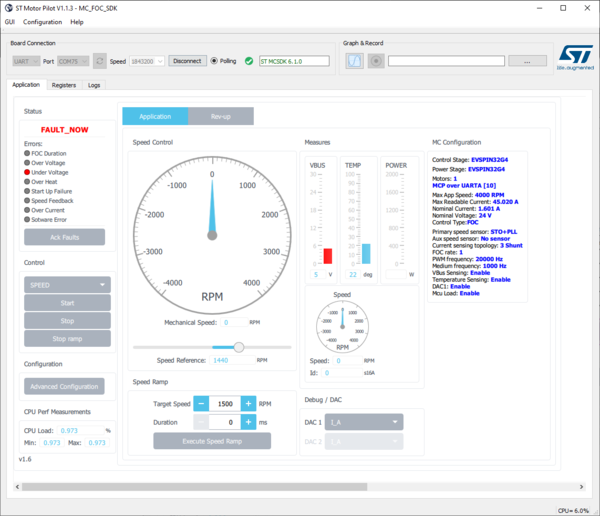
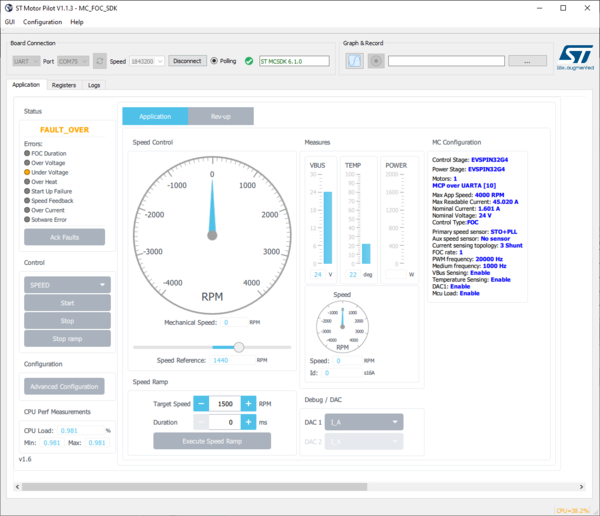
- As with the current monitor, current and past errors are indicated.
- Clicking the Ack Faults button has no effect in the FAULT_NOW state
- Wait for the fault conditions to vanish to enter the FAULT_OVER state
- Then click on Ack Faults to go back to IDLE
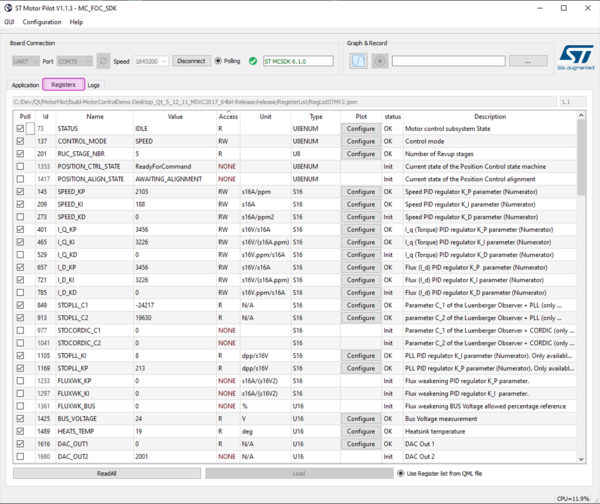
4.4. Viewing and plotting registers with low-speed plotting
With this method of plot, any register can be plot but at low rate (polling every 200 ms by default)
- Clicking the Registers tab displays the list of all registers (see (1) on the following figure)
- Click a "Click to Plot" button (see (2) on the figure)
- Opens a plot window the first time
- Lets the user decide where to plot the other times (see (3) on the figure)
- Lets the user choose to stop showing the already pointed register (see (4) on the figure).
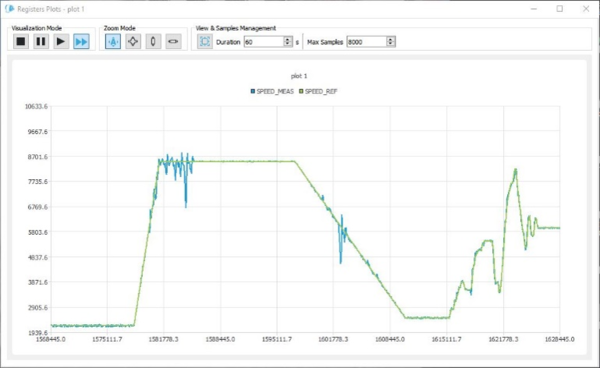
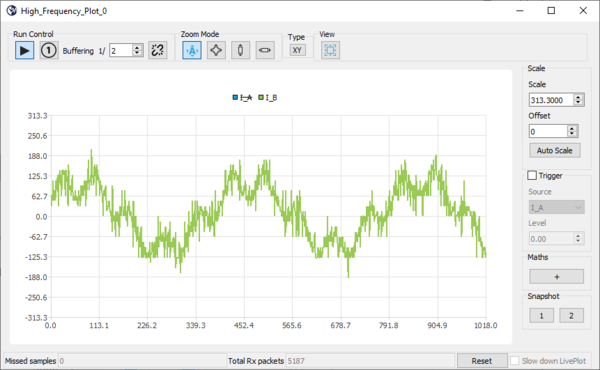
4.5. Viewing and plotting registers with high-speed plotting
With this method of plot, only a subset of registers can be plot at PWM frequency rate
- Once the motor is connected (and motor started)
- Click on the "Plot" button
- A "High Frequency Plot" window opens:
- Click again to open more plot windows
- Resize these windows to optimize the display of plots on your desktop
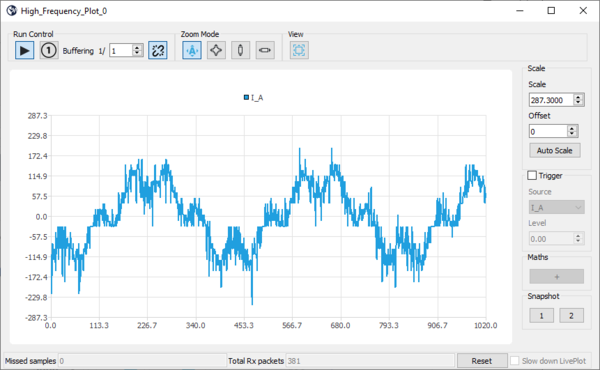
- Right-click to select the register you want to plot:
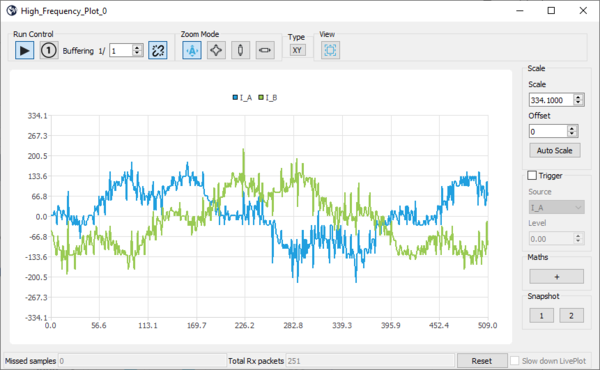
- Click again to plot more registers:
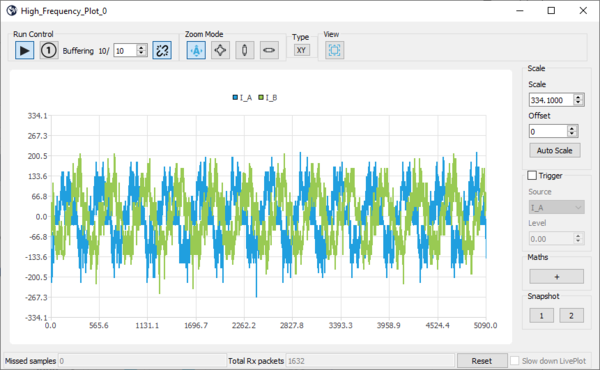
- The data display width is defined by adjusting the buffer size (change buffering to display more data):
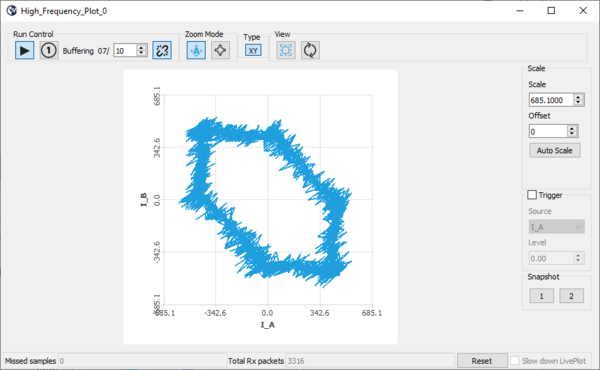
- When displaying 2 registers, you can switch to the X / Y plot:
- Dynamic plot display can be paused and resumed as desired.
- Each register plot can be hidden or displayed by double-clicking on the register name in the plot legend (then when the register plot is hidden, the corresponding register name is strikethrough).
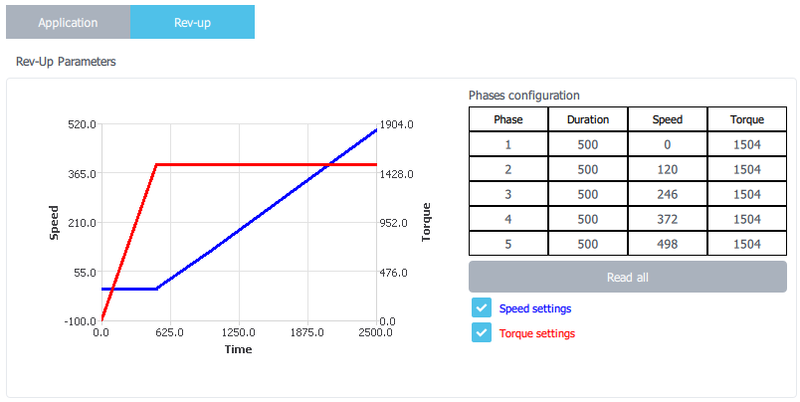
4.6. Rev-up configuration
- Click on "Rev-up" button and then the application panel is replaced by rev-up configuration panel.
- This panel allows to set up to 5 rev-up steps by direct edit in the corresponding table for which a step rev-up duration, a final torque value and a final speed value are defined. (use the same values to have less steps).
4.7. UI is changeable at run-time
- Click on menu item File => Load
- Search for a .qml file and open it.
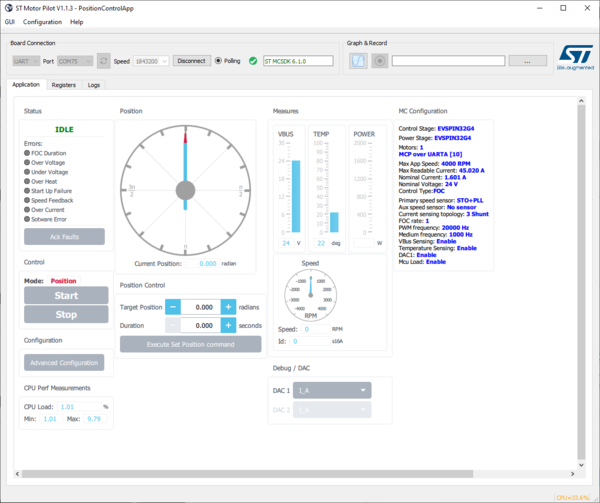
- For instance, GUI\PositionControlApp.qml found in the release.
- This loads a new GUI with other features
- In the case of PositionControlApp.qml, a position control enabled monitoring application.
- Users are able to change the UI by copying an existing ".qml" file and editing it.
5. Motor Profiler
The motor profiler software is now integrated into the motor pilot as QML file. New profiler allows the user to automatically detect the board and to do a profiling with the Halls sensors or to detect the number of Pole pairs with guided detection. The homepage keeps a similar look to the old tool, it is possible from the homepage to make a manual selection of boards, to launch the automatic detection of boards. It is also possible after having selected the board, to launch motor profiling, to launch the Hall profiling and to save the data of the profiled motor.
5.1. Start motor Profiling
5.1.1. Select board manually
To select board manually, click on the "select boards" button like on the picture below.
You will then arrive on the board selection page. You can search boards by filtering control board name (text field 1) or power board name (text field 2).
5.1.2. Connect board
After selecting the boards, the "Connect" button becomes active, and you can start the connection to the board.
In case a firmware profiler is present on the board and the board checks are error free,you can go to “set profiling parameter” chapter, otherwise the Ui proposes you to install a profiler firmware compatible. You must accept to use the profiler.
The firmware present on the board is erased, the new profiler firmware is flashed on the board, and we restart connection with the board.
If the connection is successful, you can go to “Set profiler parameter” chapter.
5.1.3. Detect boards
A new feature of this profiler is the possibility to detect control board and power board automatically, for this the motor profiler reads the information from the firmware and displays the detected boards. To start the automatic detection, click on the "Detect board" button.
Afterwards, the profiler tries to detect the boards, several tests are done:
- 1: check if an ST-Link is connected to the computer
- 2: Check if the MCU uid detected by the st-link is supported by the profiler
- 3: Check if the board name written on St-link is supported by Profiler
- 4: Try to connect with uart to the board
- 5: If the uart connection was successful, check if Firmware is Profiler firmware.
- 6: Check if the control board detected on firemware is the same board as detected with St-Link and if it is known on the profiler database.
- 7: Check if the power board detected on firemware it is known on the profiler database.
When these checks are successful, the interface displays the board, otherwise the user is offered a choice close to what has been detected.
5.1.4. profiling parameter
After connecting the card, you can start profiling. For this purpose, it is necessary to fill in the field of the Pole pair (in red). For a more efficient profiling you can fill in the fields in green if you have the necessary data. If you don't know the number of even Poles, you can go to the chapter """about Pole pairs detection""".
5.1.5. Start profiling
Click on the Start Profile to profile the motor. First, the electrical parameters are identified, then the mechanical ones. When profiling is completed, all the motor measurements are shown on bottom of screen.
If the profiling process takes too long, the information entered is incorrect, the max speed value is too high or too low.
5.1.6. Start hall profiling
A new feature has been added to the profiler, it is the hall profiling, it allows to use the hall sensors to have a better control of the motor, to run hall profiler, click on “Start Hall profiling” button.
When you click on the start hall profiling button a new interface appears in the bottom part of the profiler. A warning message appears to signal the user to check the connection of his Hall sensors.
This window warns the user that the connectors of the hall sensors are incorrectly connected and indicates which of these connectors is incorrectly connected, if you have easy access to these connectors and can easily change them, then you can make the change and click on the "Continue" button otherwise he can cancel the profiling.
You must also confirm that the motor is running in the correct direction to get consistent results.
Profiling is done on both directions of rotation and are displayed on the screen, on the left the results of the placement of the electric angle when the motor turns in the opposite direction of the desired direction and on the right the electric angle when the motor in the right direction. in the upper part is indicated the average a of the electric angle to enter on the workbench.
5.2. Save results
Click on the Save button (Top Figure) to store the motor measurements for later usage with the ST motor control workbench software tool. Figure Top shows the saving window in that case, then the user may provide the motor information: Naming profiled motor and Provide details about profiled motor, after that.
5.3. Pole pair detection
Pole pair detection is a new feature that comes with this profiler and does not require a power generator to detect the pole pair number. To use this feature, click on the "Detect pole pairs" button which will open a new window
To start detection, click on next button.
In this window you have to enter the value of the current to be injected to make the motor strong enough to be able to turn it manually afterwards. The value entered must be close to 15% of the maximum current that the motor can support, otherwise the motor may overheat.
Please apply a mark on the fixed part of the motor and the rotating part, then you can turn the rotating part and count the number of Pole Pair. The firmware then prepares the motor by applying a current ramp of the value entered in the previous step.
You have 15 seconds to make a complete rotation of the rotating part of the motor and must count the number of notches, this number will be the number of Pole Pairs. Then you must click on the finish button
Finally, you can can enter the number of Pole Pairs found, then close the window and start the motor profiling.
5.4. Errors
5.4.1. Firmware errors
- FOC Duration: This fault appears when the FOC execution rate is too high and the FOC algorithm computation does not fit in the PWM period.
- Over Voltage: This fault appears when an overvoltage is applied to the power board.
- Under Voltage: This fault appears when an undervoltage is applied to the power board.
- Over heat: This fault appears when the power board is overheated.
- Speed feed back: This fault appears when the estimated speed is not reliable during the rev-up phases.
- Over current: This fault appears when an overvoltage is applied to the power board.
- Software error: This fault appears when a software error occurs, these errors are independent of the motor operation.
5.4.2. Pole pair required
This fault appears when user forgot to write the Pole pairs value this error appears, and the pole pairs text field turns red.
5.4.3. Too many devices
This fault appears when 2 devices with St-Link are connected to the computer, only one device must be connected at a time.
5.4.4. Old firmware
This error appears when an old St-Link firmware is used, it is necessary to have a recent St-Link firmware for the checks made by the profiler to be carried out correctly
5.4.5. No ST-Link ready to use
This error appears when the St-Link are used by another software (CubeProgrammer, Iar), the checks made by the st-link are impossible which prevents the profiler from working properly.
5.4.6. Error detected
This error appears when one of the errors present in the chapter Firmware errors is present, you must acknowledge the faults to start the profile.