The MMC (MultiMediaCard) / SD (secure digital) / SDIO (secure digital input/output) subsystem implements a standard Linux® host driver to interface with MMC / SD memory cards or SDIO cards.
1. Framework purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to introduce the MMC Linux® subsystem (MMC / SD) by:
- providing general information
- describing the main components/stakeholders
The SDIO is addressed in the WLAN overview.
2. System overview[edit source]
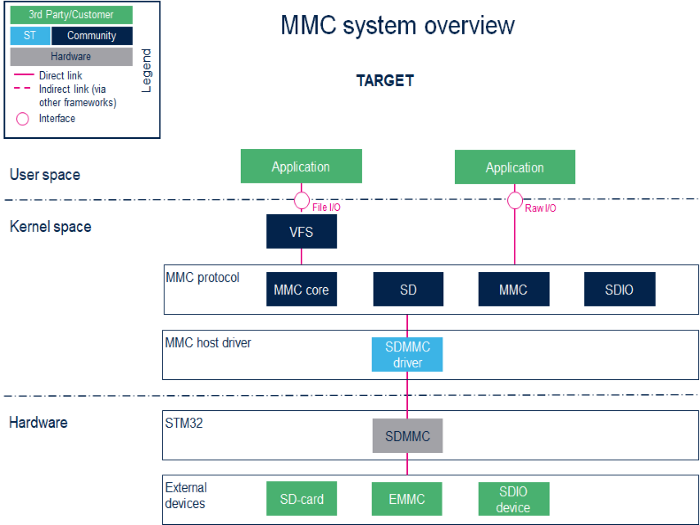
2.1. Component description[edit source]
- User space applications handle file I/O management to view the card memory as a disk, whereas programs that perform raw I/O accesses see the memory as a block device[1].
- VFS (Kernel space)
Virtual File System. Please refer to the VFS documentation [2].
- MMC core/SD/MMC/SDIO (Kernel space)
The MMC core ensures compliance with MultiMediaCard (MMC)[3] / secure digital (SD)[4] / secure digital input/output (SDIO)[5].
- SDMMC driver (Kernel space) / SDMMC (hardware)
The SDMMC driver handles:
- the registers, the clock, the interrupt and the IDMA control.
- the communications over the bus based on command/response and data transfers.
Please refer to the SDMMC internal peripheral.
2.2. API description[edit source]
The MMC core handles the file system read/write calls.
3. Configuration[edit source]
3.1. Kernel configuration[edit source]
The MMC framework is activated by default in ST deliveries. If a specific configuration is needed, this section indicates how the MMC framework can be activated/inactivated in the kernel.
The MMC framework can be activated in the kernel configuration via Linux® Menuconfig tool: Menuconfig or how to configure kernel
[*] Device Drivers [*] MMC/SD/SDIO card support <*> HW reset support for eMMC <*> Simple HW reset support for MMC <*> MMC block device driver (16) Number of minors per block device ... <*> ARM AMBA Multimedia Card Interface support [*] STMicroelectronics STM32 SDMMC Controller
3.2. Device tree configuration[edit source]
DT configuration can be done thanks to STM32CubeMX.
Please refer to the SDMMC device tree configuration.
4. How to use the framework[edit source]
A file system, which handles read/write/erase operations, can be used with the MMC framework. Please refer to the EXT4 support through MMC.
5. How to trace and debug the framework[edit source]
5.1. How to monitor[edit source]
The sysfs interface provides detailed information on each mmc device:
root:~# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/ios
clock: 50000000 Hz
vdd: 21 (3.3 ~ 3.4 V)
bus mode: 2 (push-pull)
chip select: 0 (don't care)
power mode: 2 (on)
bus width: 2 (4 bits)
timing spec: 2 (sd high-speed)
signal voltage: 0 (3.30 V)
driver type: 0 (driver type B)
5.2. How to trace[edit source]
For details on dynamic trace usage, refer to How to use the kernel dynamic debug.
root:~# echo "file drivers/mmc/* +p" > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
6. Source code location[edit source]
The MMC framework is available here .
7. References[edit source]
Please refer to the following links for a full description of the MMC framework:
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file#Block_devices
- ↑ VFS
- ↑ MultiMediaCard, embedded MultiMediaCard specification
- ↑ Secure Digital, secure digital specification
- ↑ Secure Digital Input Output, Secure Digital Input Output specification