This article shows how to start up a STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation boards (high-end development platforms for the STM32MP15 microprocessor devices). It is valid both for the STM32MP157A-EV1 and STM32MP157C-EV1 Evaluation boards: the part numbers are specified in the STM32MP15 microprocessor part numbers article.
It lists the required material, points to the board features description, and gives the step-by-step process to set up the system.
Finally, it proposes to run some basic use cases and to discover some of the board capabilities.
1. Starter Package content[edit source]
If you are not yet familiar with the STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution and its Packages, please read the following articles:
- Which STM32MPU Embedded Software Package better suits your needs (and especially the Starter Package chapter)
- STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution
If you are already familiar with the Starter Package for the STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution, the fast links to essential commands might interest you.
To sum up, this Starter Package provides:
- the software image for the STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution, which includes:
- the binaries for the OpenSTLinux distribution
- one or more firmware example(s) for the STM32Cube MPU Package
- the tool (STM32CubeProgrammer) to install this image on the STM32MP15 Evaluation board
2. Starter Package step-by-step overview[edit source]
The following steps are required to get the STM32MP15 Evaluation board up and running:
☐ Checking the material
☐ Assembling the board
☐ Installing the tools
☐ Downloading the image and flashing it on the board
☐ Booting the board
Once these steps are achieved, you are able to:
- check the boot sequence
- execute basic commands
- run basic use cases
- discover on your own the capabilities of the STM32MP15 Evaluation board
3. Checking the material[edit source]
Mandatory
| PC | Linux or Windows operating systems. See PC prerequisites for more details on the required configurations |
| STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board (STM32MP157A-EV1 or STM32MP157C-EV1) |
High-end development platform for the STM32MP15 microprocessor device including: |
| Power supply | Power supply block (5V, 3A) for the MB1263 daughterboard |
| MicroSD card | It is populated with OpenSTLinux distribution (Linux software), and provides extra storage capacity. A 2-Gbyte minimum MicroSD card is needed |
| USB micro-B cable | It connects the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to the PC through the USB micro-B (ST-LINK/V2-1) connector |
| USB micro-AB cable | It connects the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to an USB OTG device through the USB micro-AB connector |
Optional
| USB keyboard and mouse | Thanks to the USB type A connectors, the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board can be equipped with a full-size keyboard and mouse |
| Ethernet cable | It can connect the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to a network through the RJ45 connector |
| RS232 cable | It can connect the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to the PC through the UART connector as an alternative of the ST-LINK/V2-1 connection |
| CAN cable | It can connect the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to CAN devices through the CAN FD/TT connectors |
| Trace cable | It can connect the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to an external tool through the Trace connector |
| JTAG cable | It can connect the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board to an external tool through the JTAG connector |
Optionally, devices and extension boards might be plugged to the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board thanks to connectors such as:
- the Ethernet daughterboard connector
- the GPIO expansion connector
- the Motor control connector
- ...
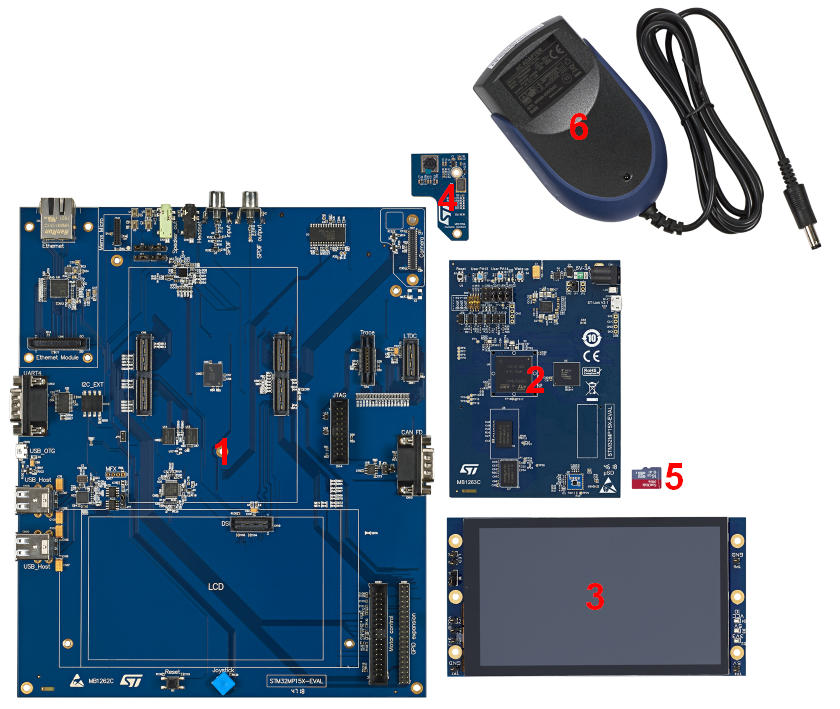
The following figure shows the material not included in STM32MP15 Evaluation board package, that is used in this Starter Package.
4. Assembling the board[edit source]
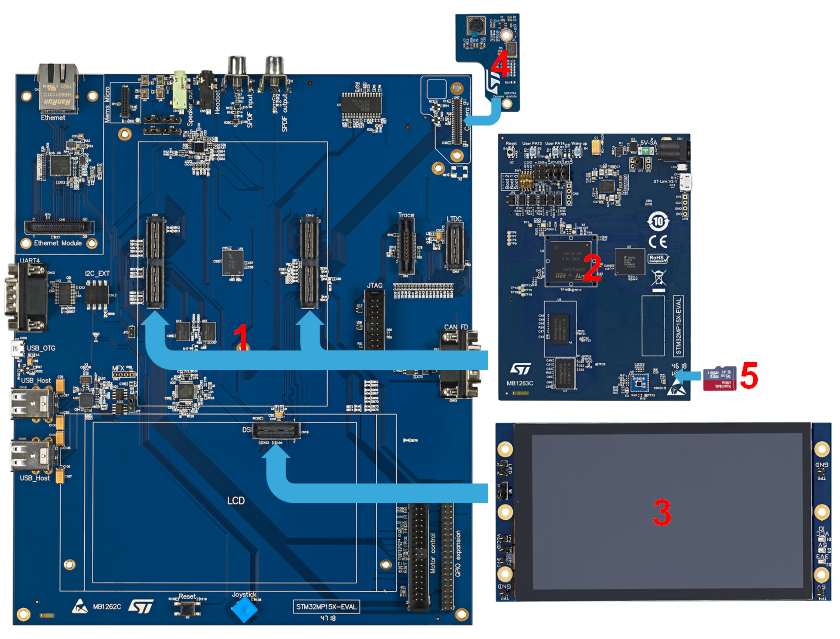
The STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation boards packages (STM32MP157A-EV1 and STM32MP157C-EV1) include all the items listed below.
| Position | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | MB1262 motherboard |
| 2 | MB1263 daughterboard |
| 3 | MB1230 DSI 720p display |
| 4 | MB1379 daughterboard camera |
| 5 | microSD card |
| 6 | Power supply block (5V, 3A) |
The following figures explain how to assemble these different items to get the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation boards.
5. Installing the tools[edit source]
5.1. Installing the STM32CubeProgrammer tool[edit source]
| STM32CubeProgrammer for Linux® host PC | STM32CubeProgrammer for Windows® host PC | |
|---|---|---|
| Download |
Version 2.4.0
| |
| Installation |
./SetupSTM32CubeProgrammer-2.4.0.linux
export PATH=<my STM32CubeProgrammer install directory>/bin:$PATH
ln -s <my STM32CubeProgrammer install directory>/bin/STM32_Programmer_CLI /home/bin/STM32_Programmer_CLI
|
|
| User manual |
| |
| Detailed release note |
| |
5.2. Preparing the USB serial link for flashing[edit source]
It is recommended to use the USB (in DFU mode) for flashing rather than the UART, which is too slow.
Below indications on how to install the USB in DFU mode under Linux and Windows OS, respectively.
- For Linux host PC or Windows host PC with VMWare:
The libusb1.0 package (including USB DFU mode) must be installed to be able to connect to the board via the USB port. This is achieved by typing the following command from the host PC terminal:
sudo apt-get install libusb-1.0-0
To allow STM32CubeProgrammer to access the USB port through low-level commands, proceed as follows:
cd <your STM32CubeProgrammer install directory>/Drivers/rules
sudo cp *.* /etc/udev/rules.d/
- For Windows host PC:
Run the “STM32 Bootloader.bat” file to install the STM32CubeProgrammer DFU driver and activate the STM32 microprocessor device in USB DFU mode. This driver (installed by STM32 Bootloader.bat) is provided within the STM32CubeProgrammer release package. It is located in the DFU driver folder, \Drivers\DFU_Driver.
In case of issue, refer to How to proceed when the DFU driver installation fails on Windows host PC.
To validate the installation, the DFU driver functionality can be verified by following the FAQ instructions provided in how to check if the DFU driver is functional.
6. Downloading the image and flashing it on the board[edit source]
6.1. Image download[edit source]
- The STM32MP1 image (binaries) is delivered through one tarball file named
- en.FLASH-stm32mp1-openstlinux-20-02-19.tar.xz for STM32MP157C-EV1 and STM32MP157X-DKX boards
- Download and install the STM32MP1 image (binaries):
The software package is provided AS IS, and by downloading it, you agree to be bound to the terms of the software license agreement (SLA). The detailed content licenses can be found here.
| STM32MP1 Starter Package image - STM32MP15-Ecosystem-v1.2.0 release | |
|---|---|
| Download |
You need to be logged on to my.st.com before accessing the following link: |
| Installation |
$ cd <working directory path>/Starter-Package
$ tar en.FLASH-stm32mp1-openstlinux-20-02-19.tar.xz
|
| Release note |
Details of the content of this software package are available in the associated STM32MP15 ecosystem release note. |
- The binaries and the Flash layout files are in the <Starter Package installation directory>/openstlinux-20-02-19/images/stm32mp1/ directory:
stm32mp1 ├── flashlayout_st-image-weston Flash layout files (description of the partitions) for the supported Flash devices and boards │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157a-dk1-basic.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and basic boot chain → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157a-dk1-extensible.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card with no userfs partition but a rootfs partition extended to sdcard size (recommended setup for package repository service) → STM32MP157A-DK1 │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157a-dk1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and trusted boot chain (recommended setup) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-dk2-basic.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and basic boot chain → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-dk2-extensible.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card with no userfs partition but a rootfs partition extended to sdcard size (recommended setup for package repository service) → STM32MP157C-DK2 │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-dk2-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and trusted boot chain (recommended setup) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ ├── FlashLayout_emmc_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for eMMC and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_emmc_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for eMMC and trusted boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nand-4-256_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for NAND Flash and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nand-4-256_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for NAND Flash and trusted boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-emmc_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and eMMC) and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-emmc_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and eMMC) and trusted boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-nand-4-256_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and NAND Flasdh) and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-nand-4-256_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and NAND Flasdh) and trusted boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and microSD card) and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_nor-sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for NOR Flash (and microSD card) and trusted boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-basic.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and basic boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ ├── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and optee boot chain → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ └── FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv Flash layout file for microSD card and trusted boot chain (recommended setup) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards ├── scripts │ └── create_sdcard_from_flashlayout.sh ├── st-image-bootfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Binary for bootfs partition ├── st-image-bootfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.manifest ├── st-image-userfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Binary for userfs partition ├── st-image-userfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.manifest ├── st-image-vendorfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Binary for vendorfs partition ├── st-image-vendorfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.manifest ├── st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Binary for rootfs partition ├── st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.license ├── st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1-license_content.html ├── st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.manifest ├── st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1_nand_4_256_multivolume.ubi ├── tee-header_v2-stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.stm32 ├── tee-header_v2-stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.stm32 ├── tee-header_v2-stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pageable_v2-stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pageable_v2-stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pageable_v2-stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pager_v2-stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pager_v2-stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.stm32 ├── tee-pager_v2-stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.stm32 ├── tf-a-stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── tf-a-stm32mp157a-dk1-trusted.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── tf-a-stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── tf-a-stm32mp157c-dk2-trusted.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards ├── tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 TF-A binary for FSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards ├── u-boot-spl.stm32-stm32mp157a-dk1-basic U-Boot binary for FSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-spl.stm32-stm32mp157c-dk2-basic U-Boot binary for FSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-spl.stm32-stm32mp157c-ev1-basic U-Boot binary for FSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards ├── u-boot-stm32mp157a-dk1-basic.img U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157a-dk1-trusted.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157a-dk1-optee.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157c-dk2-basic.img U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157c-dk2-trusted.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157c-dk2-optee.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Discovery kits ├── u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-basic.img U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (basic boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards ├── u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (trusted boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards └── u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-optee.stm32 U-Boot binary for SSBL partition (optee boot chain) → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards
6.2. Image flashing[edit source]
The STM32CubeProgrammer tool is used to flash the STM32MP15 Evaluation board with the downloaded image.
Several Flash devices (microSD, eMMC...) are available on this board: see the STM32MP15 Flash mapping article if you want to know more about the supported Flash memory technologies, and the Flash partitions. The steps below consider the microSD card as the Flash device.
As explained in the boot chains overview, the trusted boot chain is the default solution delivered by STMicroelectronics. Thus, the steps below use the image for the trusted boot chain.
Let's flash the downloaded image on the microSD card:
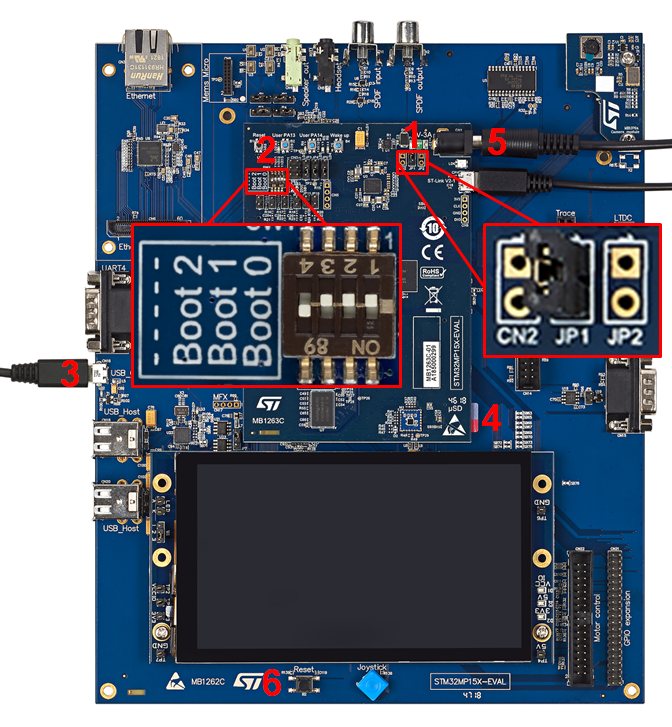
- Remove the jumper JP1 (1)
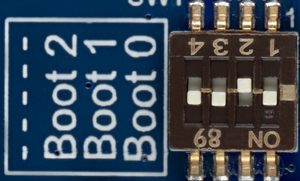
- Set the boot switches (2) to the off position
- Connect the USB micro-AB (OTG) port (3) to the host PC that contains the downloaded image
- Insert the delivered microSD card into the dedicated slot (4)
- Connect the delivered power supply to the power connector (5) of the MB1263 daughterboard
- Press the reset button (6) to reset the board
- Go to the Starter Package directory that contains the binaries and the Flash layout files
cd <Starter Package installation directory>/stm32mp1-openstlinux-4.19-thud-mp1-19-10-09/images/stm32mp1
If you have followed the the proposition to organize the working directory, the command is cd Starter-Package/stm32mp1-openstlinux-4.19-thud-mp1-19-10-09/images/stm32mp1
- Check that the STM32CubeProgrammer tool is installed and accessible; if not, go to the installation procedure (installing the tools)
STM32_Programmer_CLI --h
-------------------------------------------------------------------
STM32CubeProgrammer <tool version>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
- Get the device port location for the USB link
STM32_Programmer_CLI -l usb ------------------------------------------------------------------- STM32CubeProgrammer <tool version> ------------------------------------------------------------------- Total number of available STM32 device in DFU mode: 1 Device Index : USB1 USB Bus Number : 002 USB Address Number : 002 Product ID : DFU in HS Mode @Device ID /0x500, @Revision ID /0x0000 Serial number : 000000000000 Firmware version : 0x011a Device ID : 0x0500
- Flash the microSD card with the image for the trusted boot chain
STM32_Programmer_CLI -c port=usb1 -w flashlayout_st-image-weston/FlashLayout_sdcard_stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.tsv
- This operation takes several minutes (mainly depending of the rootfs size). A successful flashing outputs the following log:
------------------------------------------------------------------- STM32CubeProgrammer <tool version> ------------------------------------------------------------------- USB speed : High Speed (480MBit/s) Manufacturer ID : STMicroelectronics Product ID : DFU in HS Mode @Device ID /0x500, @Revision ID /0x0000 Serial number : 000000000000 Firmware version : 0x011a Device ID : 0x0500 AREA NAME SECT.NBR PARTITION.ID SIZE TYPE Partition0 0000 0x00000000 0256 KB RW SECBL 0000 0x00000001 0001 MB RW Partition2 0000 0x00000002 0001 MB RW Partition3 0000 0x00000003 0256 KB RW Partition4 0000 0x00000004 0016 MB RW virtual 0000 0x000000f1 0512 B R Device name : STM32MPxxx Device type : MPU Device CPU : Cortex-A7 Start Embedded Flashing service Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 File : tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 Size : 228536 Bytes Partition ID : 0x01 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:00.557 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x01 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x01 Flashlayout Programming ... [==================================================] 100% Running Flashlayout Partition ... Flashlayout partition started successfully Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 File : u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 Size : 728904 Bytes Partition ID : 0x03 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:00.672 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x03 reconnecting the device ... USB speed : High Speed (480MBit/s) Manufacturer ID : STMicroelectronics Product ID : USB download gadget@Device ID /0x500, @Revision ID /0x0000 Serial number : 0000000000 Firmware version : 0x0110 Device ID : 0x0500 AREA NAME SECT.NBR PARTITION.ID SIZE TYPE fsbl1 0000 0x00000001 0256 KB RW fsbl2 0000 0x00000002 0256 KB RW ssbl 0000 0x00000003 0002 MB RW bootfs 0000 0x00000011 0064 MB RW rootfs 0000 0x00000012 0768 MB RW userfs 0000 0x00000013 3003 MB RW virtual 0000 0x000000f1 0512 B RW OTP 0000 0x000000f2 0512 B RW PMIC 0000 0x000000f4 0008 B RW Start operation done successfully at partition 0x03 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 File : tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 Size : 228536 Bytes Partition ID : 0x01 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:00.096 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x01 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x01 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 File : tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 Size : 228536 Bytes Partition ID : 0x02 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:00.110 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x02 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x02 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 File : u-boot-stm32mp157c-ev1-trusted.stm32 Size : 728904 Bytes Partition ID : 0x03 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:00.307 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x03 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x03 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: st-image-bootfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 File : st-image-bootfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Size : 64 MBytes Partition ID : 0x11 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:39.707 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x11 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x11 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 File : st-image-weston-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Size : 507952 KBytes Partition ID : 0x12 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:04:23.031 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x12 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x12 Memory Programming ... Opening and parsing file: st-image-userfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 File : st-image-userfs-openstlinux-weston-stm32mp1.ext4 Size : 64 MBytes Partition ID : 0x13 Download in Progress: [==================================================] 100% File download complete Time elapsed during the download operation is: 00:00:34.205 RUNNING Program ... PartID: :0x13 Start operation done successfully at partition 0x13 Flashing service completed successfully
Go see the STM32CubeProgrammer article:
- to use another Flash device than the microSD card one
- to know more about the flashing operation
7. Booting the board[edit source]
Now that the image is flashed on the STM32MP157x-EV1 Evaluation board, let's finalize the system configuration:
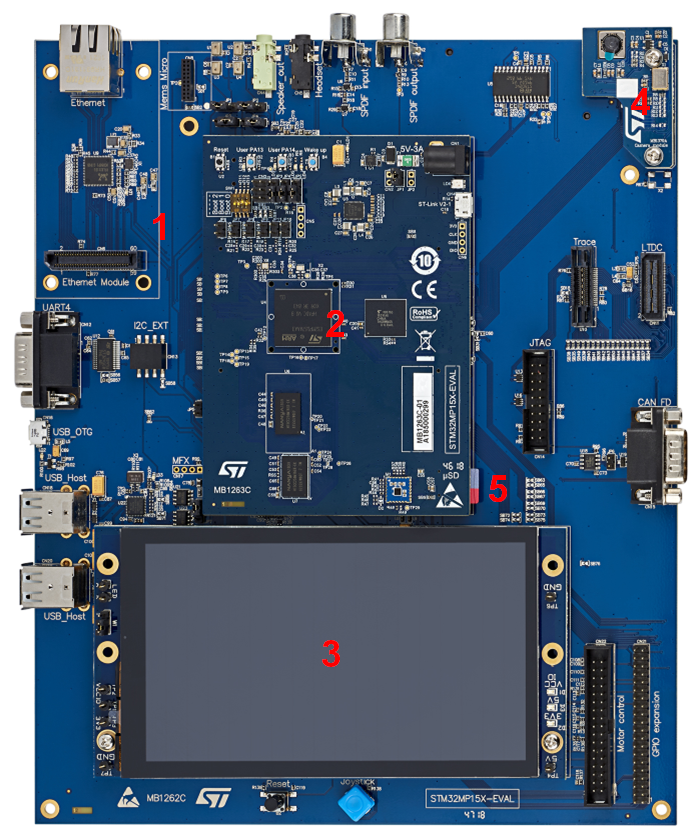
- Step 1: check the configuration of the switches and jumpers:
- The boot related switches must be configured so that the device (e.g. microSD card ) on which the image has been flashed is selected as boot source.
- The jumpers related to the UART4 of the STM32MP15 microprocessor device must be set so that UART4 is used by the ST-LINK/V2-1 controller (7)
- The figure below shows the boot switches for the recommended boot from microSD card.
- Step 2: (optionally) connect a USB keyboard and/or a USB mouse (not provided) using the USB type-A ports (10 and 11).
- Step 3: (optionally) connect an Ethernet cable (not provided) to the dedicated connector (13).
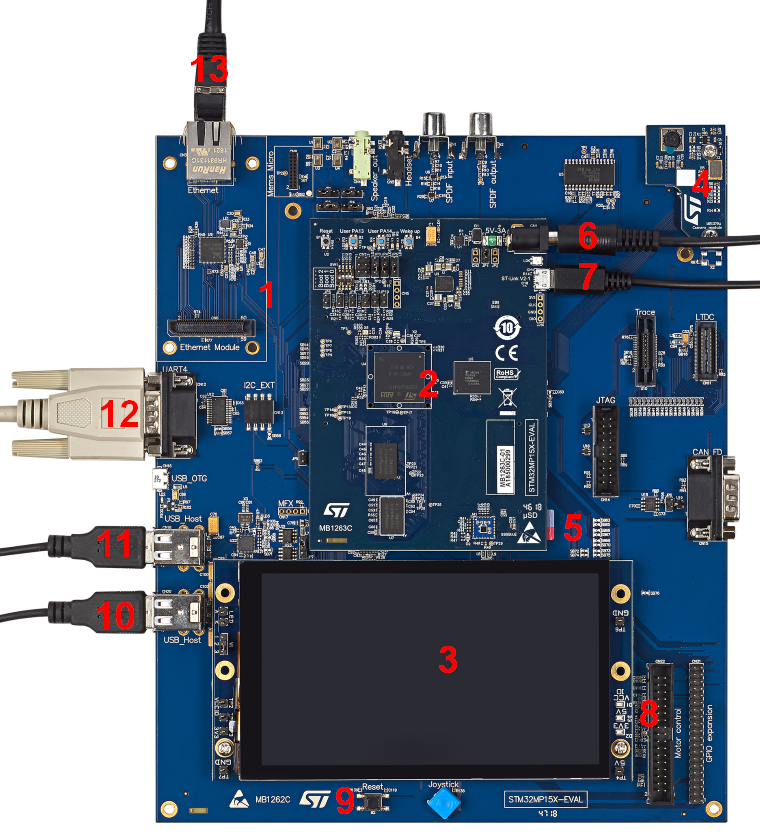

- MB1262 motherboard
- MB1263 daughterboard: STM32MP157x 18x18 PMIC DDR3
- MB1230 DSI 720p display
- MB1379 daughterboard camera
- MicroSD card slot
- MB1263 power 5V-3A
- USB micro-B (ST-LINK/V2-1) → PC virtual COM port and debug
- Display leds
- Reset button
- 2 x USB type A (host) → E.g. mouse keyboard USB driver...
- 2 x USB type A (host) → E.g. mouse Keyboard USB driver...
- UART → PC console
- Ethernet → Network
- Step 4: if the Flash device is a microSD card, check that it is inserted into the dedicated slot (5).
- Step 5: connect the delivered power supply (5V, 3A) to the power connector (6) of the MB1263 daughterboard. Check that the display board (MB1230) is well connected. In this case, the 2 green LEDs (8) are switched on.
- Step 6: (optionally) install and configure a remote Terminal program (e.g. Minicom on Ubuntu Linux PC or Tera Term on Windows PC) onto your host PC, and connect
- either the ST-LINK/V2-1 USB micro-B port (7) to a host PC that runs a Terminal program with ST-LINK/V2-1 virtual port (recommended method)
- or the RS232 UART4 connector (12) to the host PC that runs a Terminal program with COM1 port.
- the ST-LINK/V2-1 USB micro-B port (7) and the RS232 UART4 connector (12) cannot be used simultaneously: see how to set the JP4 and JP5 jumpers to select one of the two configurations
- Step 7: press the reset button (9) to reset the board
The board boots and the system will be available after few seconds.
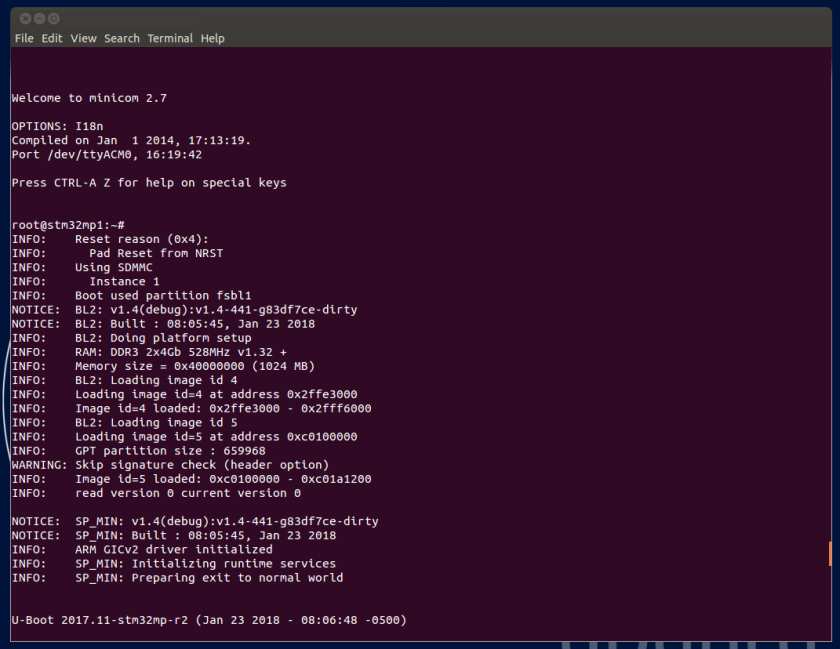
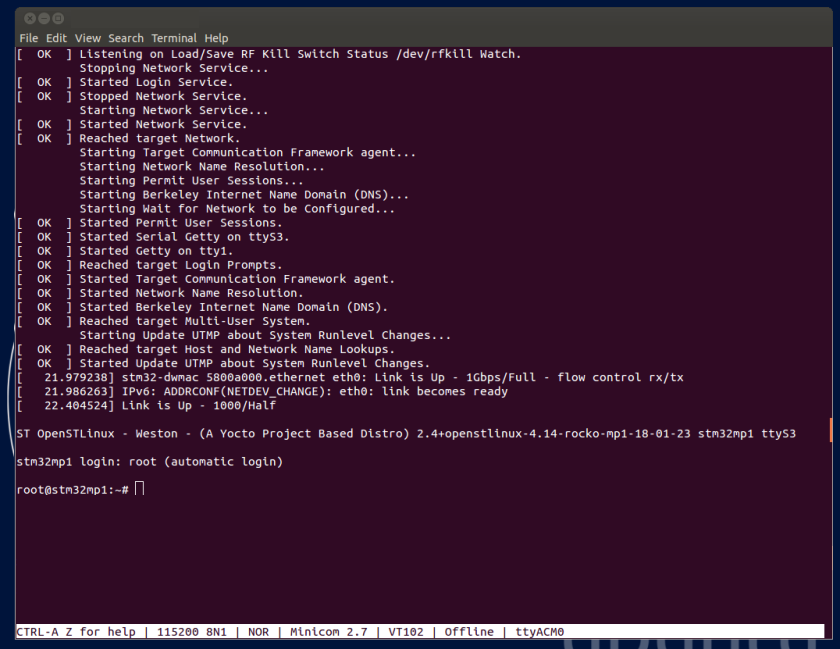
8. Checking the boot sequence[edit source]
Assuming you have performed the optional step 6 above, the information (coming successively from the U-Boot and the Linux operating system that is booting on the board), should be displayed on the host PC Terminal.
In parallel, a U-Boot splash screen picture is displayed on the DSI display (if one is connected to the board).
A user space graphical boot splash screen (PSplash) picture is then briefly displayed on the HDMI monitor if one is connected to the board, or otherwise on the DSI display (if one is connected to the board).
When the boot process is complete, the launcher application is shown on the HDMI monitor if one is connected to the board, or otherwise on the DSI display (if one is connected to the board).
More detail about this launcher application in GTK demo launcher page.
9. Mouse, keyboard and Ethernet hot-plugs[edit source]
Let's assume that the optional step 2 and step 3 were not achieved when setting up the system above.
When connecting a USB mouse, the following information is displayed by the Terminal program:
[ 926.786326] usb 2-1.1: new low-speed USB device number 3 using ehci-platform [ 926.961413] input: Logitech Optical USB Mouse as /devices/platform/soc/5800d000.usbh-ehci/usb2/2-1/2-1.1/2-1.1:1.0/0003:046D:C016.0001/input/input2 [ 926.975098] hid-generic 0003:046D:C016.0001: input: USB HID v1.10 Mouse [Logitech Optical USB Mouse] on usb-5800d000.usbh-ehci-1.1/input0
When connecting a USB keyboard, the following information is displayed by the Terminal program:
[ 1009.026567] usb 2-1.3: new low-speed USB device number 4 using ehci-platform [ 1009.193990] input: Dell Dell USB Keyboard as /devices/platform/soc/5800d000.usbh-ehci/usb2/2-1/2-1.3/2-1.3:1.0/0003:413C:2003.0002/input/input3 [ 1009.280101] hid-generic 0003:413C:2003.0002: input: USB HID v1.10 Keyboard [Dell Dell USB Keyboard] on usb-5800d000.usbh-ehci-1.3/input0
When connecting an Ethernet cable, the following information is displayed by the Terminal program:
[ 1215.356377] stm32-dwmac 5800a000.ethernet eth0: Link is Up - 1Gbps/Full - flow control rx/tx
[ 1215.363377] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_CHANGE): eth0: link becomes ready
[ 1215.391068] Link is Up - 1000/Half
10. Remote and local Terminal programs[edit source]
As already explained in the step 6 above, a remote Terminal program can be installed and configured on your host PC in order to communicate with the board through a serial link or an Ethernet link: see How to get Terminal.
The remote Terminal on your host PC can be used to enter command lines, as shown below with the ifconfig command to query the network interface parameters:
A local Terminal program can be launched directly on the board. Click on the small icon at the top left corner of the display (see the red arrow on the figure below):
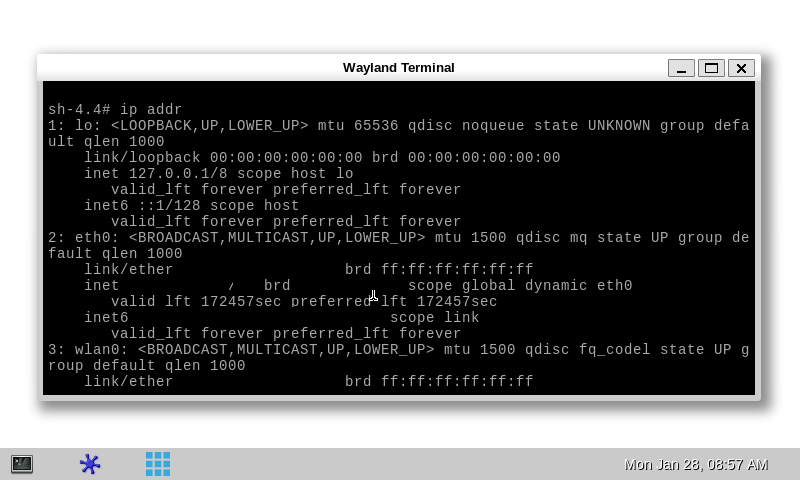
Then the on-board Wayland Terminal can be used to directly enter command lines as shown below, still with the ip addr command to query the network interface parameters:
Consequently, unless an explicit restriction is mentioned, command lines can be run from both Terminals.
Note: in this article, any command executed on the board (through the remote Terminal or the Wayland Terminal) starts with , while any command executed on the host PC starts with .
11. Executing basic commands[edit source]
11.1. Having a look at the OpenSTLinux directory structure[edit source]
The directory structure and directory contents in the OpenSTLinux distribution is standard. Some details are available in the OpenSTLinux directory structure article.
11.2. Identifying the software running on board[edit source]
For ecosystem release v1.2.0  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Software | How to get its version | Output example |
|---|---|---|
| TF-A | TF-A Version number |
NOTICE: BL2: v2.0-r3.0(debug):v2.0-r3.0 |
| U-Boot | See the version displayed in the console |
U-Boot 2018.11-stm32mp-r4 [...] |
| Linux kernel |
cat /proc/version
|
Linux version 4.19.94 (xxxx@yyyy) (gcc version 8.2.0 (GCC)) [...] |
| GCC |
cat /proc/version
|
Linux version 4.19.94 (xxxx@yyyy) (gcc version 8.2.0 (GCC)) [...] |
| Yocto Project |
lsb_release -c
|
Codename: thud |
| Weston |
weston --version
|
weston 5.0.0 |
| GStreamer |
gst-play-1.0 --version
|
GStreamer 1.14.4 |
| GPU |
cat /sys/kernel/debug/gc/version
|
6.2.4.p4.190076 built [...] |
For ecosystem release v1.1.0  [edit source]
[edit source]
For ecosystem release v1.0.0  [edit source]
[edit source]
11.3. Configuration tips[edit source]
11.4. Getting board IP address[edit source]
Prerequisite: your board is connected to your local network through the Ethernet connector (see step 3).
- Get the IP address of your board with the ip Linux command line (recommended method):
ip addr show eth0 3: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet xx.xx.xx.xx/xx brd xx.xx.xx.xx scope global dynamic eth0 valid_lft 159045sec preferred_lft 159045sec inet6 xxxx::xx:xx:xx:xx/xx scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- Get the IP address of your board with the ifconfig Linux command line (a deprecated but well-known command):
ifconfig eth0 eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx inet addr:xx.xx.xx.xx Bcast:xx.xx.xx.xx Mask:255.255.252.0 inet6 addr: xxxx::xx:xx:xx:xx/xx Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:2619 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:1311 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:353250 (344.9 KiB) TX bytes:118305 (115.5 KiB) Interrupt:247
11.5. Copying a file from your host PC to your board (and reciprocally)[edit source]
- How to transfer a file over network (recommended method)
11.6. Miscellaneous commands[edit source]
11.6.1. Printing distribution specific information[edit source]
lsb_release -a
LSB Version: core-5.0-noarch:core-5.0-arm
Distributor ID: openstlinux-weston
Description: ST OpenSTLinux - Weston - (A Yocto Project Based Distro) 2.6-...
Release: 2.6...
Codename: thud
Where:
| LSB Version | Version of LSB (Linux Standard Base) against which distribution is compliant |
| Distributor ID | String identifier of distributor |
| Description | Single line text description of distribution |
| Release | Release number of distribution |
| Codename | Codename according to distribution release |
11.6.2. Printing system information[edit source]
uname -a Linux stm32mp1 4.19.49 #1 SMP PREEMPT Sun Jun 9 07:17:25 UTC 2019 armv7l armv7l armv7l GNU/Linux
Where:
| Linux | Kernel name |
| stm32mp1 | Network node hostname |
| 4.19.49 | Kernel release |
| #1 SMP PREEMPT Sun Jun 9 07:17:25 UTC 2019 | Kernel version |
| armv7l | Machine hardware name |
| GNU/Linux | Operating system |
11.6.3. Printing Linux kernel and GCC versions[edit source]
cat /proc/version Linux version 4.19.49 (xxxx@yyyy) (gcc version 8.2.0 (GCC)) #1 SMP PREEMPT Sun Jun 9 07:17:25 UTC 2019
Where:
| Linux | Kernel name |
| version 4.19.49 | Kernel release |
| (xxxx@yyyy) | Person (xxxx) who compiled the kernel, and machine (yyyy) where it happened |
| (gcc version 8.2.0 (GCC) ) | Version of the GCC compiler used to compile the kernel |
| #1 SMP PREEMPT Sun Jun 9 07:17:25 UTC 2019 | Kernel version; type of kernel (SMP) and date and time of the kernel compilation |
11.6.4. Printing the amount of disk space available on all mounted file systems[edit source]
df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/root 719M 342M 339M 51% /
devtmpfs 372M 0 372M 0% /dev
tmpfs 436M 0 436M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 436M 14M 423M 4% /run
tmpfs 436M 0 436M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
tmpfs 436M 4.0K 436M 1% /tmp
/dev/mmcblk0p4 58M 8.2M 46M 16% /boot
/dev/mmcblk0p7 6.4G 68M 6.1G 2% /usr/local
tmpfs 436M 128K 436M 1% /var/volatile
/dev/mmcblk0p5 15M 8.2M 5.3M 61% /vendor
tmpfs 88M 0 88M 0% /run/user/0
Where:
| Filesystem | Source of the mount point, usually a device |
| Size | Total size in human readable format (e.g. 1K, 234M, 2G) |
| Used | Used size in human readable format |
| Available | Available size in human readable format |
| Use% | Percentage of used size divided by the total size |
| Mounted on | Mount point |
Note: the user file system (userfs) and the boot file system (bootfs) are accessible respectively through the /usr/local mounting point, and the /boot mounting point (see Flash partitions for a description of the file systems).
12. Examples[edit source]
12.1. Examples running on Cortex-A7[edit source]
The table below gathers links towards articles proposing examples of peripherals usage.
| Link to the example |
|---|
| Playing an audio/video local file |
| Playing an audio/video stream |
| Displaying an image |
| Running a simple 3D example (GPU usage) |
| Displaying a fullscreen camera preview |
| Taking a picture |
12.2. Examples running on Cortex-M4[edit source]
Please read STM32CubeMP1 Package article.
13. Fast links to essential commands[edit source]
If you are already familiar with the Starter Package for the STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution, fast links to the essential commands are listed below.
14. How to go further?[edit source]
Now that the image is flashed on the STM32MP15 Evaluation board, you might want to switch to the STM32MP1 Developer Package, in order to modify or tune the STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution with your own developments.