1. Article Purpose[edit source]
This article gives information about the hardware random (HWRNG) framework.
2. Framework purpose[edit source]
The Hardware random framework is integrated in the kernel. It provides access to RNG peripherals and focuses on supporting the hardware number generator.
3. System overview[edit source]
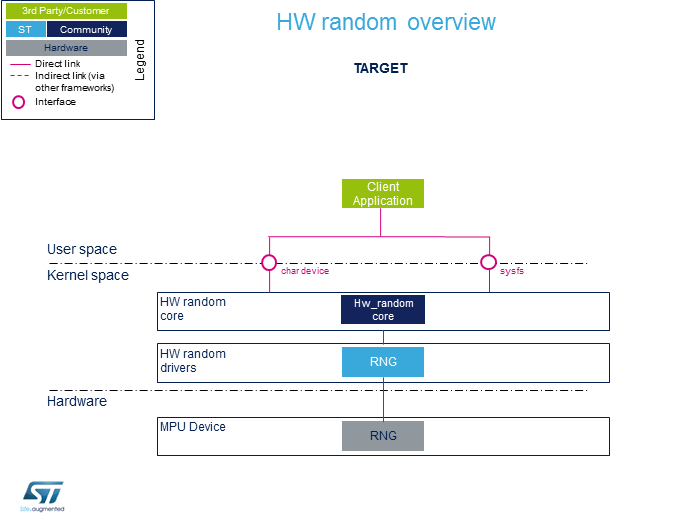
The HW random framework allows retrieving random numbers in userland.
3.1. Component description[edit source]
- HW random core (Kernel space)
Generic interface in kernel space. This layer is in charge of creating the character device (char device) and sysfs to access hw_random.
- RNG (Kernel space)
Hardware random Linux® drivers handling the HW blocks.
- RNG (Hardware)
HW blocks handling the RNG peripheral.
3.2. API description[edit source]
The Hardware random framework uses char device API[1] ioctl operations. For additional information, refer to:
- sysfs interface.
- Kernel Documentation directory[2]
4. Configuration[edit source]
4.1. Kernel configuration[edit source]
The Hardware random support is activated by default in ST deliveries. No specific configuration is required apart from enabling or disabling peripheral support using Linux® Menuconfig tool. Refer to Menuconfig or how to configure kernel and select:
[*] Device Drivers --->
[*] Character devices --->
[*] Hardware Random Number Generator Core support --->
[*] STMicroelectronics STM32 random number generator
4.2. Device tree configuration[edit source]
DT configuration can be done thanks to the STM32CubeMX.
A detailed device tree configuration is described in RNG device tree configuration.
5. How to use the framework[edit source]
The framework provides external interfaces from userland : How to control RNG.
5.1. How to use from char device[edit source]
The community tool for using Hardware random framework is rng_tools[3] which provides a complete set of utilities related to random number generators:
- rngd: runs a background daemon that opens /dev/hwrng file (default) to connect and retrieve random numbers.
- rngtest: runs different tests that check the entropy and verify the compliance regarding FIPS 140-2 standard.
5.2. How to use from sysfs[edit source]
Available devices compatible with Hardware framework can be listed using sysfs commands:
cat /sys/class/misc/hw_random/rng_available stm32-rng
The selected device is shown here:
cat /sys/class/misc/hw_random/rng_current stm32-rng
To select a different device:
echo "stm32-rng"> /sys/class/misc/hw_random/rng_current
6. How to trace and debug the framework[edit source]
Light information on the framework can be accessed by using sysfs.
By default, the framework does not provide any specific debug output or dynamic debugging tool.
7. Source code location[edit source]
Hardware random drivers and framework are available here[4].
8. To go further[edit source]
Code examples are directly available from rng-tools[3] github.
9. References[edit source]