1. Article Purpose[edit source]
This section details the process used to build TF-A from sources and to deploy it on your target.
The build example is based on the OpenSTLinux environment:
- Developer Package
- Distribution Package
2. Overview[edit source]
TF-A is the FSBL for the ST trusted boot chain. It must be configured or updated depending on your platform.
Cross compilation of TF-A is only required if it is to be modified. By default, in the Starter Package, the TF-A image is named: tf-<board>-trusted.stm32.
In changes are made, you must rebuild TF-A and update all the FSBL partitions of your boot device with this new image. A second FSBL image is used as a backup image.
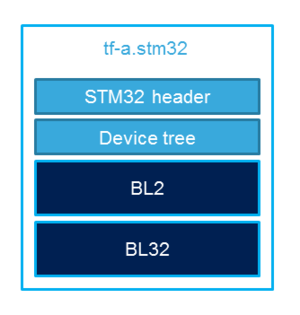
The build process creates a full STM32 image that can be used for Flash integrating a specific header.
This trusted firmware-A image contains a device tree, a BL2 and a BL32 stage.
These binaries are built in a single step during the build process.
3. Developer Package[edit source]
3.1. Install sources[edit source]
The Developer Package contains OpenSTLinux and TF-A sources: TF-A Installation
3.2. Official source tree[edit source]
Download source code from the official github
git clone https://github.com/ARM-software/arm-trusted-firmware.git
3.3. Build Process[edit source]
3.3.1. Initialise the cross compile environment[edit source]
Setup Cross compile environment
3.3.2. TF-A Build flags[edit source]
For ecosystem release ≥ v1.2.0 ![]()
Mandatory flags:
- ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7: the major version of ARM Architecture to target (STM32MP15 is ARMv7 architecture based)
- ARCH=aarch32: specify aarch32 architecture to be built
- PLAT=stm32mp1: builds an stm32mp1 platform
- DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb: this must be defined to build the proper target and include the correct DTB file into the final file
- AARCH32_SP=<monitor>
- sp_min: builds the BL32 secure monitor if required
- optee: do not include BL32 and prepare BL2 for optee-specific load which also requires to build with the 'STM32MP_BOOT_ONLY=1' option.
Optional flags:
- STM32MP_BOOT_ONLY=1: Build all storage driver supports except serial (no stm32_programmer support). Required for OP-TEE mode.
- STM32MP_FLASHLOADER_ONLY=1: Build only serial link driver support (UART/USB) and stm32_programmer support.
- DEBUG=1: add debug information in all binaries
- V=1: print verbose compilation traces
For ecosystem release v1.1.0 ![]()
Mandatory flags:
- ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7: the major version of ARM Architecture to target (STM32MP15 is ARMv7 architecture based)
- ARCH=aarch32: specify aarch32 architecture to be built
- PLAT=stm32mp1: builds an stm32mp1 platform
- DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb: this must be defined to build the proper target and include the correct DTB file into the final file
- AARCH32_SP=<monitor>
- sp_min: builds the BL32 secure monitor if required
- optee: do not include BL32 and prepare BL2 for optee-specific load
Optional flags:
- DEBUG=1: add debug information in all binaries
- V=1: print verbose compilation traces
3.4. Build command[edit source]
From the Developer Package tarball, a Makefile.sdk is present and must be used to build the target.
It automatically sets the proper configuration for the TF-A build.
make -f Makefile.sdk TF_A_CONFIG=trusted TFA_DEVICETREE=stm32mp157c-<board>
The latest version of the helper file is also available in this user guide: README.HOW_TO.txt.
If no Makefile.sdk exists, you must add your own environment flags:
unset LDFLAGS;
unset CFLAGS;
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 AARCH32_SP=sp_min DTB_FILE_NAME=stm32mp157c-<board>.dtb
3.5. Final image[edit source]
Final image is available for Flash or SD card update in the corresponding folder:
build/<target>/<debug|release>/tf-a-<target>.stm32 Ex: build/stm32mp1/debug/tf-a-stm32mp157c-ev1.stm32
4. Distribution Package[edit source]
For an OpenSTLinux distribution, the TF-A image is built in release mode by default. The yocto recipe can be found in:
meta-st/meta-st-stm32mp/recipes-bsp/trusted-firmware-a/tf-a-stm32mp_<version>.bb
If you want to modify the TF-A code source, use the following steps starting from an already downloaded and built OpenSTLinux distribution.
4.1. Access sources[edit source]
You can use devtool to access the source.
cd <baseline root directory> devtool modify tf-a-stm32mp sources/boot/tf-a
By going to the sources/boot/tf-a folder, you can manage and modify the TF-A sources. To rebuild it, go back to the build-<distribution> folder and launch the TF-A recipe:
bitbake tf-a-stm32mp
The final image is deployed in the image default output folder.
5. Update software on board[edit source]
5.1. Partitioning of binaries[edit source]
The TF-A build provides a binary named tf-a-stm32mp157c-<board>.stm32 that MUST be copied to a dedicated partition named "fsblX" (X depends of needed backup).
5.2. Update via SDCARD[edit source]
If you use an SD card, you can simply update TF-A using the dd command on your host.
Plug your SD card into the computer and copy the binary to the dedicated partition; on an SDCard/USB disk the "fsbl1" partition is partition 1:
- SDCARD: /dev/mmcblkXp1 (where X is the instance number) - SDCARD via USB reader: /dev/sdX1 (where X is the instance number)
- Linux
dd if=<tf-a file> of=/dev/<device partition> bs=1M conv=fdatasync
- Windows
There is an existing dd for Windows that makes binary copying possible.
5.3. Update via USB mass storage on U-boot[edit source]
See How to use USB mass storage in U-Boot
Follow the previous section to put tf-a-<board>.stm32 onto SDCard/USB disk
5.4. Update your boot device (including SD card on the target)[edit source]
Refer to the STM32CubeProgrammer documentation to update your target.