| Coming soon |
1. Introduction[edit source]
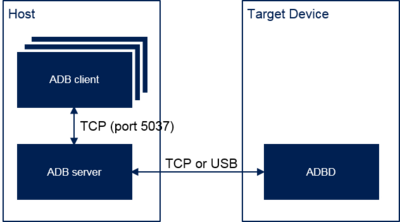
Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a versatile command-line tool that lets you communicate with a device (an emulator or a connected Android device).
- ADB clients = executable with subcommand (ex: adb shell, adb logcat)
- ADB server = act as proxy between adb clients and adbd
- ADBD daemon = started by init on the target device
The target device can be connected using different solutions:
As soon as connected, it's possible to start testing your application with Android Studio.
It's also possible to execute all ADB commands (see ADB commands for more details).
For that purpose, you have to find ADB tool within your environment: Host computer installation
2. Host computer installation[edit source]
ADB is available by default within Android Studio IDE (part of the Android SDK). It's available for Linux, Windows and OS X.
When required, it's possible to execute directly ADB commands within Android Studio Terminal.
It's required to go to the correct directory (<SDK path>/platform-tools)
cd <SDK path>
cd platform-tools
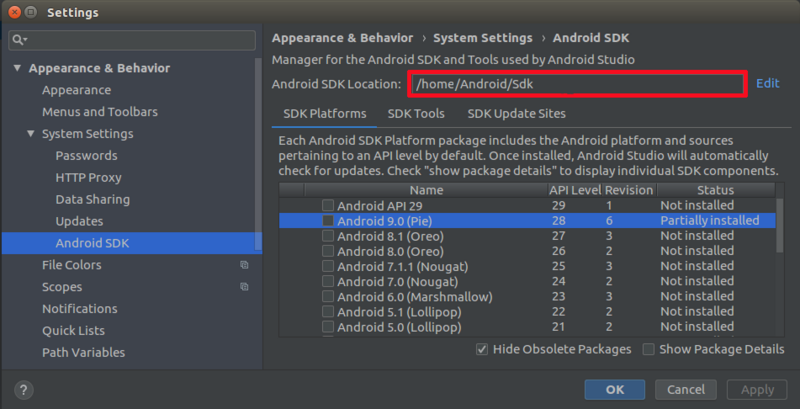
The <SDK path> can be recovered opening the SDK Manager (from Android studio: "Tools/Android/SDK Manager" menu):
Distribution case
See Host computer installation for Expert
3. Commands[edit source]
The ADB commands facilitate a variety of device actions, such as installing and debugging apps, and it provides access to a Unix shell that you can use to run a variety of commands on a device.
See ADB commands summary for more information
4. Device Connection[edit source]
4.1. How to connect over USB[edit source]
Several steps are required to connect your device:
4.1.1. Host computer configuration[edit source]
The required installation and configuration depends on the host computer OS used:
4.1.1.1. Linux Host (Ubuntu)[edit source]
In Linux environment, the Android USB drivers are built-in. It's only required to set the target device information.
For that purpose, you have to open a terminal and:
- create (or update if already exists) the 51-android.rules file in /etc/udev/rules.d/ with the following information
- idVendor = 0483 (STMicroelectronics vendor)
- idProduct = df11 (ADB on STMicroelectronics device)
- Mode = 0666 (read/write permissions)
- Group = plugdev (Unix group which owns the device node)
Example:
# ADB on STMicroelectronics devices
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="0483", ATTR{idProduct}=="df11", MODE="0660", GROUP="plugdev"
- insure that the file created has the correct access rights:
chmod a+r /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
At this stage, you have an USB driver correctly installed and configured.
4.1.1.2. Windows Host[edit source]
In Windows environments, it's required to install the USB driver and to set the target device information.
Follow the instructions from the Android Studio website to get back the USB driver: Get the Google USB Driver
Then, you have to:
- edit the file android_winusb.inf available in the usb_driver directory and add under each section (ex: under [Google.NTx86] and under [Google.NTamd64]) the following data:
%SingleAdbInterface% = USB_Install, USB\VID_0483&PID_DF11 %CompositeAdbInterface% = USB_Install, USB\VID_0483&PID_DF11&MI_00 %SingleAdbInterface% = USB_Install, USB\VID_0483&PID_DF11&REV_0409 %CompositeAdbInterface% = USB_Install, USB\VID_0483&PID_DF11&REV_0409&MI_00
Depending on your Windows OS version, the driver installation procedure can differ: Installing a USB Driver
At this stage, you have an USB driver correctly installed and configured.
4.1.1.3. OS X Host[edit source]
In OS X environment, the Android USB drivers are built-in and it's not required to update configuration.
At this stage, you have an USB driver correctly installed and configured.
4.1.2. Target device configuration[edit source]
Prerequisite: the target device is started with the ST Android distribution and you can access the Android user interface.
On the target device, you have to:
- disconnect the USB cable between the target device and the host computer (if already connected)
- find the Settings > Developer options configuration screen on your target device (If it's not visible, you must select Settings > About device and tap the Build number seven times).
- enable the USB Debugging option from Settings > Developer options.
- re-connect the USB cable between the target device and the host computer
- if you see an alert on your target device requesting permission to "Allow USB debugging," click OK. It's recommended to check "Always allow from this computer" to avoid this step each time the target device is connected on the same host computer.
4.1.3. Check device connection[edit source]
First, insure that the device is connected on the host computer using an USB cable and that the device is started.
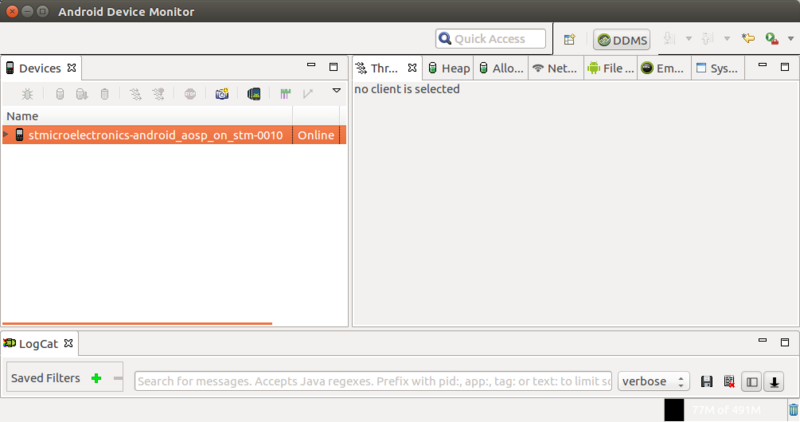
Android Studio integrates a tool named Device Monitor (from Android studio: "Tools/Android/Android Device Monitor" menu). You can launch it and check that you can see the target device in the list (name of the device starting by stmicroelectronics).
4.2. How to connect over Ethernet[edit source]
To allow using Ethernet connection for ADB, you have to connect the host computer on the same network than the target device.
First, you have to follow instruction in How to connect over USB.
Then, you have to:
- connect the USB cable between the target device and the host computer
- open a terminal on your host computer
- go on the cd <SDK path>/platform-tools/ directory (see Host computer installation to know how to get back the <SDK path>)
- execute adb shell ifconfig to get back IP address <device_ip_address>
- execute adb tcpip 5555 to set the TCP/IP connection on port 5555
- disconnect the USB cable between the target device and the host computer
- execute adb connect <device_ip_address> to reconnect on the device through Ethernet
4.3. How to connect over Wi-Fi[edit source]
Follow the instructions from the Android Studio website: Connect to a device over Wi-Fi
5. ADB for Distribution Package[edit source]
5.1. Host computer installation for Distribution Creator[edit source]
By default, ADB is built when you compile the ST Android distribution. It's automatically added within your PATH.
Another possibility is to install ADB: apt-get install android-tools-adb
The device is not necessarilly seen in the terminal when executing adb devices. You have to:
- create a file within ~/.android/ directory named adb_usb.ini
- add one line with the STMicrolectronics idVendor
0x0483
5.2. ADB implementation[edit source]
ADB source code is stored in system/core/adb (common files between host and target device are differentiated by ADB_HOST tag).
Three properties are available for ADB (set within the device/stm/<BoardId>/device.mk):
- persist.adb.trace_mask → used to enable or disable ADBD traces on target device (0x7FF for full trace, 0 to disable).
- ro.adb.secure → used to enable or disable authentication mechanism (1 to enable authentication, 0 to disable), this property can't be modified dynamically. This property is considered only in case of eng or userdebug build. Otherwise, it's ignored (authentication mechanism is enabled by default for user build).
- service.adb.tcp.port → used to set TCP/IP port if a wireless connection is used (this property is not set by default as not required in case of USB)
ADB is an Android specific gadget device available in user space. It's required to mount functionfs as it's used to create this gadget device and register it to the USB Device Controller (UDC). Three EndPoints are used (one for control, one for data input, one for data output).
It's also possible to create a composite device between ADB and other protocols using the configfs mechanism.
You can open the device/stm/<BoardId>/init.stm.usb.rc file to understand how the USB is configured for ADB and the file system/core/rootdir/init.usb.configfs.rc to understand what are the USB composite devices available (by default).
ADB over USB is the default configuration within the Android baseline with following properties set:
- persist.adb.trace_mask: [0] → no ADB trace by default
- ro.adb.secure: [1] → authentication mechanism enabled by default (need to accept connection through popup on target device)
- persist.sys.usb.config: [adb] → USB ADB gadget device
- sys.usb.config: [adb] → USB ADB gadget device
- sys.usb.state: [adb] → USB ADB gadget device
It's possible to set the ADB over wireless connection within your distribution (Ethernet or Wi-Fi) adding following property in /device/stm/<BoardId>/device.mk:
PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += service.adb.tcp.port=5555