1. Article purpose[edit source]
This article intends to a Developer profile end user (see Which Package better suits your needs for more information).
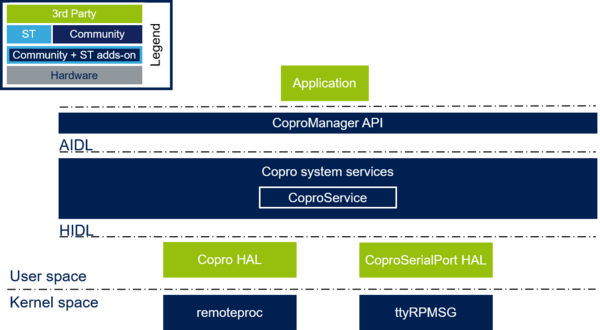
This article explains how to use CoproService which is a SystemService embedded in Android framework, allowing to use a tty driver to communicate with a Cortex M4 embedded in a compatible hardware board.
Please have a look into STM32MPU Embedded Software for Android architecture overview to get information on compatible hardware boards.
2. Pre-requisite[edit source]
The used environment must have been installed following the Developer Package adapted to your selected microprocessor device. See the list of Android distribution Packages here.
The firmware built for the Cortex M4 has to use RemoteProc and RPMSG, and has to instantiate a ttyRPMSG unit during its initialization.
3. CoproService[edit source]
CoproService is composed of 2 parts: Firmware management and TTY management.
3.1. Firmware management[edit source]
Cortex M4 will be used to offload real time algorithms, such as MotorControl, new Connectivity mediums like LORA and so on.
Users will develop their Firmwares thanks to CubeMX and SW4STM32 tools.
The Firmware will be embedded in the vendor partition in the specific directory "/vendor/firmware/copro/".
The CoproService will look at the content of "/vendor/firmware/copro/" to get available Firmware. It will then, on user/application request load the requested Firmware.
3.2. TTY management[edit source]
When the right Firmware is loaded and running, a /dev/ttyRPMSG0 driver is available to communicate with Cortex M4.
It is up to users to define and write their own protocol on top of ttyRPMSG0.
Application will then be able to:
- open ttyRPMSG0
- write to ttyRPMSG0
- read from ttyRPMSG0
- close ttyRPMSG0
4. API[edit source]
4.1. CoproManager API[edit source]
The CoproManager API gives access to the Firmware management.
- CoproManager getInstance() : Get the instance of the CoproManager available to start using it.
- FirmwareInfo[] getFirmwareList() : Return the list of available firmawre present in "/vendor/firmware/copro/"
- FirmwareInfo getFirmwareByName(String name) : Search in the folder "/vendor/firmware/copro/" if the Firmware match "name" and return it's info overwise null
- boolean isFirmwareRunning(int id) : Return true if the Firmware having "id" is running else it will return false.
- void startFirmware(int id) : Start the Firmware define by "id"
- void stopFirmware() : Stop any Firmware running
- ICoproSerialPort getSerialPort() : Get access to CoproSerialPort to interact with the Firmware. See below for more info.
4.2. FirmwareInfo API[edit source]
The FirmwareInfo API gives information about Firmwares.
- int getId() : get the ID given by the CoproService to this Firmware
- String getName() : get the file name of this Firmware
- boolean getState() : give the acutual state of the Firmware (running or stopped)
4.3. CoproSerialPort API[edit source]
The CoproSerialPort API gives access to the /dev/ttyRPMSG0 driver available when a Firmware is running. I allow the application to open and close the interface and also to send and receive data.
- void open(int mode) : open a fb to /dev/ttyRPMSG0 with the given mode : 0 for normal mode, 1 for raw mode
- void close() : close the fd to /dev/ttyRPMSG0
- String read() : read available bytes if the fd is open overwise an empty string is return.
- void write(String command) : write the given "command" to the fd.
5. Developping a Copro application[edit source]
In order to build the application, make sure you are using the approriate Android SDK embedded the CoproService How to build and install an SDK.
In AndroidStudio create a new application.
Then, do not forget to select the right API level in the application Manifest, in order to be sure that CoproService is available.
To use the CoproService you need to get the instance to the CoproManager, then you will be available to use the CoproManager API has defined above:
CoproManager mCoproManager = CoproManager.getInstance();
To be able to communicate with the running Firmware you need to get a CoproSerialPort from CoproManager, then you will be available to use the CoproSerialPort API has defined above :
ICoproSerialPort mCoproSerialPort = mCoproManager.getSerialPort();
The serial communication is possible only if a Firmware is running. Make sure to close the serial communication when you stop a firmware and open it when you start one.