| Coming soon |
This article explains what is UART and how to use it through examples
1. What is a Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)?
The universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver transmitter (USART/UART) offers a flexible means of Full-duplex data exchange with external equipment requiring an industry standard NRZ asynchronous serial data format. The USART offers a very wide range of baud rates using a programmable baud rate generator. It supports synchronous one-way communication and Half-duplex Single-wire communication, as well as multiprocessor communications. It also supports the LIN (Local Interconnect Network), Smartcard protocol and IrDA (Infrared Data Association) SIR ENDEC specifications and Modem operations (CTS/RTS). High speed data communication is possible by using the DMA (direct memory access) for multibuffer configuration. Also, the UART can be used with interrupt.
The main of this article is to describe the UART features and precisely:
- Simple UART Communication
- UART with Interrupt
- UART with DMA
2. Objectives
Learn how to setup UART and generate code with STM32CubeIDE and how to use HAL functions.
3. Create the project in STM32CubeIDE
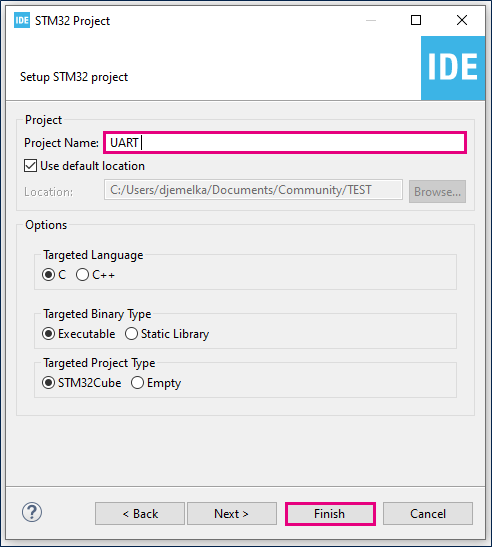
- File > New > STM32 Project in main panel.
This example uses the NUCLEO-L476RG board.
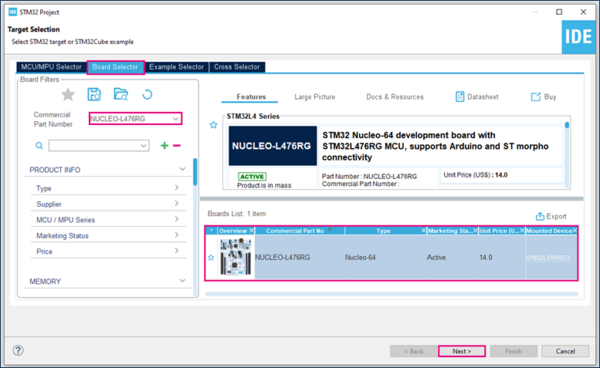
- Select NUCLEO-L476RG board using Board Selector as shown in the figure below:
In case you haven't downloaded the STM32L476 Cube library, it will be downloaded automatically. This however may take some time.
- Save the project.
- Initialize all peripherals with their default settings.
Answer “Yes” to initialize all peripherals with their default mode? Popup as below:
4. UART Configuration
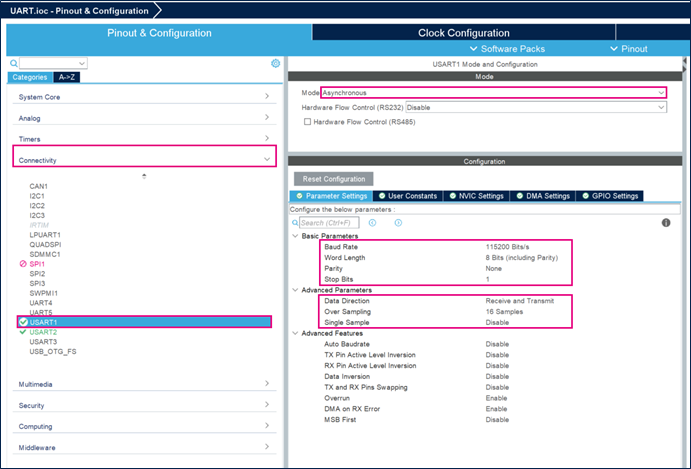
- Set USART1 mode to Asynchronous mode
- Set Parameter Settings as shown in the figure below:
5. GPIO Configuration
To select the correct GPIOs pins, it is necessary to refer to the datasheet. Look for the alternate function table.
STM32L476 USART1 uses PA9 for transmission (TX) and PA10 for reception (RX) as shown below:
File:STM32L476 datasheet table.png
PA9 and PA10 should be configured as follows.
File:GPIO configuration.png
6. Generate source code
Click "Ctrl+S" to generate the project
6.1. Simple UART Communication
6.1.1. Hardware preparation
You will need a pair of boards, one will act as transmitter and the other as receiver.
The two boards should be connected as follows:
- Board 1 RX connected to board 2 TX
- Board 1 TX connected to board 2 RX
- Board 1 GND connected to board 2 GND
File:Hardware USART communication.png
6.1.2. Edit main.c
- definite buffer
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint8_t tx_buff[]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t rx_buff[10];
/* USER CODE END 0 */
- Transmit and Receive data
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_UART_Receive(&huart1,rx_buff,10,1000);
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1,tx_buff,10,1000);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
- Complete callback
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP(); //check if we receive all data
}
void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP(); //check if we transmit all data
}
/* USER CODE END 4 */
- Compile and flash
First of all, build your project ![]() .
.
Then debug it ![]() when you used only NUCLEO-L476RG.
when you used only NUCLEO-L476RG.
Connect the second NUCLEO-L476RG.
Click Reset button of board 1 then Click Reset button of board 2 and finally Click Reset button of board 1.
Click on Resume button ![]() to execute the code.
Click on suspend
to execute the code.
Click on suspend ![]() to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
File:Expressions show UART.png
6.2. UART with Interrupt
6.2.1. Hardware preparation
Connect RX to TX to create a loopback as shown in the figure below:
File:Hardware USART Interrupt.png
6.2.2. Configure UART Interrupt
Open the UART.ioc file in the STM32Cube IDE project as shown in the figure below:
Enable the USART2 global interrupt.
File:Configure UART Interrupt.png
6.2.3. Generate project and edit main.c
Click "Ctrl+S" to generate the project
- Definite buffer
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint8_t tx_buff[]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t rx_buff[10];
/* USER CODE END 0 */
- Send and Receive data
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1,rx_buff,10);
HAL_UART_Transmit_IT(&huart1,tx_buff,10);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
- Complete callback
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP();//check if we receive all data
}
void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP();//check if we transmit all data
}
/* USER CODE END 4 */
- Compile and flash
First of all, build your project ![]()
Then debug it ![]()
Click on Resume button ![]() to execute the code.
Click on suspend
to execute the code.
Click on suspend ![]() to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
File:Expressions show view UART with Interrupt.png
6.3. UART with DMA
6.3.1. Hardware preparation
Connect Rx with Tx to create hardware loopback as already mentioned in 6.2.1 Hardware preparation section.
6.3.2. Configure UART DMA
Open the UART.ioc file in the STM32CubeIDE project as shown in the figure below:
Add the DMA request as shown in the figure below:
File:Configure UART DMA.png
6.3.3. Generate project and edit main.c
Click "Ctrl+S" to generate the project
- Definite buffer
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint8_t tx_buff[]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
uint8_t rx_buff[10];
/* USER CODE END 0 */
- Send and Receive data
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1,rx_buff,10);
HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1,tx_buff,10);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
- Complete callback
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP();//check if we receive all data
}
void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
__NOP();//check if we transmit all data
}
- Compile and flash
First of all, build your project ![]()
Then debug it ![]()
Click on Resume button ![]() to execute the code.
Click on suspend
to execute the code.
Click on suspend ![]() to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
to show the expressions in the tx_buff and rx_buff.
File:Expressions show view UART with DMA.png
[[category:Getting_started_with_STM32_system_peripherals | 35]]