This article explains what WDG is and how to use it through examples.
1. What is a HRTIM ?
HRTIM stands for High Resolution Timer. HRTIM is a highly accurate timer which can generate complex waveforms such as PWM, phase-shifted... It's made up of six 16-bits up counter and a master timer with highly very fine timing resolution (184 ps on the STM32G4 series). They can be used independently or synchronized. HRTIM applications are various : from digital power conversion (digital SMPS, solar converters, motor control) to also for general-purpose applications.
1.1. Counter operating modes
Up-counters can operate in three modes :
- Continuous (also called Free-running) : it rolls over to zero when it exceeds the value programmed in the period register (HRTIM_PERxR)
- Single shot Retriggerable : It starts with a reset event occurs and stops when it reaches the period value (HRTIM_PERxR). In this mode, the user can reset at any time.
- Single shot Non-Retriggerable : Same principle as Single shot Retriggerable but in this mode, reset events are discarded if they occur before the end of counting phase.
1.2. Block diagram overview
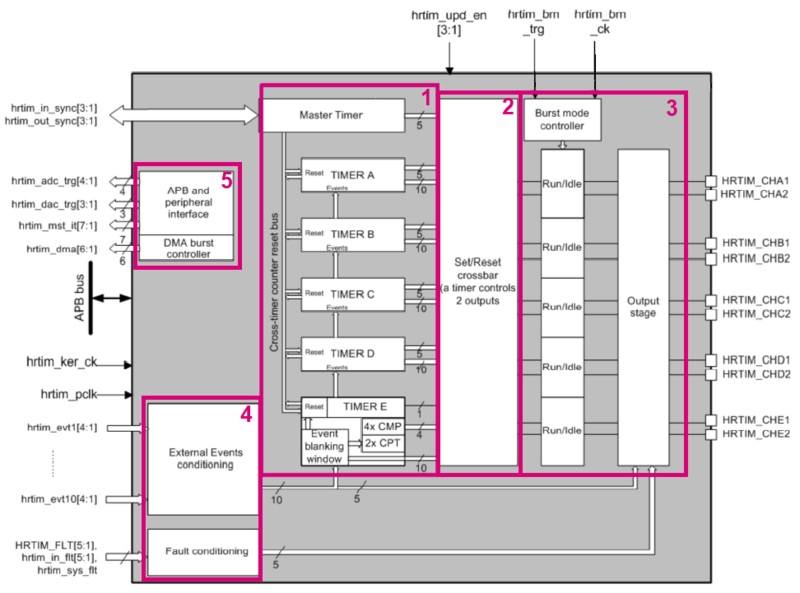
As we can see on the figure below, the HRTIM have a modular architecture. Let's have a look at each block :
- Block 1 Timing units are six 16-bit up-counter with a programmable overflow, 2 capture registers and 4 compare registers. Compare event can be generated when the counter is equal to the compare value (HRTIM_CMP1xR).
- Block 2 Set/Reset Crossbar allows to have the output pairs controlled not only by related timing unit but by external event and other timers.
- Block 3 Output stage manage pair of outputs with any kind of logic (polarity, safe states, asynchronous fault protection...).
- Block 4 Input block includes ten external events, five fault signals (protect the power stages and shutdown PWM outputs).
- Block 5 Interface part link the HRTimer with other timers, DMA, ADC and DAC with internal STM32 connections.
2. Configure the HRTIM to generate a simple PWM
2.1. Objective
- In this project, you will learn how to setup HRTIM in STM32CubeIDE
- How to Generate Code in STM32CubeIDE and use HAL functions
- Provide a simple application to create a single PWM
- Configure timer in continuous mode, crossbar and output stage
2.2. Creating the project in STM32CubeIDE
- File > New > STM32 Project in main panel.
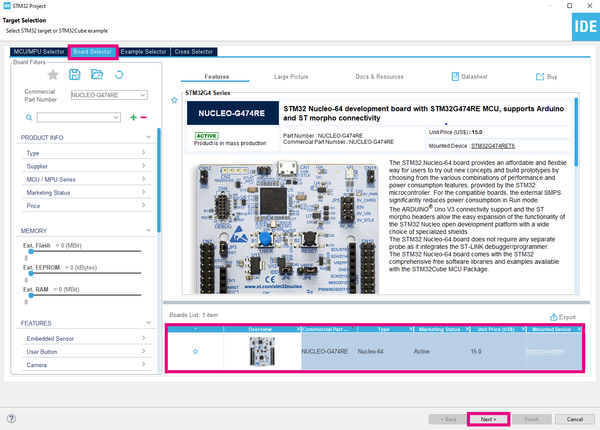
Select the NUCLEO-G474RE board using the Board Selector, as shown in the figure below:
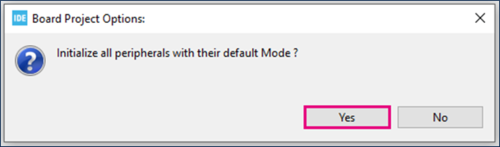
Answer “Yes” to initialize all peripherals with their default mode? Popup as below:
- If not downloaded previously, the download of the STM32CubeG4 Cube library starts automatically. The download may take some time.
- Save the project.
2.3. Configure HRTIM
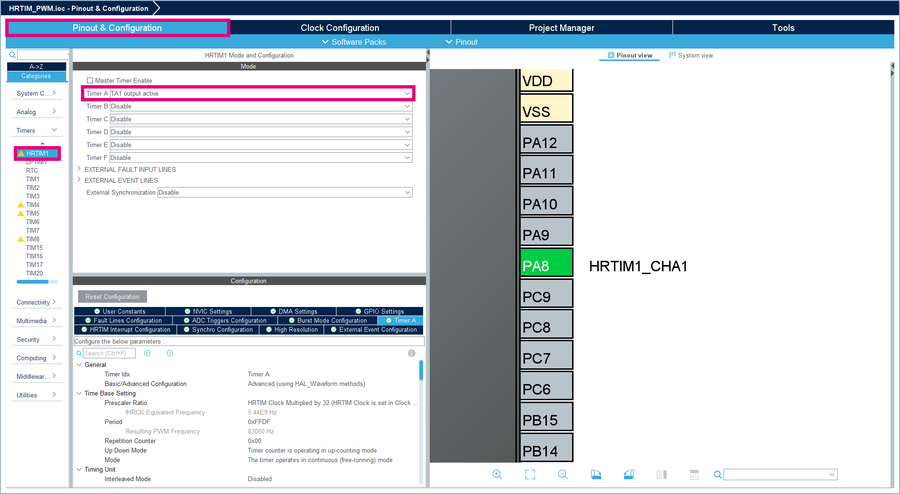
- In the Pinout & Configuration window, select HRTIM1 and choose TA1 output active.
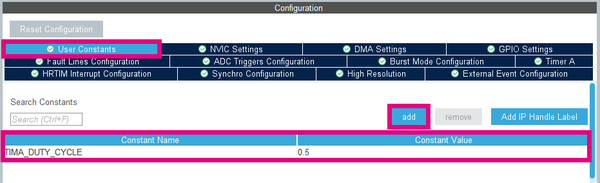
- In User Constants, click on add and enter this constant name TIMA_DUTY_CYCLE with the value 0.5.
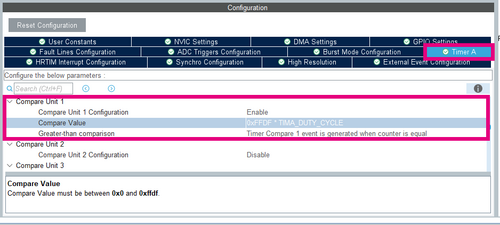
- In Timer A, in section Time Base Setting ,
- Scroll down until Compare Unit 1, and fill as below
- Scroll down until Output 1 Configuration
2.4. Generate project and edit main.c
The easiest way to generate the code is to save your current project : Ctrl + S