1. Article purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the ETZPC peripheral and its main features
- indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- explain how it can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- explain how to configure the ETZPC peripheral if necessary.
2. Peripheral overview[edit source]
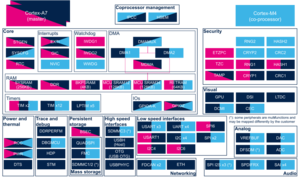
The ETZPC peripheral is used to configure TrustZone security in a STM32 MPU device. That STM32 MPU device has bus masters and slaves with programmable-security attributes (securable resources) such as:
- on-chip RAM/ROM with programmable secure region size
- AHB and APB peripherals to be made secure
- AHB masters to be granted secure rights
The ETZPC peripheral also allows peripheral isolation. With MCU isolation, some peripherals can be assigned to Cortex-M4 context execution only. Those peripherals will not be accessible for Cortex-A7 contexts (secure and non-secure).
2.1. Features[edit source]
Refer to the STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features. Refer also to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
2.2. Security support[edit source]
The ETZPC is a secure peripheral.
3. Peripheral usage and associated software[edit source]
3.1. Boot time[edit source]
The ETZPC is configured at boot time to setup the platform security.
3.2. Runtime[edit source]
3.2.1. Overview[edit source]
The ETZPC is a system peripheral and is controlled by the Arm® Cortex®-A7 secure.
3.2.2. Software frameworks[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Security | ETZPC | TF-A(BL32) or OP-TEE ETZPC driver Read/Write access |
U-Boot Read only access |
Resource Manager Utility Read only access |
Configuration made by A7 secure. U-Boot updates the Linux device tree. |
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit source]
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in a secure context.
This configuration is done in TF-A(BL32) or OP-TEE, through device tree.
Refer to ETZPC device tree configuration.
3.2.4. Peripheral assignment[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Security | ETZPC | ETZPC | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
4. How to go further[edit source]
The ETZPC is an STMicroelectronics extension of the Arm® peripheral: TrustZone Protection Controller[1].
5. References[edit source]
.
.