Registered User (Add U-boot as runtime and removal of _ in the PMIC page link (related to boot time)) |
Registered User mNo edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude>{{ApplicableFor | |||
|MPUs list=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x | |||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x,STM32MP15x | |||
}}</noinclude> | |||
== Article purpose == | == Article purpose == | ||
The purpose of this article is to: | The purpose of this article is to: | ||
* briefly introduce the I2C peripheral and its main features | * briefly introduce the I2C peripheral and its main features | ||
* indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | * indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block | ||
* explain how each instance can be allocated to the | * explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components | ||
* explain, when necessary, how to configure the I2C peripheral. | * explain, when necessary, how to configure the I2C peripheral. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
** Alert | ** Alert | ||
Refer to the [[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP15 reference manuals]] for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented. | Refer to the [[STM32MP13 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP13 reference manuals]] or [[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP15 reference manuals]] for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented. | ||
===Security support=== | ===Security support=== | ||
* There are six I2C instances | ==== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}} ==== | ||
There are five I2C instances: | |||
*I2C instances 1 and 2 are '''non-secure'''. | |||
*I2C instances 3, 4 and 5 can be '''secure''' (under [[ETZPC_internal_peripheral|ETZPC]] control). | |||
==== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} ==== | |||
There are six I2C instances: | |||
*I2C instances 1, 2, 3 and 5 are '''non-secure'''. | |||
*I2C instances 4 and 6 can be '''secure''' (under [[ETZPC_internal_peripheral|ETZPC]] control). | |||
==Peripheral usage and associated software== | ==Peripheral usage and associated software== | ||
===Boot time=== | ===Boot time=== | ||
The I2C peripheral is usually not used at boot time. But it may be used by the SSBL and/or FSBL (see [[Boot | The I2C peripheral is usually not used at boot time. But it may be used by the SSBL and/or FSBL (see [[Boot chain overview]]), for example, to configure a PMIC (see [[PMIC hardware components]]), or to access data stored in an external EEPROM. | ||
===Runtime=== | ===Runtime=== | ||
====Overview==== | ====Overview==== | ||
Secure instances can be allocated to: | |||
* the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7 secure core to be controlled in OP-TEE by the [[OP-TEE_overview|OP-TEE I2C driver]] | * the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7 secure core to be controlled in OP-TEE by the [[OP-TEE_overview|OP-TEE I2C driver]] | ||
All I2C instances can be allocated to: | All I2C instances can be allocated to: | ||
* the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in U-Boot or Linux<sup>®</sup> by the [[I2C overview|I2C framework]] | * the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in U-Boot or Linux<sup>®</sup> by the [[I2C overview|I2C framework]] | ||
On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}}, all but I2C4&6 instances can be allocated to: | |||
* the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M4 to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by [[STM32CubeMP1 architecture|STM32Cube I2C driver]] | * the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M4 to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by [[STM32CubeMP1 architecture|STM32Cube I2C driver]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 59: | ||
====Software frameworks==== | ====Software frameworks==== | ||
{{: | ===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}} ===== | ||
{{:STM32MP13 internal peripherals software table template}} | |||
| Low speed interface | |||
| [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | |||
| [[OP-TEE_overview|OP-TEE I2C driver]] | |||
| [[I2C overview| I2C Engine framework]] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} ===== | |||
{{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_software_table_template}} | |||
| Low speed interface | | Low speed interface | ||
| [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | | [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 87: | ||
====Peripheral assignment==== | ====Peripheral assignment==== | ||
{{: | ===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=13}} ===== | ||
< | {{:STM32MP13_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | ||
<section begin=stm32mp13 /> | |||
| rowspan="5" | Low speed interface | |||
| rowspan="5" | [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | |||
| I2C1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| I2C2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| I2C3 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| Assignment (single choice) | |||
|- | |||
| I2C4 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| Assignment (single choice) | |||
|- | |||
| I2C5 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| Assignment (single choice) | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp13 /> | |||
|} | |||
===== On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}} ===== | |||
{{:STM32MP15_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp15 /> | |||
| rowspan="6" | Low speed interface | | rowspan="6" | Low speed interface | ||
| rowspan="6" | [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | | rowspan="6" | [[I2C internal peripheral|I2C]] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 146: | ||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | | <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | ||
| | | | ||
| Assignment (single choice). <br />Used for PMIC control on [[:Category: | | Assignment (single choice). <br />Used for PMIC control on [[:Category:STM32 MPU boards|ST boards]]. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| I2C5 | | I2C5 | ||
| Line 108: | Line 160: | ||
| Assignment (single choice) | | Assignment (single choice) | ||
|- | |- | ||
</ | <section end=stm32mp15 /> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 18 January 2023
1. Article purpose[edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the I2C peripheral and its main features
- indicate the level of security supported by this hardware block
- explain how each instance can be allocated to the runtime contexts and linked to the corresponding software components
- explain, when necessary, how to configure the I2C peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit source]
The I2C bus interface serves as an interface between the microcontroller and the serial I2C bus.
It provides multi-master capability, and controls all I2C bus-specific sequencing, protocol, arbitration and timing.
The I2C controller allows to be a slave as well if need be.
It is also SMBus 2.0 compatible.
For more information about I2C please refer to this link: I2C wikipedia[1] or i2c-bus.org[2]
For more information about SMBus please refer to this link: SMBus wikipedia[3] or i2c-bus.org[4]
2.1. Features[edit source]
Here are the main features:
- Multi-master
- Standard (100 KHz) and fast speed modes (400 KHz and Plus 1 MHz)
- I2C 10-bit address
- I2C slave capabilities (programmable I2C address)
- DMA capabilities
- SMBus 2.0 compatible
- Standard bus protocol (quick command; byte, word, block read/write)
- Host notification
- Alert
Refer to the STM32MP13 reference manuals or STM32MP15 reference manuals for the complete list of features, and to the software components, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
2.2. Security support[edit source]
2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
There are five I2C instances:
- I2C instances 1 and 2 are non-secure.
- I2C instances 3, 4 and 5 can be secure (under ETZPC control).
2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
There are six I2C instances:
- I2C instances 1, 2, 3 and 5 are non-secure.
- I2C instances 4 and 6 can be secure (under ETZPC control).
3. Peripheral usage and associated software[edit source]
3.1. Boot time[edit source]
The I2C peripheral is usually not used at boot time. But it may be used by the SSBL and/or FSBL (see Boot chain overview), for example, to configure a PMIC (see PMIC hardware components), or to access data stored in an external EEPROM.
3.2. Runtime[edit source]
3.2.1. Overview[edit source]
Secure instances can be allocated to:
- the Arm® Cortex®-A7 secure core to be controlled in OP-TEE by the OP-TEE I2C driver
All I2C instances can be allocated to:
- the Arm® Cortex®-A7 non-secure core to be controlled in U-Boot or Linux® by the I2C framework
On STM32MP15x lines ![]() , all but I2C4&6 instances can be allocated to:
, all but I2C4&6 instances can be allocated to:
- the Arm® Cortex®-M4 to be controlled in STM32Cube MPU Package by STM32Cube I2C driver
Chapter Peripheral assignment describes which peripheral instance can be assigned to which context.
3.2.2. Software frameworks[edit source]
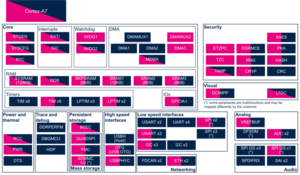
3.2.2.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | |||
| Low speed interface | I2C | OP-TEE I2C driver | I2C Engine framework | |
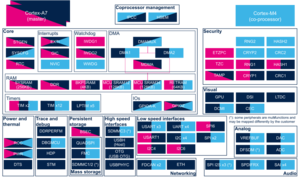
3.2.2.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
| Domain | Peripheral | Software components | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP-TEE | Linux | STM32Cube | |||
| Low speed interface | I2C | OP-TEE I2C driver | I2C Engine framework | STM32Cube I2C driver | |
3.2.3. Peripheral configuration[edit source]
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context to which the peripheral is assigned. The configuration can be done alone via the STM32CubeMX tool for all internal peripherals, and then manually completed (particularly for external peripherals), according to the information given in the corresponding software framework article.
For Linux® kernel configuration, please refer to I2C configuration.
Please refer to I2C device tree configuration for detailed information on how to configure I2C peripherals.
3.2.4. Peripheral assignment[edit source]
3.2.4.1. On STM32MP13x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) | |||
| Low speed interface | I2C | I2C1 | ☐ | ||
| I2C2 | ☐ | ||||
| I2C3 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | ||
| I2C4 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | ||
| I2C5 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | ||
3.2.4.2. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit source]
[edit source]
Click on the right to expand the legend...
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Low speed interface | I2C | I2C1 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |
| I2C2 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |||
| I2C3 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |||
| I2C4 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice). Used for PMIC control on ST boards. | |||
| I2C5 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |||
| I2C6 | ☐ | ☐ | Assignment (single choice) | |||
4. References[edit source]