Registered User mNo edit summary |
Registered User mNo edit summary Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude>{{ApplicableFor | <noinclude>{{ApplicableFor | ||
|MPUs list=STM32MP15x | |MPUs list=STM32MP15x, STM32MP25x | ||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x | |MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x, STM32MP25x | ||
}}</noinclude> | }}</noinclude> | ||
==Article purpose== | ==Article purpose== | ||
The inter-processor communication controller | The purpose of this article is to: | ||
* briefly introduce the IPCC peripheral and its main features, | |||
* indicate the peripheral instances assignment at boot time and their assignment at runtime (including whether instances can be allocated to secure contexts), | |||
* list the software frameworks and drivers managing the peripheral, | |||
* explain how to configure the peripheral. | |||
==Peripheral overview== | |||
The '''IPCC''' (inter-processor communication controller) peripheral is used to exchange data between two processors. | |||
It provides a non blocking signaling mechanism to post and retrieve information in an atomic way. | It provides a non blocking signaling mechanism to post and retrieve information in an atomic way. | ||
Note that shared memory buffers are allocated in the [[STM32MP15 MCU SRAM internal memory|MCU SRAM]], which is not part of the IPCC block. | Note that shared memory buffers are allocated in the [[STM32MP15 MCU SRAM internal memory|MCU SRAM]], which is not part of the IPCC block. | ||
The IPCC peripheral provides a hardware support to manage inter-processor communication between two processor instances. Each processor owns specific register bank and interrupts. | |||
The | |||
The IPCC provides the signaling for ''' six bidirectional''' channels. <br> | The IPCC provides the signaling for ''' six bidirectional''' channels. <br> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 43: | ||
** Any processor can post asynchronously a message by setting the subchannel status flag to occupied. The "receiver" processor clears the flag when the message is treated. This mode can be considered as a combination of two simplex modes on a given channel. | ** Any processor can post asynchronously a message by setting the subchannel status flag to occupied. The "receiver" processor clears the flag when the message is treated. This mode can be considered as a combination of two simplex modes on a given channel. | ||
Refer to the reference manuals<ref name="stm32mp157-Reference-manual">[[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals| STM32MP15 reference manuals]]</ref><ref name="stm32mp257-Reference-manual">[[STM32MP25 resources#Reference manuals| STM32MP25 reference manuals]]</ref> for the complete list of features, and to the software frameworks and drivers, introduced below, to see which features are implemented. | |||
Refer to [[STM32MP15 resources#Reference manuals|STM32MP15 reference manuals]] for the complete features | |||
==Peripheral usage== | |||
This chapter is applicable in the scope of the '''OpenSTLinux BSP''' running on the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A processor(s), and the '''STM32CubeMPU Package''' running on the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M processor. | |||
===Processor interface assignment === | |||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}}==== | |||
STMicroelectronics distribution uses the IPCC peripheral for inter-processor communication with the following configuration: | |||
* The IPCC processor 1 interface (PROC1)is assigned to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A7, non-secure context. | |||
* The IPCC processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assigned to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M4 context. | |||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=25}}==== | |||
* The IPCC1 peripheral is dedicated for the communication between the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A35 and the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M33. The interfaces are assigned in hardware to the Cortexes : | |||
** The processor 1 interface (PROC1) is assigned by hardware to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A35, secure and non-secure context. | |||
** The processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assigned by hardware to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M33, secure and non-secure context. | |||
* The IPCC2 peripheral is dedicated for the communication between the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A35 or the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M33 and the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M0+. | |||
** The processor 1 interface (PROC1) is assigned by hardware to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M0+. | |||
** The processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assignable to the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-A35 or the Arm<sup>®</sup> Cortex<sup>®</sup>-M33, secure and non-secure context. | |||
=== | ===Boot time assignment=== | ||
The IPCC is | ====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}}==== | ||
The IPCC peripheral is not used at boot time. | |||
== | ====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=25}}==== | ||
=== | {{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp2_a35_boottime}} | ||
The | <section begin=stm32mp25_a35_boottime /> | ||
| rowspan="2" | Coprocessor | |||
| rowspan="2" | [[IPCC internal peripheral | IPCC]] <span title="RIF-aware internal peripheral"><sup>[[File:Info.png|15px|link=]]</sup></span> | |||
| IPCC1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the [[IPCC internal peripheral#stm32mp2_IPCC1_a35_boottime_rif | boot time allocation per feature]] | |||
|- | |||
| IPCC2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the [[IPCC internal peripheral#stm32mp2_IPCC2_a35_boottime_rif | boot time allocation per feature]] | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp25_a35_boottime /> | |||
|} | |||
<BR/> | |||
<span id="stm32mp2_IPCC1_a35_boottime_rif"></span>The below table shows the possible boot time allocations for the features of the '''IPCC1''' instance. | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp2_a35_boottime_rif}} | |||
| PROC1 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 5 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 6 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 7 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 8 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 9 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 10 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 11 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 12 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 13 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 14 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 15 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 16 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 5 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 6 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 7 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 8 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 9 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 10 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 11 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 12 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 13 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 14 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 15 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 16 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
<span id="stm32mp2_IPCC2_a35_boottime_rif"></span>The below table shows the possible boot time allocations for the features of the '''IPCC2''' instance. | |||
=== | {{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp2_a35_boottime_rif}} | ||
== | | PROC1 channel 1 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
< | | | ||
|- | |||
< | | PROC1 channel 2 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral but not supported" style="font-size:21px">⬚</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==== | ===Runtime assignment=== | ||
==== | It does not make sense to allocate the IPCC to a single runtime execution context. It is consequently enabled by default for both cores in the [[STM32CubeMX]]. | ||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=15}}==== | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP1_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp15_runtime}} | |||
<section begin=stm32mp15_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="1" | Coprocessor | |||
| rowspan="1" | [[IPCC internal peripheral|IPCC]] | |||
| IPCC | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| Shared (none or both) | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp15_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
{| class="st-table" style="text-align: center;" width=80% | {| class="st-table" style="text-align: center;" width=80% | ||
! rowspan="2" style="text-align: center; width:10%;" | '''Processor interface''' | ! rowspan="2" style="text-align: center; width:10%;" | '''Processor interface''' | ||
! colspan="2" style="text-align: center; width:38%;" | '''Context''' | |||
! colspan="2" style="text-align: center; width:38%;" | '''Comment''' | |||
|- | |||
| style="color: white; background: {{STDarkBlue}}; width:19%;" | '''Cortex-A7 non-secure''' <br /> (Linux) | |||
| style="color: white; background: {{STLightBlue}}; width:19%;" | '''Cortex-M4''' <br /> (STM32Cube) | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 1 | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | | <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑ | ||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | * The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | ||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 2 | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 3 | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|Simplex communication used by the [[Linux remoteproc framework overview |remote framework]] to request the Cortex-M4 to shutdown. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 5 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 6 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|Simplex communication used by the [[Linux remoteproc framework overview |remote framework]] to request the Cortex-M4 to shutdown. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 5 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 6 | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
====On {{MicroprocessorDevice | device=25}}==== | |||
{| | {{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp25_runtime}} | ||
<section begin=stm32mp25_a35_runtime /> | |||
| rowspan="2" | Coprocessor | |||
| rowspan="2" | [[IPCC internal peripheral | IPCC]] <span title="RIF-aware internal peripheral"><sup>[[File:Info.png|15px|link=]]</sup></span> | |||
| IPCC1 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the [[IPCC internal peripheral#stm32mp25_IPCC1_a35_runtime_rif | runtime allocation per feature]] | |||
|- | |||
| IPCC2 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the [[IPCC internal peripheral#stm32mp25_IPCC2_a35_runtime_rif | runtime allocation per feature]] | |||
|- | |||
<section end=stm32mp25_a35_runtime /> | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
<span id="stm32mp25_IPCC1_a35_runtime_rif"></span>The below table shows the possible runtime allocations for the features of the '''IPCC1''' instance. | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp25_runtime_rif}} | |||
| PROC1 channel 1 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | * The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | ||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | * The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | ||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 2 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | | | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | * The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | ||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | * The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | ||
==== | |- | ||
| PROC1 channel 3 | |||
{{: | | <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | ||
< | | <span title="assigned peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|Simplex communication used by the [[Linux remoteproc framework overview | remoteproc framework]] to request the Cortex-M33 to shutdown. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
</ | | | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 5 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 6 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 7 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 8 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 9 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 10 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 11 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 12 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 13 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"| Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 14 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"| Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 15 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"| Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 16 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"| Allocated to secure world but not used. {{ReviewsComments | [[User:Valentin Caron|Valentin Caron]] ([[User talk:Valentin Caron|talk]]) 15:29, 11 June 2024 (CEST) - Should become "Used by [[SCMI overview|SCMI]]." and affected to OP-TEE for v6.0}} | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|[[Coprocessor_management_overview#Inter_processor_communication |RPMsg]] transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M | |||
Full-duplex communication: | |||
* The Cortex-A core uses this channel to indicate that a message is available | |||
* The Cortex-M core uses this channel to indicate that the message is treated | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☑</span> | |||
| | |||
| style="text-align: left;"|Simplex communication used by the [[Linux remoteproc framework overview| remoteproc framework]] to request the Cortex-M33 to shutdown. | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 5 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 6 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 7 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 8 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 9 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 10 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 11 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 12 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 13 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 14 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 15 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 16 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| {{ReviewsComments | [[User:Valentin Caron|Valentin Caron]] ([[User talk:Valentin Caron|talk]]) 15:29, 11 June 2024 (CEST) - Should become "Used by [[SCMI overview|SCMI]]." and affected to M33 Cube for v6.0}} | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br/> | |||
<span id="stm32mp25_IPCC2_a35_runtime_rif"></span>The below table shows the possible runtime allocations for the features of the '''IPCC2''' instance. | |||
{{#lst:STM32MP2_internal_peripherals_assignment_table_template|stm32mp25_runtime_rif}} | |||
| PROC1 channel 1 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 2 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 3 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span><sup>OP-TEE</sup> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| <span title="assignable peripheral" style="font-size:21px">☐</span> | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Software frameworks and drivers== | |||
Below are listed the software frameworks and drivers managing the IPCC peripheral for the embedded software components listed in the above tables. | |||
* '''Linux<sup>®</sup>''': [[Linux Mailbox framework overview|mailbox framework]] | |||
< | * '''STM32Cube''': [[STM32CubeMP15 Package architecture|IPCC HAL driver]] and {{CodeSource | STM32CubeMP1 | Drivers/STM32MP1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/stm32mp1xx_hal_ipcc.h | header file of IPCC HAL module}} | ||
==How to assign and configure the peripheral== | |||
The peripheral assignment can be done via the [[STM32CubeMX]] graphical tool (and manually completed if needed).<br /> | |||
This tool also helps to configure the peripheral: | |||
* partial device trees (pin control and clock tree) generation for the OpenSTLinux software components, | |||
* HAL initialization code generation for the STM32CubeMPU Package. | |||
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context in which the peripheral is assigned.The IPCC peripheral is shared between the Arm Cortex-A and Cortex-M contexts. A particular attention must therefore be paid to have a complementary configuration on both contexts. | |||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
[[Category:Coprocessor management peripherals]] | |||
{{ArticleBasedOnModel | Internal peripheral article model}} | {{ArticleBasedOnModel | Internal peripheral article model}} | ||
{{PublicationRequestId | 10289 | 2019-01-14 | AnneJ}} | {{PublicationRequestId | 10289 | 2019-01-14 | AnneJ}} | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:48, 24 July 2024
1. Article purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this article is to:
- briefly introduce the IPCC peripheral and its main features,
- indicate the peripheral instances assignment at boot time and their assignment at runtime (including whether instances can be allocated to secure contexts),
- list the software frameworks and drivers managing the peripheral,
- explain how to configure the peripheral.
2. Peripheral overview[edit | edit source]
The IPCC (inter-processor communication controller) peripheral is used to exchange data between two processors. It provides a non blocking signaling mechanism to post and retrieve information in an atomic way. Note that shared memory buffers are allocated in the MCU SRAM, which is not part of the IPCC block.
The IPCC peripheral provides a hardware support to manage inter-processor communication between two processor instances. Each processor owns specific register bank and interrupts.
The IPCC provides the signaling for six bidirectional channels.
Each channel is divided into two subchannels that offer a unidirectional signaling from the "sender" processor to the "receiver" processor:
- P1_TO_P2 subchannel
- P2_TO_P1 subchannel
A subchannel consists in:
- One flag that toggles between occupied and free: the flag is set to occupied by the "sender" processor and cleared by the "receiver" processor.
- Two associated interrupts (shared with the other channels):
- RXO: RX channel occupied, connected to the "receiver" processor.
- TXF: TX channel free, connected to the "sender" processor.
- Two associated interrupt masks multiplexing channel IRQs.
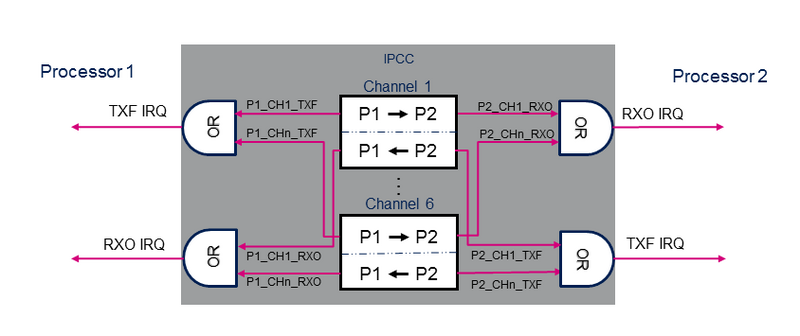
The IPCC supports the following channel operating modes:
- Simplex communication mode:
- Only one subchannel is used.
- Unidirectional messages: once the "sender" processor has posted the communication data in the memory, it sets the channel status flag to occupied. The "receiver" processor clears the flag when the message is treated.
- Half-duplex communication mode:
- Only one subchannel is used.
- Bidirectional messages: once the "sender" processor has posted the communication data in the memory, it sets the channel status flag to occupied. The "receiver" processor clears the flag when the message is treated and the response is available in shared memory.
- Full-duplex communication mode:
- The subchannels are used in Asynchronous mode.
- Any processor can post asynchronously a message by setting the subchannel status flag to occupied. The "receiver" processor clears the flag when the message is treated. This mode can be considered as a combination of two simplex modes on a given channel.
Refer to the reference manuals[1][2] for the complete list of features, and to the software frameworks and drivers, introduced below, to see which features are implemented.
3. Peripheral usage[edit | edit source]
This chapter is applicable in the scope of the OpenSTLinux BSP running on the Arm® Cortex®-A processor(s), and the STM32CubeMPU Package running on the Arm® Cortex®-M processor.
3.1. Processor interface assignment[edit | edit source]
3.1.1. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
STMicroelectronics distribution uses the IPCC peripheral for inter-processor communication with the following configuration:
- The IPCC processor 1 interface (PROC1)is assigned to the Arm® Cortex®-A7, non-secure context.
- The IPCC processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assigned to the Arm® Cortex®-M4 context.
3.1.2. On STM32MP25x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
- The IPCC1 peripheral is dedicated for the communication between the Arm® Cortex®-A35 and the Arm® Cortex®-M33. The interfaces are assigned in hardware to the Cortexes :
- The processor 1 interface (PROC1) is assigned by hardware to the Arm® Cortex®-A35, secure and non-secure context.
- The processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assigned by hardware to the Arm® Cortex®-M33, secure and non-secure context.
- The IPCC2 peripheral is dedicated for the communication between the Arm® Cortex®-A35 or the Arm® Cortex®-M33 and the Arm® Cortex®-M0+.
- The processor 1 interface (PROC1) is assigned by hardware to the Arm® Cortex®-M0+.
- The processor 2 interface (PROC2) is assignable to the Arm® Cortex®-A35 or the Arm® Cortex®-M33, secure and non-secure context.
3.2. Boot time assignment[edit | edit source]
3.2.1. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
The IPCC peripheral is not used at boot time.
3.2.2. On STM32MP25x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
- ⬚ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given boot time context, but this configuration is not supported in STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ☐ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given boot time context.
- ☑ means that the peripheral is assigned by default to the given boot time context and that the peripheral is mandatory for the STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ✓ is used for system peripherals that cannot be unchecked because they are hardware connected in the device.
The present chapter describes STMicroelectronics recommendations or choice of implementation. Additional possibilities might be described in STM32MP25 reference manuals.
| Domain | Peripheral | Boot time allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (ROM code) |
Cortex-A35 secure (TF-A BL2) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (U-Boot) | |||
| Coprocessor | IPCC |
IPCC1 | ⬚ | ⬚ | Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the boot time allocation per feature | |
| IPCC2 | ⬚ | ⬚ | Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the boot time allocation per feature | |||
The below table shows the possible boot time allocations for the features of the IPCC1 instance.
| Feature | Boot time allocation |
Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A35 secure (ROM code) |
Cortex-A35 secure (TF-A BL2) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (U-Boot) | ||
| PROC1 channel 1 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 2 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 3 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 4 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 5 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 6 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 7 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 8 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 9 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 10 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 11 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 12 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 13 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 14 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 15 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC1 channel 16 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC2 channel 1 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 2 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 3 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 4 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 5 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 6 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 7 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 8 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 9 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 10 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 11 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 12 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 13 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 14 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 15 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 16 | ||||
The below table shows the possible boot time allocations for the features of the IPCC2 instance.
| Feature | Boot time allocation |
Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A35 secure (ROM code) |
Cortex-A35 secure (TF-A BL2) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (U-Boot) | ||
| PROC1 channel 1 | ||||
| PROC1 channel 2 | ||||
| PROC1 channel 3 | ||||
| PROC1 channel 4 | ||||
| PROC2 channel 1 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC2 channel 2 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC2 channel 3 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
| PROC2 channel 4 | ⬚ | ⬚ | ||
3.3. Runtime assignment[edit | edit source]
It does not make sense to allocate the IPCC to a single runtime execution context. It is consequently enabled by default for both cores in the STM32CubeMX.
3.3.1. On STM32MP15x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
Check boxes illustrate the possible peripheral allocations supported by STM32 MPU Embedded Software:
- ⬚ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given runtime context, but this configuration is not supported in STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ☐ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given runtime context.
- ☑ means that the peripheral is assigned by default to the given runtime context and that the peripheral is mandatory for the STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ✓ is used for system peripherals that cannot be unchecked because they are hardware connected in the device.
Refer to How to assign an internal peripheral to an execution context for more information on how to assign peripherals manually or via STM32CubeMX.
The present chapter describes STMicroelectronics recommendations or choice of implementation. Additional possiblities might be described in STM32MP15 reference manuals.
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A7 secure (OP-TEE) |
Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| Coprocessor | IPCC | IPCC | ☑ | ☑ | Shared (none or both) | |
| Processor interface | Context | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A7 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube) | |||
| PROC1 channel 1 | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A
Full-duplex communication:
| ||
| PROC1 channel 2 | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M
Full-duplex communication:
| ||
| PROC1 channel 3 | ☑ | Simplex communication used by the remote framework to request the Cortex-M4 to shutdown. | ||
| PROC1 channel 4 | ☐ | |||
| PROC1 channel 5 | ☐ | |||
| PROC1 channel 6 | ☐ | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A
Full-duplex communication:
| ||
| PROC2 channel 2 | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M
Full-duplex communication:
| ||
| PROC2 channel 3 | ☑ | Simplex communication used by the remote framework to request the Cortex-M4 to shutdown. | ||
| PROC2 channel 4 | ☐ | |||
| PROC2 channel 5 | ☐ | |||
| PROC2 channel 6 | ☐ | |||
3.3.2. On STM32MP25x lines  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Click on ![]() to expand or collapse the legend...
to expand or collapse the legend...
Check boxes illustrate the possible peripheral allocations supported by STM32 MPU Embedded Software:
- ⬚ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given runtime context, but this configuration is not supported in STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ☐ means that the peripheral can be assigned to the given runtime context.
- ☑ means that the peripheral is assigned by default to the given runtime context and that the peripheral is mandatory for the STM32 MPU Embedded Software distribution.
- ✓ is used for system peripherals that cannot be unchecked because they are hardware connected in the device.
The present chapter describes STMicroelectronics recommendations or choice of implementation. Additional possibilities might be described in STM32MP25 reference manuals.
| Domain | Peripheral | Runtime allocation | Comment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instance | Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 non-secure (STM32Cube) |
Cortex-M0+ (STM32Cube) | |||
| Coprocessor | IPCC |
IPCC1 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the runtime allocation per feature | |
| IPCC2 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | Shareable at internal peripheral level thanks to the RIF: see the runtime allocation per feature | ||
The below table shows the possible runtime allocations for the features of the IPCC1 instance.
| Feature | Runtime allocation |
Comment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 non-secure (STM32Cube) |
Cortex-M0+ (STM32Cube) | ||
| PROC1 channel 1 | ☐OP-TEE | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A
Full-duplex communication:
| |||
| PROC1 channel 2 | ☐OP-TEE | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M
Full-duplex communication:
| |||
| PROC1 channel 3 | ☐OP-TEE | ☑ | Simplex communication used by the remoteproc framework to request the Cortex-M33 to shutdown. | |||
| PROC1 channel 4 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 5 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 6 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 7 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 8 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 9 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 10 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 11 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 12 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ||||
| PROC1 channel 13 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
| PROC1 channel 14 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
| PROC1 channel 15 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
| PROC1 channel 16 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | Allocated to secure world but not used. | |||
| PROC2 channel 1 | ☐ | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-M to Cortex-A
Full-duplex communication:
| |||
| PROC2 channel 2 | ☐ | ☑ | RPMsg transfer from Cortex-A to Cortex-M
Full-duplex communication:
| |||
| PROC2 channel 3 | ☐ | ☑ | Simplex communication used by the remoteproc framework to request the Cortex-M33 to shutdown. | |||
| PROC2 channel 4 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 5 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 6 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 7 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 8 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 9 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 10 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 11 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 12 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 13 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 14 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 15 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
| PROC2 channel 16 | ☐ | ☐ | ||||
The below table shows the possible runtime allocations for the features of the IPCC2 instance.
| Feature | Runtime allocation |
Comment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A35 secure (OP-TEE / TF-A BL31) |
Cortex-A35 non-secure (Linux) |
Cortex-M33 secure (TF-M) |
Cortex-M33 non-secure (STM32Cube) |
Cortex-M0+ (STM32Cube) | ||
| PROC1 channel 1 | ☐ | |||||
| PROC1 channel 2 | ☐ | |||||
| PROC1 channel 3 | ☐ | |||||
| PROC1 channel 4 | ☐ | |||||
| PROC2 channel 1 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ||
| PROC2 channel 2 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ||
| PROC2 channel 3 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ||
| PROC2 channel 4 | ☐OP-TEE | ☐ | ☐ | ☐ | ||
4. Software frameworks and drivers[edit | edit source]
Below are listed the software frameworks and drivers managing the IPCC peripheral for the embedded software components listed in the above tables.
- Linux®: mailbox framework
- STM32Cube: IPCC HAL driver and header file of IPCC HAL module
5. How to assign and configure the peripheral[edit | edit source]
The peripheral assignment can be done via the STM32CubeMX graphical tool (and manually completed if needed).
This tool also helps to configure the peripheral:
- partial device trees (pin control and clock tree) generation for the OpenSTLinux software components,
- HAL initialization code generation for the STM32CubeMPU Package.
The configuration is applied by the firmware running in the context in which the peripheral is assigned.The IPCC peripheral is shared between the Arm Cortex-A and Cortex-M contexts. A particular attention must therefore be paid to have a complementary configuration on both contexts.