This article explains how to get started on the face recognition application.
1. Description[edit source]
The face recognition application is capable of recognizing faces of known (enrolled) users.
The application demonstrates a computer vision use case for face recognition
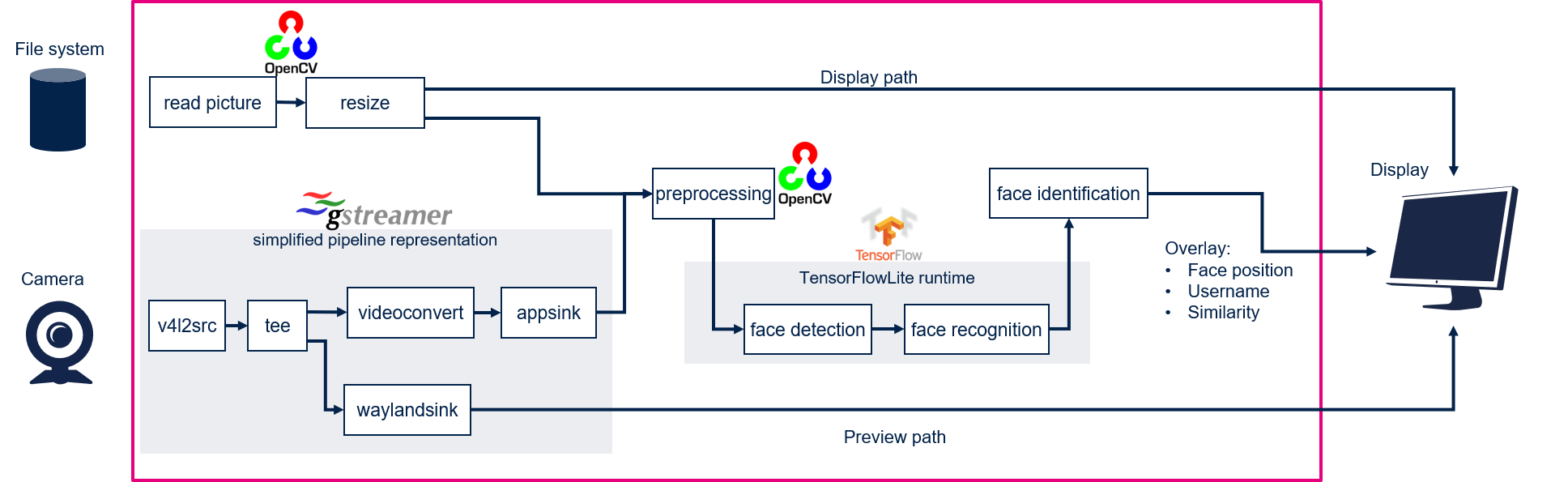
- In camera mode, frames are grabbed from a camera input (/dev/videox) and processed by two neural network models (face detection and face recognition) interpreted by the TensorFlow™ Lite[1] framework. A GStreamer pipeline is used to stream camera frames (using v4l2src), to display a preview (using waylandsink), and to execute neural network inference (using appsink).
- In file system mode, pictures are read from the file system. In that case Gstreamer pipeline is replaced by OpenCV functions.
The result of the inference is displayed using overlay generated by GtkWidgets with Cairo.
This combination is quite simple and efficient in terms of CPU overhead.
1.1. Frame processing flow[edit source]
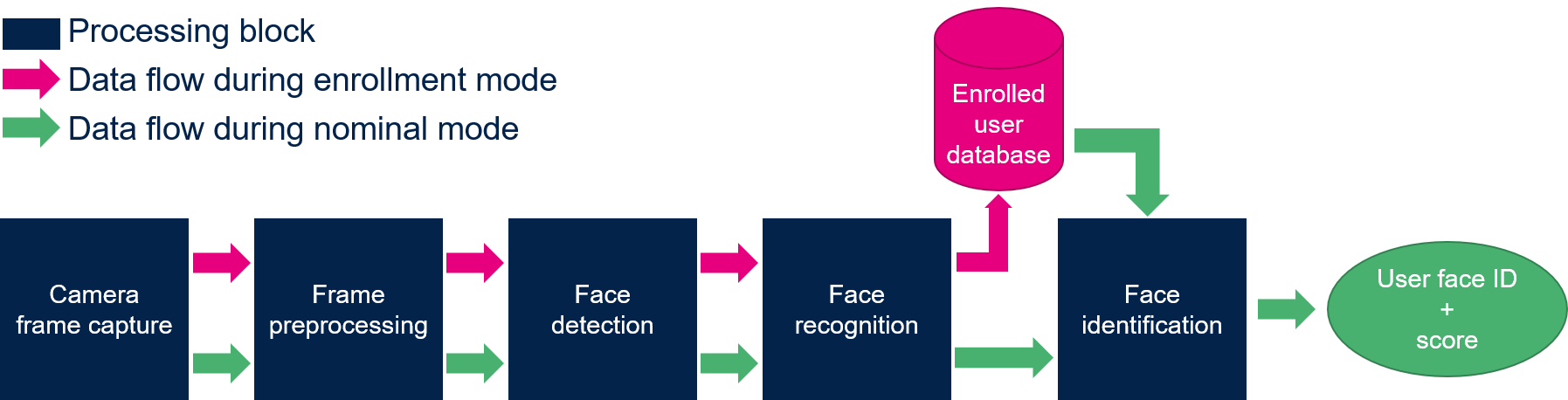
The figure below shows the different frame processing stages involved in the face recognition application:
1.1.1. Camera frame capture[edit source]
The camera frames are captured by the GStreamer pipeline in a YUV422 VGA (640 x 480) resolution (this is the default resolution of the application).
1.1.2. Frame preprocessing[edit source]
The main preprocessing stage is the pixel color format conversion from YUV422 captured frames into RGB888 frames.
1.1.3. Face detection[edit source]
The face detection block is in charge of finding the faces present in the input frame (VGA, RGB888). The output of this block is a frame of resolution 96 x 96 that contains the faces found in the input captured frame.
1.1.4. Face recognition[edit source]
The face Recognition block is in charge of extracting features from the face and computing a signature (embedding vector) corresponding to the input face.
1.1.5. Face identification[edit source]
The face identification block is in charge of computing the distance between:
- the vector produced by the face recognition block, and
- each of the vectors stored in memory (and corresponding to the enrolled faces)
The output face identification block generates the two following outputs:
- a User Face ID corresponding to the minimum distance
- a similarity score
2. Installation[edit source]
2.1. copy the face recognition binary[edit source]
scp path/to/the/deb/package/tflite-cv-apps-face-recognition-c++_1.2.0-r0.0_armhf.deb root@<board_ip_address>:/home/root
2.2. deploy the face recognition binary[edit source]
After having configured the AI OpenSTLinux package, you can deploy the application that will need to download dependencies:
cd /home/root
apt-get install ./tflite-cv-apps-face-recognition-c++_1.2.0-r0.0_armhf.deb
Then restart the demo launcher:
systemctl restart weston@root
3. How to use the application[edit source]
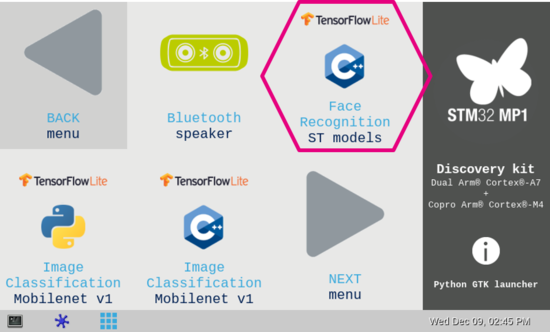
3.1. Launching via the demo launcher[edit source]
3.2. Executing with the command line[edit source]
The facereco_tfl_gst_gtk C/C++ application is located in the userfs partition:
/usr/local/demo-ai/computer-vision/tflite-face-recognition/bin/facereco_tfl_gst_gtk
It accepts the following input parameters:
Usage: ./facereco_tfl_gst_gtk [option]
--reco_simultaneous_faces: enable multiple face recognition (default is single face recognition)
--reco_threshold <val>: face recognition threshold for face similarity (default is 0.70 = 70%)
--max_db_faces <val>: maximum number of faces to be stored in the database (default is 200)
-d --database <directory path>: provide the directory where the face recognition database is stored (else default location is used)
-i --image <directory path>: image directory with images to be classified
-v --video_device <n>: video device (default /dev/video0)
--frame_width <val>: width of the camera frame (default is 640 pixels)
--frame_height <val>: height of the camera frame (default is 480 pixels)
--framerate <val>: frame rate of the camera (default is 15 fps)
--validation: enable the validation mode
--help: show this help
- launch face recognition based on the pictures located in /usr/local/demo-ai/computer-vision/tflite-face-recognition/testdata directory
/usr/local/demo-ai/computer-vision/tflite-face-recognition/bin/launch_bin_facereco_tfl_model_testdata.sh
3.3. In practice[edit source]
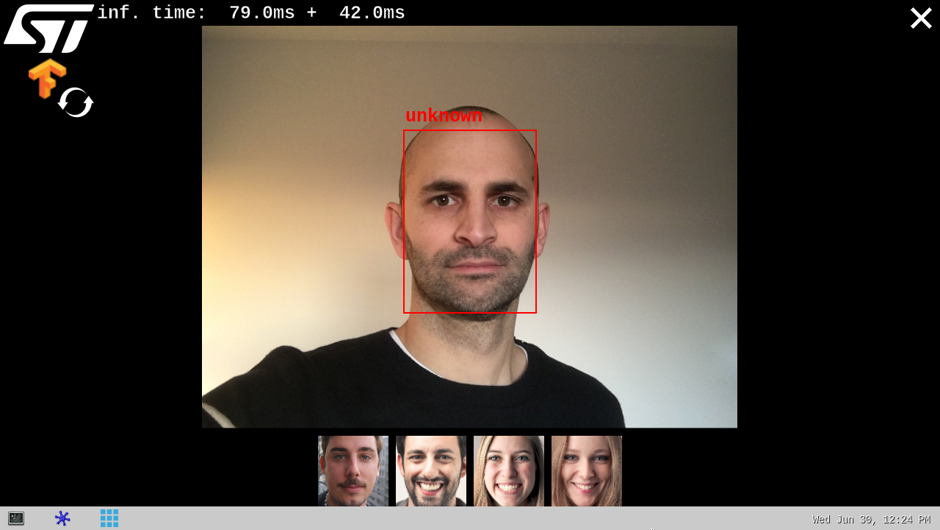
As soon as a face is detected within the camera captured frame, a rectangle box is drawn around it.
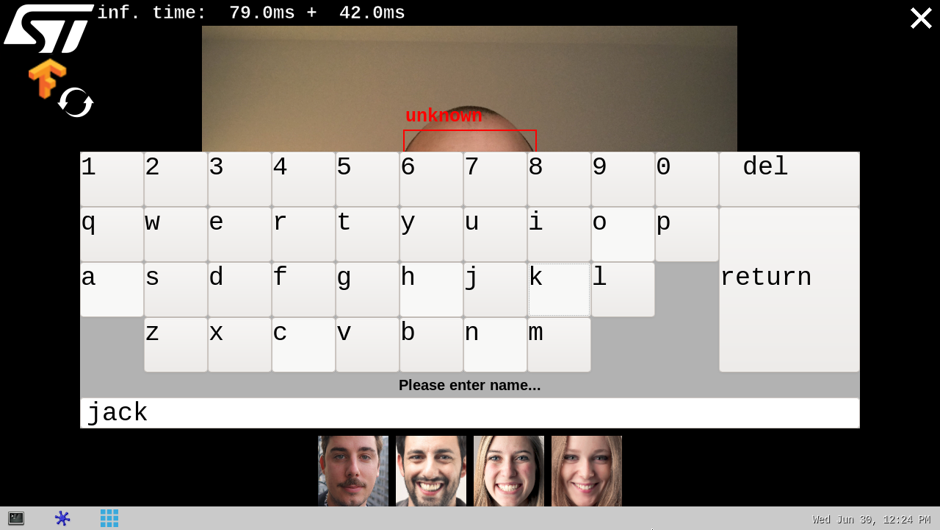
If the system is not able to match the detected face with one of the enrolled faces (either because the user's face is not yet enrolled or because the face identification similarity score is lower than the default recognition threshold), the rectangle box is drawn in red with the unknown identity.
To enroll a new user, simply touch (or click) inside the red rectangle. The virtual keyboard is then displayed to enter the user's name. To finish the enrollment process, simply press the return key.
Note that the face picture is captured when the red rectangle is touched (or clicked).
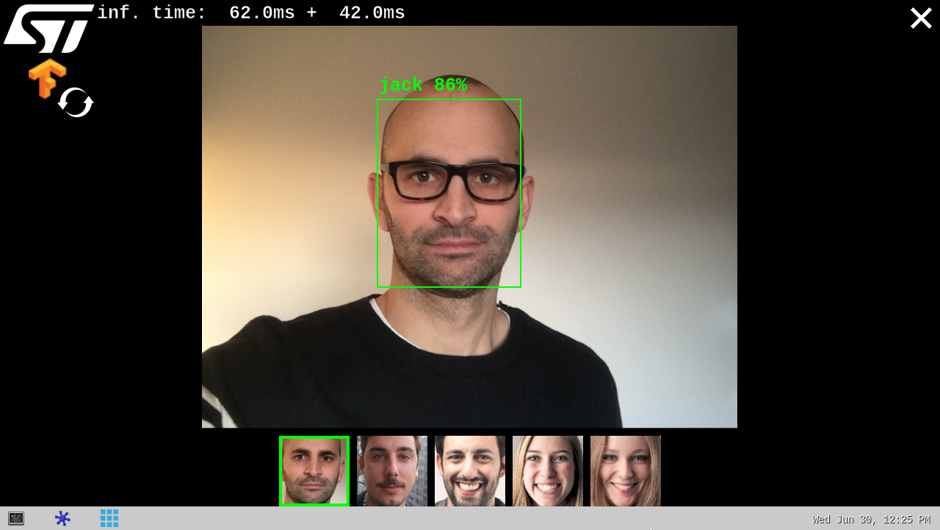
If the system is able to match the detected face with one of the enrolled faces, the rectangle box is drawn in green and the registered user's name is displayed with the similarity score expressed in percentage (%). The thumbnail (representing the user's enrolled face matching the detected face) is displayed and highlighted with a green rectangle in the banner located at the bottom of the preview.
The information displayed at the top of the display provide performance figures:
- disp. fps is the average frame rate of the preview expressed in frame per second (display when camera input mode is selected)
- inf. fps is the average frame rate for both face detection and face recognition inferences grouped together (display when camera input mode is selected)
- inf. time is the instant measure of inference time for the face detection processing and the face recognition processing.
3.4. The database[edit source]
- The database is stored in the file system:
ls -l /usr/local/demo-ai/computer-vision/tflite-face-recognition/database
total 115
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23976 Dec 16 09:37 john.png
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23336 Dec 16 09:37 jack.png
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24881 Dec 16 09:37 lily.png
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 20928 Dec 16 09:37 jen.png
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 21550 Dec 16 09:37 marc.png
Every user is represented with a .png file representing the user's registered face. The name of the .png file is the name of the user the face is referring to.
- To get the number of registered users execute the following command:
find /usr/local/demo-ai/computer-vision/tflite-face-recognition/database -type f | wc -l
5
- To unregister users from the database, two solutions exist:
- In the thumbnail banner, touch the thumbnail face of the user you want to remove
- In the database directory, delete the file of the user you want to remove
3.5. Performance[edit source]
- The average execution frame rate to execute both face detection and face recognition on 1 face is around 5 fps:
- face detection execution time ~70 ms
- face recognition execution time ~55 ms
- The recognition threshold corresponds to the similarity score above which the input face is successfully mapped to one of the enrolled faces.
- The default recognition threshold is set to 0.70 and its value is configurable.
- TAR (True Acceptance Rate) and FAR (False Acceptance Rate) are the metrics used to compute the recognition threshold default value.
- The True Acceptance Rate represents the degree at which the system can correctly match the biometric information from the same person.
- The False Acceptance Rate is the probability of cases for which the system fallaciously authorizes an unauthorized person.
- A recognition threshold of 0.70 corresponds to a FAR of ~1% when plotting the TAR=f(FAR) graph using a dedicated (non-public) test database.
4. References[edit source]