1. Article purpose[edit source]
This section details the TF-A FIP (Trusted Firmware-A Firmware Image Package) binary management for the STM32 MPU boot chain. It explains how to use it in STM32 MPU context and describes the build/update process that is required to deploy it on your target.
2. Overview[edit source]
As explained in the TF-A Overview, this binary is used by the TF-A BL2 to load and authenticate the next stage binaries. It can contains:
- Boot stage binaries
- Configuration file (Device tree)
- Certificate (X509.3 based) for authentication
3. Package structure[edit source]
The FIP binary has a specific layout that is parsed by the BL2 during the load processing.
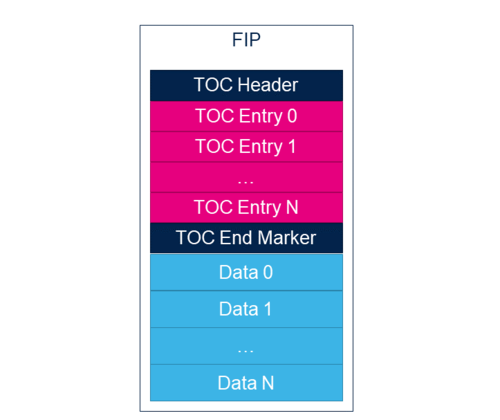
The FIP binary starts with a table of contents (ToC) that is recognized by the BL2. Each entry is identified by its UUID, offset in the package, size and flags. The end-of-ToC marker is used to define the start of the binary section. All the corresponding binaries are appended according to the offset defined in the ToC entry.
This structure is automatically built using the fiptool command. It appends all the binaries and creates the associated ToC.
4. Fiptool command[edit source]
fiptool is a host tool that must be used to generate the proper FIP binary.
By default, the OpenSTLinux SDK provides the fiptool. You do not need to regenerate it to update (or create) a FIP binary.
fiptool provides a set of useful commands to manage the FIP binary.
All options can be listed using the following command:
fiptool help
- info: The
fiptoolinfo provides information on a generated FIP binary
fiptool info fip.bin Secure Payload BL32 (Trusted OS): offset=0x100, size=0x1347C, cmdline="--tos-fw" Non-Trusted Firmware BL33: offset=0x1357C, size=0xEDDE2, cmdline="--nt-fw" FW_CONFIG: offset=0x10135E, size=0x226, cmdline="--fw-config" HW_CONFIG: offset=0x101584, size=0x1E412, cmdline="--hw-config" TOS_FW_CONFIG: offset=0x11F996, size=0x45AC, cmdline="--tos-fw-config"
- update: Update allows one or more images to be replaced in an existing FIP binary
fiptool update --tos-fw bl32.bin fip.bin
The optional argument below can be used to avoid erasing the initial FIP binary:
fiptool update --tos-fw bl32.bin --out new_fip.bin fip.bin
- unpack: Extracts all binaries from a FIP binary
fiptool unpack fip.bin
- remove: Removes a binary from FIP binary
fiptool remove --tos-fw bl32.bin fip.bin
4.1. Tool generation[edit source]
The tool is provided within the TF-A sources tools/fiptool . It can be built for Linux® or Windows® platforms. A dedicated rule is available to generate the tool:
make fiptool
It generates the tool under the tools/fiptool/fiptool source path.
4.2. TF-A build[edit source]
When the TF-A component build process is complete, the FIP binary can be automatically generated. In this case the fiptool is automatically generated too and the FIP binaries are part of the output folder.
5. Cert_create command[edit source]
When the TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT feature is enabled, the FIP must contain the binaries and their associated certificate as described in the TBBR[1] Chain of Trust (CoT).
These certificates can be created using the cert_create command that is provided in the TF-A sources tools/cert_create .
By default, the OpenSTLinux SDK provides the cert_create. You do not need to regenerate it to regenerate certificates.
The cert_create tool is able to generate the self-signed certificate used to complete the trusted boot chain. It requires a large set of arguments linked to the CoT.
cert_create --help
cert_create creates the certificate if it does not exist yet or uses the available one to generate the CoT.
The certificate content must be regenerated if the associated binary has been updated.
5.1. TF-A build[edit source]
TF-A generic Makefile can help to automatically build the certificate using some dedicated flags that can be enabled to generate the certificate and append them into the FIP:
- GENERATE_COT=1 : Enable the
cert_createtool - ROT_KEY : Specify the root private key to be used
6. FIP binary creation[edit source]
Below the list of the different ways by which the FIP binary can be generated:
- Using the dedicated
fiptoolcommand - Using the TF-A official Makefile
The FIP binary content may depend on the TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT feature enable. In this case, a prior certificate generation is mandatory to include them into the FIP binary.
6.1. STM32MP1[edit source]
The OpenSTLinux boot flow requires the following stages to be loaded:
- BL32: Secure OS and Secure Monitor (it can be eiher SP-MIN or OP-TEE OS)
- BL33: The non-secure firmware (recommended U-Boot)
- HW_config: The OpenSTLinux uses the hw_config as the non-secure device tree
- FW_config: Firmware configuration file listing the previous images and defining their size and the load address
To create the FIP binary, all the following binaries must be built:
- Secure OS or Secure Monitor
- U-Boot.
- Firmware configuration file related to the loaded binaries*.
When the TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT feature is enabled in BL2, the associated certificate must be generated as per the TBBR CoT requirements.
The fiptool is used to create or update a FIP file.
The TF-A Makefile with fip target and some variables uses fiptool to automatically create the new FIP after the TF-A compilation.
With U-Boot as a non-secure firmware, the paths for the files used in next chapters are the following:
| Description | Makefile variable |
fiptool option | file path for OP-TEE | file path for SP_MIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secure OS (OP-TEE) or Secure Monitor (SPMIN) |
BL32 | --tos-fw | <optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin | <tfa_path>/bl32.bin |
| OP-TEE pager | BL32_EXTRA1 | --tos-fw-extra1 | <optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin | - |
| OPTEE pageable | BL32_EXTRA2 | --tos-fw-extra2 | <optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin | - |
| Firmware configuration file | FW_CONFIG | --fw-config | <tfa_path>/fw-config.dtb | |
| U-Boot device tree | BL33_CFG | --hw-config | <u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb | |
| U-Boot | BL33 | --nt-fw | <u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin | |
In the next chapter, all the files are assumed present in the current directory.
6.1.1. Trusted boot chain[edit source]
6.1.1.1. Non-secure boot[edit source]
The following command generates the FIP package that is required by the BL2 to boot. You can create the FIP binary by using the fiptool command:
fiptool create --fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--tos-fw-config bl32.dtb \
--tos-fw bl32.bin \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin \
fip.bin
You can also use the TF-A Makefile:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<tfa_path>/bl32.bin \ FW_CONFIG=<tfa_path>/fw-config.dtb \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ fip
Adding the AARCH32_SP=sp_min automatically manages the BL32 and FW_CONFIG path:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ AARCH32_SP=sp_min \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ fip
6.1.1.2. Secure boot[edit source]
You can create the certificate and FIP binary by using the cert_create and fiptool command:
cert_create \
-n --tfw-nvctr 0 --ntfw-nvctr 0 \
--key-alg ecdsa --hash-alg sha256 \
--rot-key privateKey.pem \
--tb-fw bl2.bin \
--tb-fw-cert tb_fw.crt \
--tos-fw-config bl32.dtb \
--fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--trusted-key-cert trusted_key.crt \
--tos-fw-key-cert tos_fw_key.crt \
--tos-fw-cert tos_fw_content.crt \
--tos-fw bl32.bin \
--nt-fw-key-cert nt_fw_key.crt \
--nt-fw-cert nt_fw_content.crt \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin
You can now generate the FIP trusted package:
fiptool create \
--tb-fw-cert tb_fw.crt \
--fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--trusted-key-cert trusted_key.crt \
--tos-fw-key-cert tos_fw_key.crt \
--tos-fw-config bl32.dtb \
--tos-fw-cert tos_fw_content.crt \
--tos-fw bl32.bin \
--nt-fw-cert nt_fw_content.crt \
--nt-fw-key-cert nt_fw_key.crt \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin \
fip-trusted.bin
You can also use the TF-A Makefile:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<tfa_path>/bl32.bin \ FW_CONFIG=<tfa_path>/fw-config.dtb \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1 GENERATE_COT=1 ROT_KEY=<path_to_private_key>.pem \ fip
Adding the AARCH32_SP=sp_min automatically manages the BL32 and FW_CONFIG path:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ AARCH32_SP=sp_min \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1 GENERATE_COT=1 ROT_KEY=<path_to_private_key>.pem \ fip
6.1.2. OP-TEE boot chain[edit source]
6.1.2.1. Non-secure boot[edit source]
You can create the FIP binary by using the fiptool command:
fiptool create --fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin \
--tos-fw tee-header_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra1 tee-pager_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra2 tee-pageable_v2.bin \
fip-optee.bin
You can also use the TF-A Makefile:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA1=<optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA2=<optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ FW_CONFIG=<tfa_path>/fw-config.dtb fip
Adding the AARCH32_SP=optee automatically manages the FW_CONFIG path:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 AARCH32_SP=optee \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA1=<optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ BL32_EXTRA2=<optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin fip
6.1.2.2. Secure boot[edit source]
You can create the certificate and FIP binary by using the cert_create and fiptool command:
cert_create \
-n --tfw-nvctr 0 --ntfw-nvctr 0 \
--key-alg ecdsa --hash-alg sha256 \
--rot-key privateKey.pem \
--tb-fw bl2.bin \
--tb-fw-cert tb_fw.crt \
--tos-fw tee-header_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra1 tee-pager_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra2 tee-pageable_v2.bin \
--fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--trusted-key-cert trusted_key.crt \
--tos-fw-key-cert tos_fw_key.crt \
--tos-fw-cert tos_fw_content.crt \
--nt-fw-key-cert nt_fw_key.crt \
--nt-fw-cert nt_fw_content.crt \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin
You can now generate the FIP trusted package:
fiptool create \
--tb-fw-cert tb_fw.crt \
--fw-config fw-config.dtb \
--hw-config u-boot.dtb \
--trusted-key-cert trusted_key.crt \
--tos-fw-key-cert tos_fw_key.crt \
--tos-fw-cert tos_fw_content.crt \
--tos-fw tee-header_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra1 tee-pager_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra2 tee-pageable_v2.bin \
--nt-fw-cert nt_fw_content.crt \
--nt-fw-key-cert nt_fw_key.crt \
--nt-fw u-boot-nodtb.bin \
fip-optee-trusted.bin
You can also use the TF-A Makefile:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA1=<optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA2=<optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin \ FW_CONFIG=<tfa_path>/fw-config.dtb \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1 GENERATE_COT=1 ROT_KEY=<path_to_private_key>.pem fip
Adding the AARCH32_SP=optee automatically manages the FW_CONFIG path:
make ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1 AARCH32_SP=optee \ BL33=<u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin \ BL33_CFG=<u-boot_path>/u-boot.dtb \ BL32=<optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA1=<optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin \ BL32_EXTRA2=<optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin \ DTB_FILE_NAME=<fdt file name>.dtb \ TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1 GENERATE_COT=1 ROT_KEY=<path_to_private_key>.pem fip
6.2. Updating the FIP binary[edit source]
When modifying a component included in the FIP binary, it is possible to update only part of the binary. To do this, use the fiptool update command:
6.2.1. Updating TF-A SP-MIN[edit source]
When a modification is made in the SP-MIN binary (or its device tree), the SP-MIN must be updated in the FIP binary:
- Full SP-MIN update
fiptool update --tos-fw <tfa_path>/bl32.bin --tos-fw-config <tfa_path>/bl32.dtb fip.bin
- SP-MIN core binary
fiptool update --tos-fw <tfa_path>/bl32.bin fip.bin
- SP-MIN device tree update
fiptool update --tos-fw-config <tfa_path>/bl32.dtb fip.bin
6.2.2. Updating U-Boot[edit source]
When a new U-Boot is generated, the FIP must be updated using the following commands:
- Full U-Boot update
fiptool update --nt-fw <u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin --hw-config u-boot.dtb fip.bin
- U-Boot core binary
fiptool update --nt-fw <u-boot_path>/u-boot-nodtb.bin fip.bin
- U-Boot device tree update
fiptool update --hw-config u-boot.dtb fip.bin
6.2.3. Updating OP-TEE[edit source]
The OP-TEE OS rebuild is required to update the FIP package.
fiptool update --tos-fw <optee_path>/tee-header_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra1 <optee_path>/tee-pager_v2.bin \
--tos-fw-extra2 <optee_path>/tee-pageable_v2.bin \
fip-optee.bin
The OP-TEE OS build process generates the static binary location.
In case of mapping modification, the firmware configuration file must be adapted accordingly
6.2.4. Updating FW_CONFIG[edit source]
In case of change in the firmware configuration file, you must also update the FIP binary:
fiptool update --fw-config fw-config.dtb fip.bin
7. Updating the software on board[edit source]
7.1. Partitioning of binaries[edit source]
The FIP build provides a binary named fip.bin (or fip-<board-name>-<bootchain>.bin from official release) that MUST be copied to a dedicated partition named "fip".
7.2. Updating via SDCard[edit source]
If you use an SDCard, simply update the FIP binary by using the dd command on your host.
Plug your SDCard into the computer and copy the binary to the dedicated partition; on an SDCard/USB disk the "fip" partition is partition 3:
- SDCard: /dev/mmcblkXp3 (where X is the instance number)
- SDCardvia USB reader: /dev/sdX3 (where X is the instance number)
- Under Linux®
dd if=<fip binary file> of=/dev/<device partition> bs=1M conv=fdatasync
- Under Windows®
CoreUtils [2] that includes the dd command is available for Windows.
7.3. Updating via USB mass storage on U-boot[edit source]
See How to use USB mass storage in U-Boot.
Refer to the previous section to put FIP binary into SDCard/USB disk.
7.4. Updating your boot device via STM32CubeProgrammer[edit source]
Refer to the STM32CubeProgrammer documentation for details on how to update your target.
8. References[edit source]