This article explains what the Memory Mapping Tool (MMT) is and how to use it through examples.
1. What is MMT ?
MMT stands for Memory Management Tool. This STM32CubeMX feature handles the memory mapping in a more visual way. The main tool goal is to make easy the creation, the partition and the deletion of memory blocks in RAM, FLASH or external memory (thanks to connectivity IP : OctoSPI, FMC...). In fact, the MMT abstracts the difficulty from the linker file by providing a simple use. Also, the MMT configures memory management peripherals such as MPU, SAU, GTZC and FLASH.
2. Visual presentation
The MMT is under Tools > Memory Management.
2.1. Trustzone aware Project (with secure and non secure Application)
Let's introduce the Memory Management Tool with the picture below. This feature is available since the 6.9.0 STM32CubeMX version and this Getting Started has been realized with the 6.9.1 STM32CubeMX version.
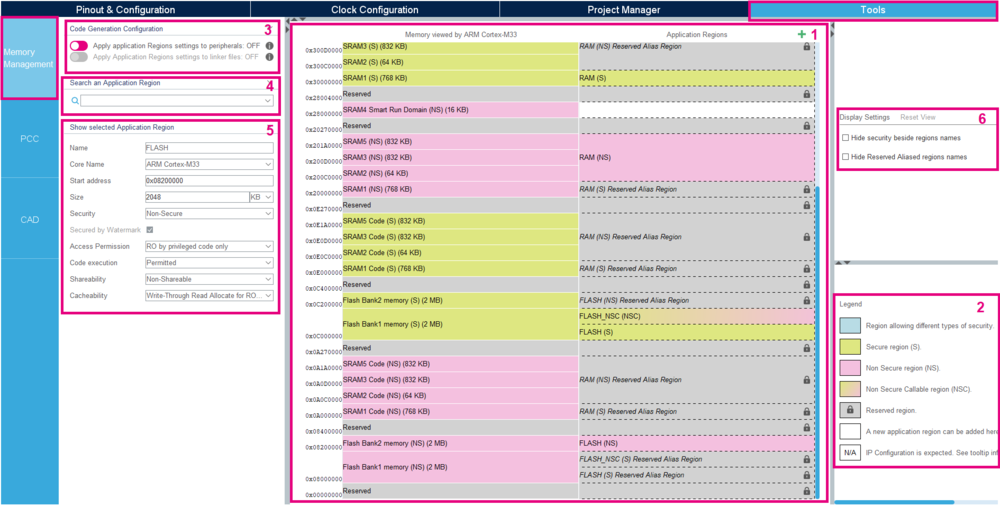
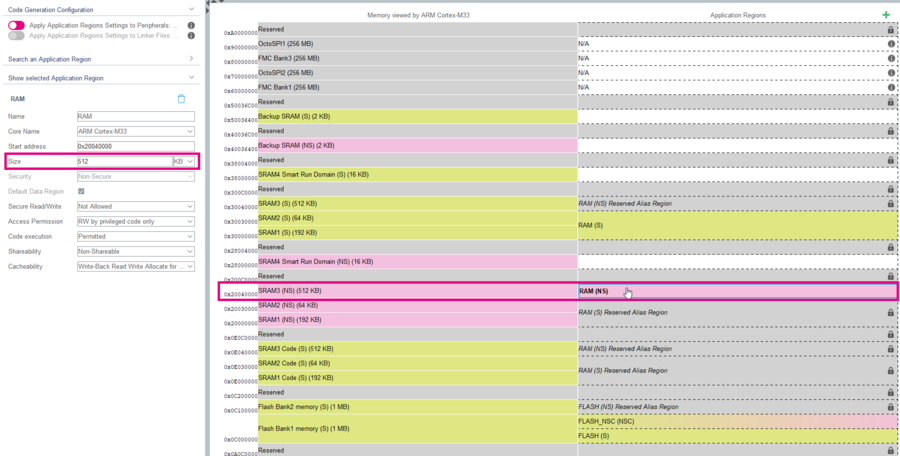
The MMT pannel is split in 6 parts:
1. The main pannel is a memory view by the CPU (left hand) and the application regions (right hand) with addresses on the left.
2. The second point is the legend indicating the corresponding color from memory.
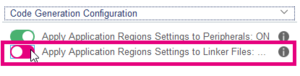
3. The third block is composed of two toggle buttons which indicates the Code Generation Configuration :
- if the application regions settings are applied to peripherals
- if the application regions settings will be applied into linker files during code generation.
4. This Search bar allows to easily find an application region
5. This fifth section shows the selected Application Region in the main pannel. It lists many useful information. (Code Name, Start address, Size, Security, Access Permission, Code execution, Shareability and Cacheability)
6. The Display Settings and Reset View configure the memory view.
2.2. Non Trustzone aware Project (with only non secure Application)
The Non Secure aware project have exactly the same interface except there is only one type of Application Region. However, the principle remains strictly the same.
3. Configure MMT to handle memory
3.1. Objectives
- Create a simple project with a Secure (S) and a Non-Secure (NS) application.
- Learn how to configure the memory through the tool.
- Verify the correct functionality by checking the linker file.
3.2. Create the project in STM32CubeMX
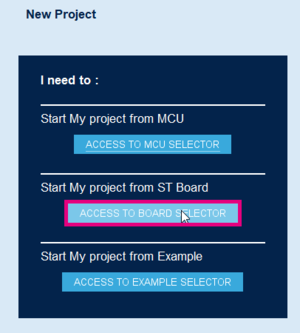
- File > New Project > Board Selector in the main panel or click on the shortcut Access to Board Selector.
The example uses the NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q board.
- Enter NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q in the Commercial Part Number as shown in the figure below.
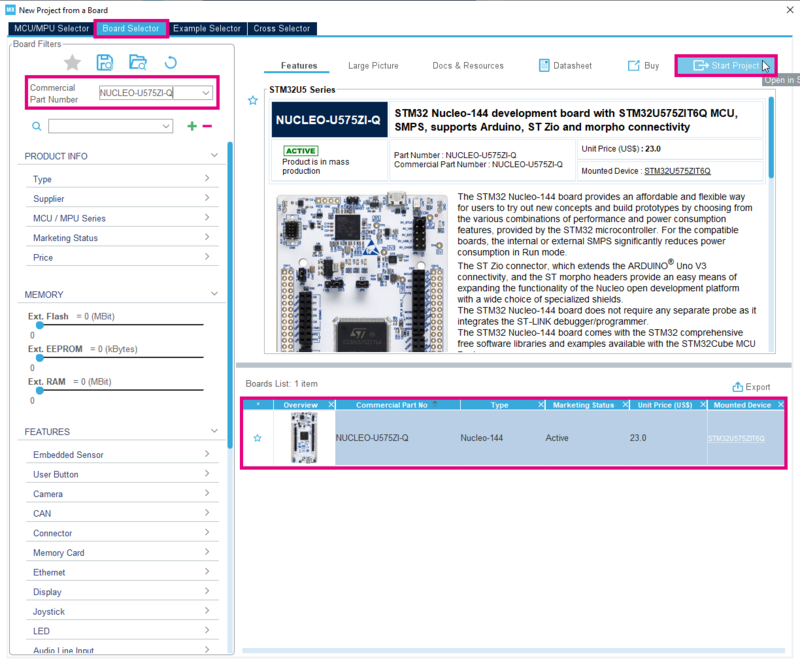
- Select the NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q in the Board List
- And then click on Start Project.
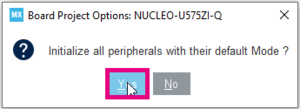
- Select Yes in the pop-up window to initialize all peripherals with their default mode.
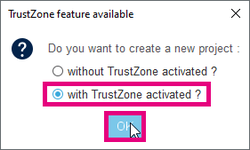
- Answer with TrustZone activated to the question "Do you want to create a new project ?" and OK
3.3. Memory zone definition
Go to the Memory Management Tool located under Tools > Memory Management.
By default, the RAM & FLASH regions are created because they are necessary to link applications. In this part, we are gonna create two more Application Regions:
- App_Secure
- App_NonSecure
3.3.1. Secure Application Region
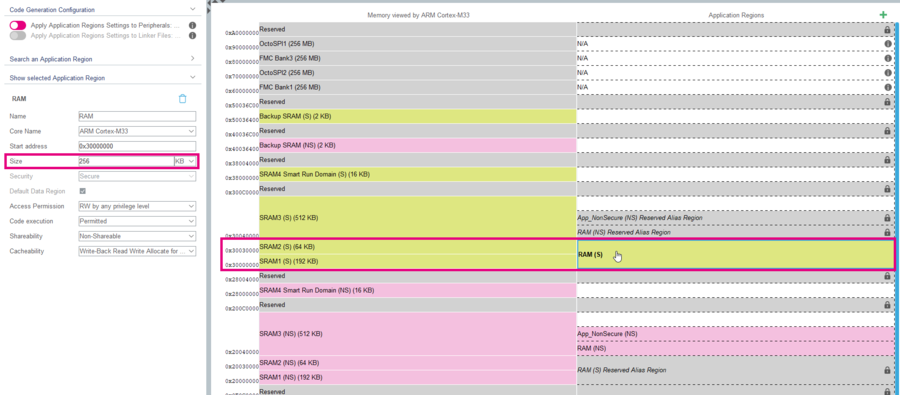
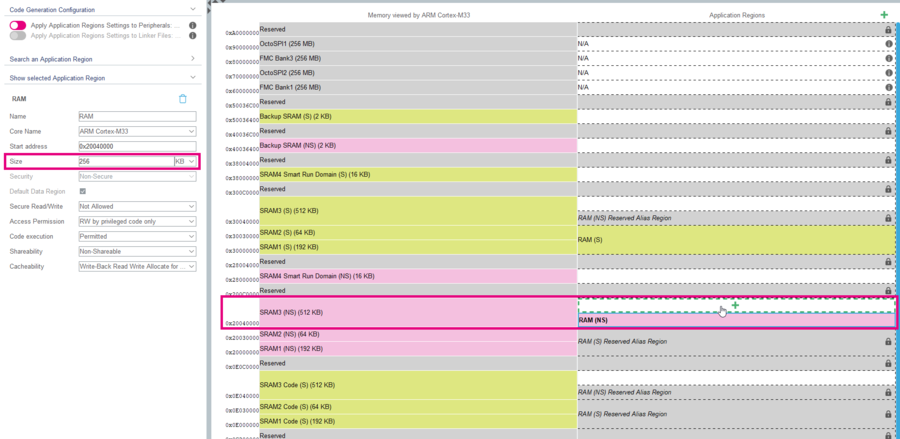
- Select the RAM (S) region at the address 0x30000000.
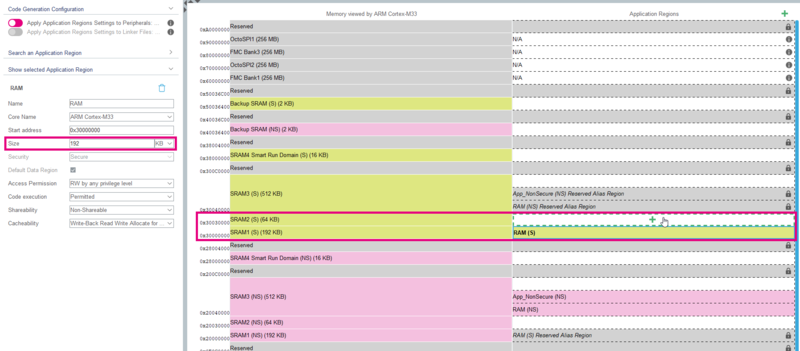
- Change the size to 192kB.
- A new memory region available for an Application Region appears in white, when you mouse over it, a green cross appears.
- Click on this green cross section and the popup below pops up.
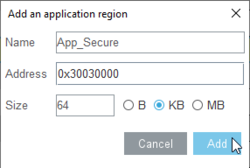
- In the Name field, enter App_Secure.
- The Address is the base address from the selected memory block, you can keep it by default.
- Keep the Size of 64 kB.
- Click on Add
3.3.2. Non Secure Application Region
- Select the RAM (NS) region at the address 0x20040000.
- Change the size to 256 kB.
- A new memory region available for an Application Region appears in white, when you mouse over it, a green cross appears.
- Click on this green cross section and the popup below pops up.
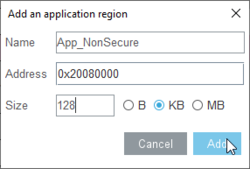
- In the Name field, enter App_NonSecure.
- The Address is the base address from the selected memory block, you can keep it by default.
- Change the Size to 128 kB.
- Click on Add
3.3.3. Apply MMT
Go to code generation configuration as below:
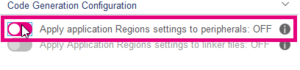
- Click on the first toggle button to apply Application Regions to Peripherals :
- And Click on the second button to apply Application Regions into linker files during the code generation :
3.4. Pinout & Configuration
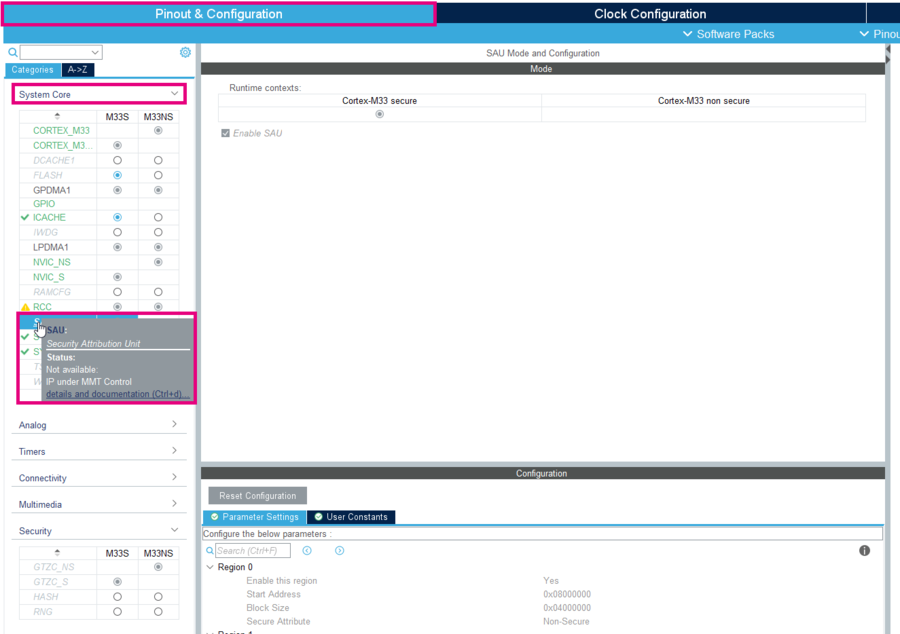
- Now, go to Pinout & Configuration > System Core > SAU, the SAU is under MMT control and is Read Only.
3.5. Generate project and edit linker file
The easiest way to generate the code is to :
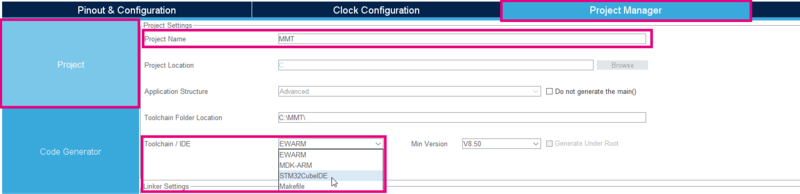
- Click on Project Manager > Project > Project Settings
- Enter a Project Name and select STM32CubeIDE in the ToolChain / IDE
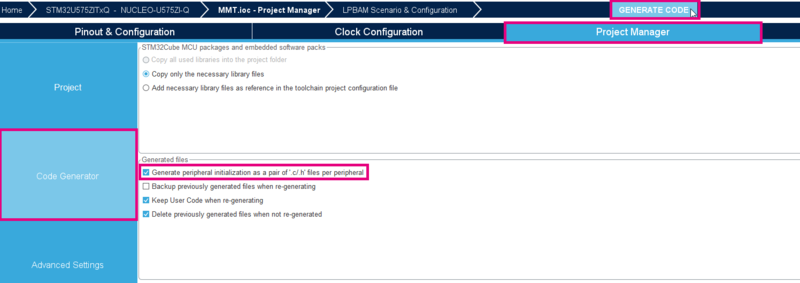
- Then select the Code Generator menu
- Check the box to Generate peripheral initialization as a pair of '.c/.h' files per peripheral (optional)
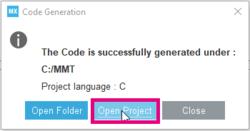
- Click on Generate Code
- Click on Open Project
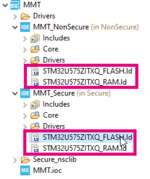
- On the left side of the screen in the project explorer, expand the tree structure (NS & S project).
- Open the linker files (.ld)
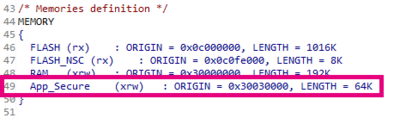
Look at the memory definition :
- Check the "App_Secure" 's declaration in the Secure world and the "App_NonSecure" in the Non Secure world.
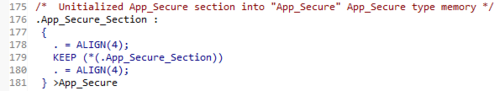
- Check also the section definition below.
3.6. Compile
3.7. Edit main.c
Create an array to place in the App_Secure region :
- Open the main.c file which is the main source file for this secure project
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
#define LOCATE_FUNC __attribute__((section(".App_Secure_Section")))
#define SIZE 100
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint32_t LOCATE_FUNC Array[SIZE] = {0};
/* USER CODE END 0 */
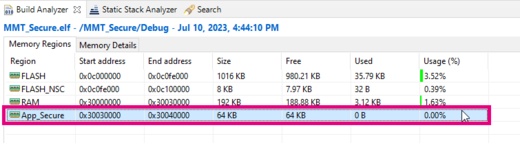
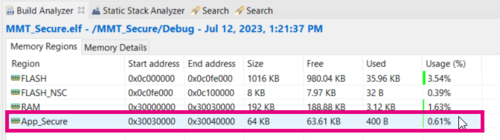
- Check other values for SIZE (200, 5000, 30000)
- Conclude about the change by watching the section in Build Analyzer
4. External memory
To go further, it's possible to manage external memory through MMT.
Go to Pinout & Configuration > Connectivity to configure interfaces.
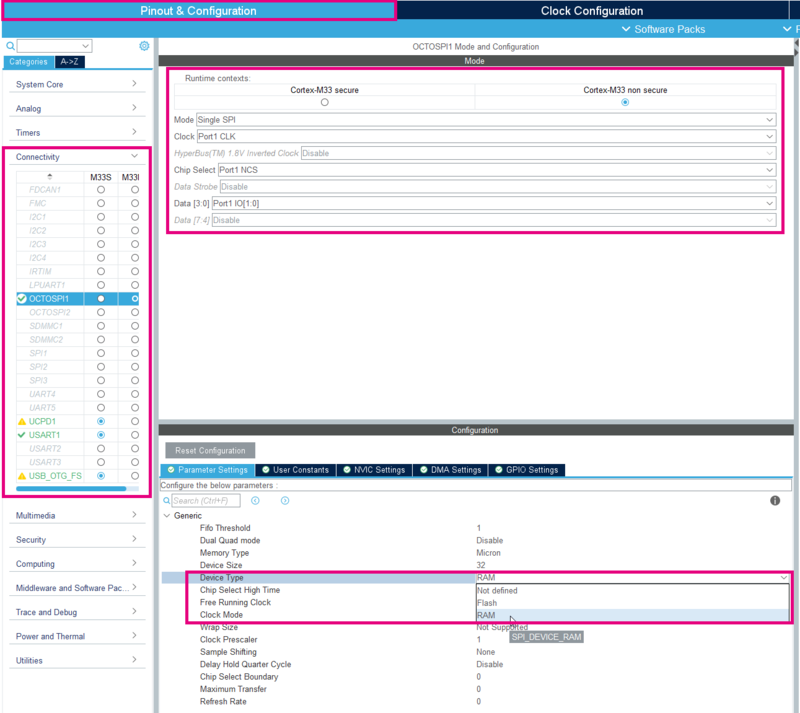
4.1. OctoSPI
Active the OctoSPI in Non Secure as shown on the picture below.
- Set the mode in Single SPI.
- Select Port1 CLK for the CLK, Port1 NCS for the Chip Select and Port1 IO[1:0] for Data [3:0].
- Choose the Device Type : RAM.
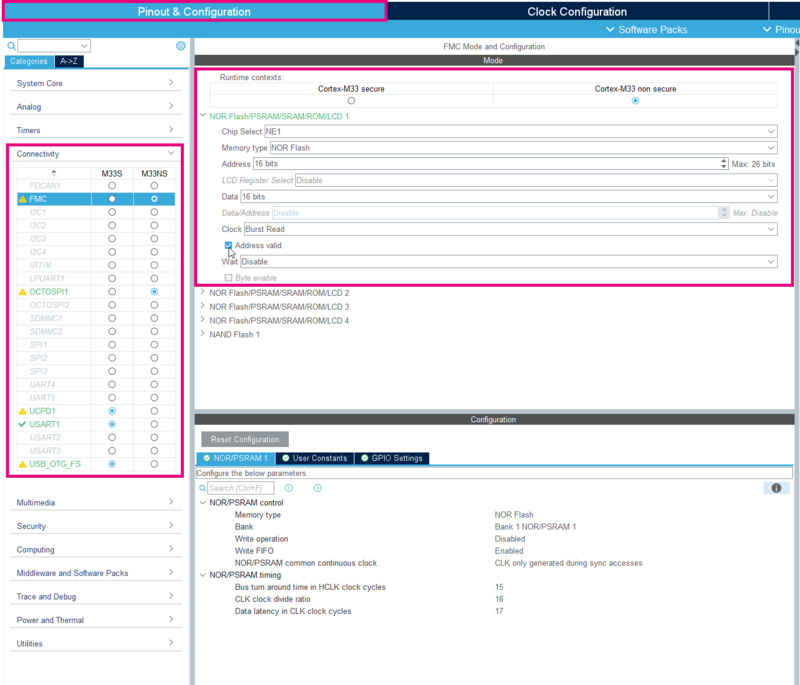
4.2. FMC Bank
Active the FMC in Non Secure as shown on the picture below.
- Choose the NE1 for the Chip Select
- Configure the Memory type to NOR Flash.
- Select 16bits for the Address (mandatory to be 128 KBytes aligned), 16 bits for Data and Burst Read regarding the clock.
- Tick the Address valid.
4.3. MMT
Once the configuration above is done,
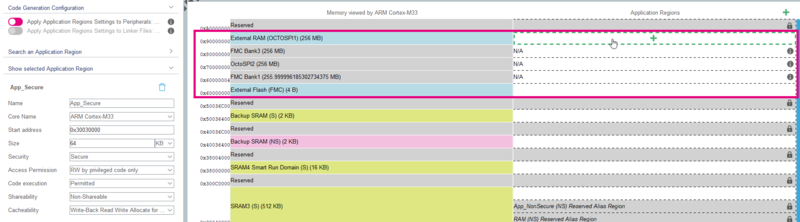
- Go to the MMT under Tools > Memory Management
- Observe the activation of the External RAM (OctoSPI1) and the External Flash (FMC)
- Create your application regions as needed (128 KBytes aligned)
5. Frequent error cases
Here is a list of the most common errors :
- Alignment : Regions must be aligned. (eg : 32 Bytes for Backup SRAM, 512 Bytes for SRAM, 8192 Bytes for FLASH and 128 KBytes for external memories).
- Naming : 2 regions with the same name cannot coexist in the same context (eg : 2 secure regions cannot have the same name).
- Overlap : 2 regions cannot overlap AND a region cannot span on a reserved area.