This article describes how to obtain and use the Developer Package of the STM32MPU Embedded Software for Android™ for any STM32MP1 family development platform (STM32MP15 boards) in order to develop applications on it.
It details some prerequisite knowledge and the development environment, and gives step-by-step instructions to download and install the STM32MPU Embedded Software for Android components for the Package.
Finally, it gives guidelines on upgrading (to add, remove, configure, or improve) any piece of software.
1. Developer Package content[edit source]
If you are not familiar with the STM32MPU Embedded Software for Android distribution and its Packages, please read the following articles:
- Which STM32MPU Embedded Software Package for Android better suits your needs (and especially the Developer Package chapter)
- STM32MPU Embedded Software distribution for Android
In summary, this Developer Package provides:
- for the STM32MPU distribution for Android™ (development on Arm® Cortex®-A processor):
- the software development kit (SDK) update associated with Android Studio IDE, adding a service to connect your application to the co-processor (customization)
- for the STM32Cube MPU Package (development on Arm® Cortex®-M processor):
- Source code for all pieces of software (BSP, HAL, middleware and applications)
- the integrated development environment (IDE) (STM32-CoPro-MPU Eclipse plugin)
2. Prerequisite knowledge[edit source]
The STM32MP1 Developer Package aims to enrich Linux-based software for the targeted product. A basic knowledge of Linux and Android is recommended in order to make the most of this Package. Reading the STM32MPU Embedded Software for Android architecture overview is also highly recommended.
3. Installing the components to develop software running on Arm Cortex-A (STM32MPU distribution for Android)[edit source]
3.1. Installing the Android Studio IDE[edit source]
The IDE is available in the Android developer site[1].
3.2. Installing the SDK update[edit source]
The official SDK for Android must be loaded through Android Studio using the SDK manager, selecting the correct version for the Starter package version used.
The SDK can then be updated by replacing the android.jar file (JAVA archive file for Android) of the loaded SDK with the one provided within the Developer package (adding the co-processor service classes).
| Delivery for Android coming soon (Q4 2019) |
4. Installing the components needed to develop software running on the Arm Cortex-M4 (STM32Cube MPU Package)[edit source]
4.1. Installing the Eclipse IDE[edit source]
The table below explains how to download and install the System Workbench for the STM32 IDE, which is the AC6 product addressing the STM32 MCU, and the STM32-CoPro-MPU plugin, which provides support for Cortex-M inside the STM32 MPU. STM32-CoPro-MPU plugin release note
4.2. Installing the STM32Cube MPU Package[edit source]
Prerequite: the Eclipse IDE is installed.
- The STM32CubeMP1 Package is delivered through an archive file named en.STM32Cube_FW_MP1_V1.6.0.zip.
- Download and install the STM32CubeMP1 Package
The software package is provided AS IS, and by downloading it, you agree to be bound to the terms of the software license agreement (SLA0048). The detailed content licenses can be found here..
| STM32MP1 Developer Package STM32CubeMP1 Package - v5.0.0 release | |
|---|---|
| Download |
|
| Installation |
cd <working directory path>/Developer-Package
unzip en.STM32Cube_FW_MP1_V1.6.0.zip |
| Release note |
Details about the content of the STM32CubeMP1 Package are available in the STM32Cube_FW_MP1_V1.6.0/Release_Notes.html file.
|
- The STM32CubeMP1 Package installation directory is in the <Developer Package installation directory> directory, and is named STM32Cube_FW_MP1_V1.6.0:
STM32Cube_FW_MP1_V1.6.0 STM32CubeMP1 Package: details in STM32CubeMP1 Package content article ├── Drivers │ ├── BSP BSP drivers for the supported STM32MP1 boards │ │ └── [...] │ ├── CMSIS │ │ └── [...] │ └── STM32MP1xx_HAL_Driver HAL drivers for the supported STM32MP1 devices │ └── [...] ├── _htmresc │ └── [...] ├── License.md ├── Middlewares │ └── [...] ├── package.xml ├── Projects │ ├── STM32CubeProjectsList.html List of examples and applications for STM32CubeMP1 Package │ ├── STM32MP157C-DK2 Set of examples and applications → STM32MP15 Discovery kits │ │ └── [...] │ └── STM32MP157C-EV1 Set of examples and applications → STM32MP15 Evaluation boards │ └── [...] ├── Readme.md ├── Release_Notes.html Release note for STM32CubeMP1 Package └── Utilities └── [...]
The STM32Cube MPU Package is now installed: let's develop software running on Arm Cortex-M.
5. Developing Android application running on Arm Cortex-A7[edit source]
Please refer to the Android developer guide[2] for generic informations about standard Android application development.
Then based on the SDK delivered within the Developer Package for Android (see Installing the SDK update), this is possible to develop an application which can use the co-processor service (CoproManager), in order to interact with remote Arm Cortex-M4 core software.
5.1. Using co-processor service (CoproManager)[edit source]
Co-processor service detailed information and API are described in dedicated page. Please see How to use coprocessor service for Android.
6. Developing software running on Arm Cortex-M4 with STM32CubeMP1 Developer Package[edit source]
This is possible to develop Arm Cortex-M4 software based on the default resources allocated in the Linux kernel device-tree (detailed in Default resources allocation for Arm Cortex-M4 in Developer Package for Android).
6.1. Prerequisites[edit source]
Main components to be used:
- Eclipse IDE (See Installing the Eclipse IDE)
- Developer Package for STM32CubeMP1 (eclipse plugin for IDE software, i.e. System workbench for STM32)
6.2. Creating new project from CubeMx[edit source]
Please refer to the STM32CubeMX wiki page.
As an initial CubeMx default configuration project which include supported resources allocations for Cortext-M4, please load this ioc file.
6.3. How to use the Eclipse IDE with an existing example[edit source]
The example in this paragraph is based on the co-processor service (CoproManager). See How to use coprocessor service for Android page for details.
6.3.1. Get the source code of the example[edit source]
Source code of the Arm Cortex-M4 software example is available on github: STCoproM4Example. .
6.3.2. How to rebuild the example[edit source]
6.3.3. How to download and run the example on the target[edit source]
- The board is booted, ST-Link connected to your PC (for getting console through virtual communication port), and USB OTG also connected to your PC (for getting ADB link)
- Open the serial console to check connection to the board is ok
- Click Open console on serial device button
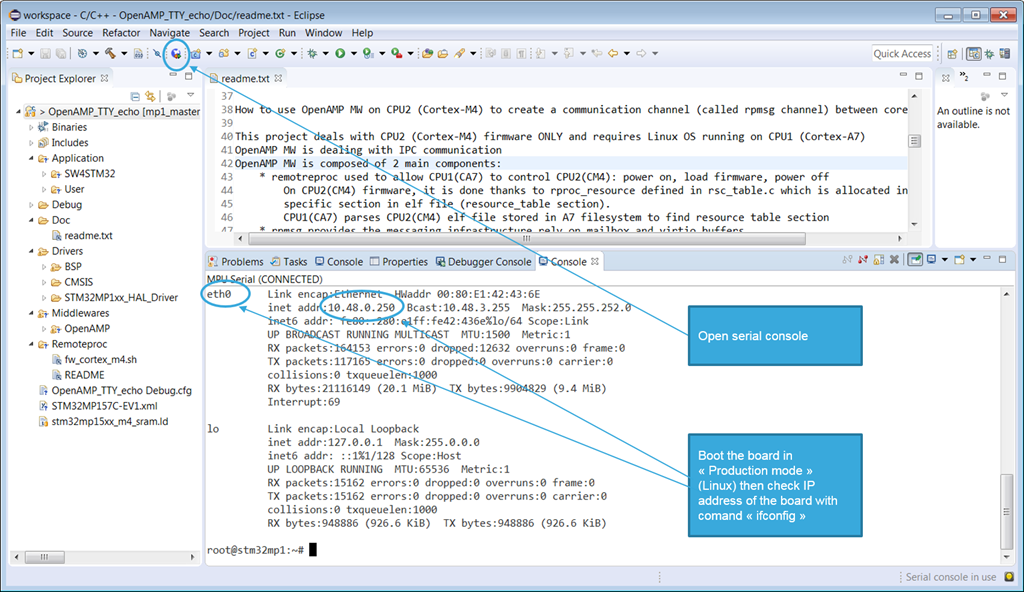
- A dedicated Console panel is open with prompt. You can then check you are connected to the board
console:/ $ ls /
acct data init.recovery.stm.rc oem storage
bin default.prop init.usb.configfs.rc postinstall sys
bugreports dev init.usb.rc proc system
cache etc init.zygote32.rc product ueventd.rc
charger init lost+found res vendor
config init.environ.rc mnt sbin
d init.rc odm sdcard
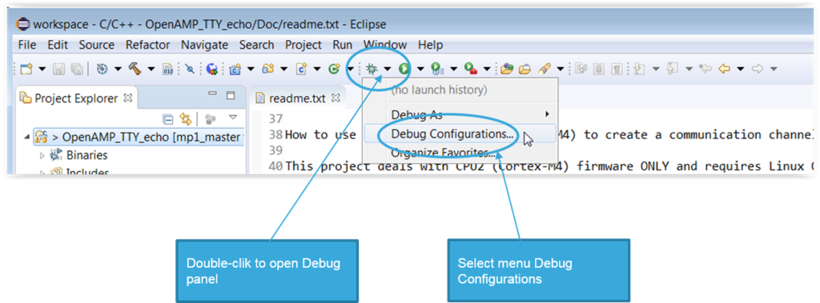
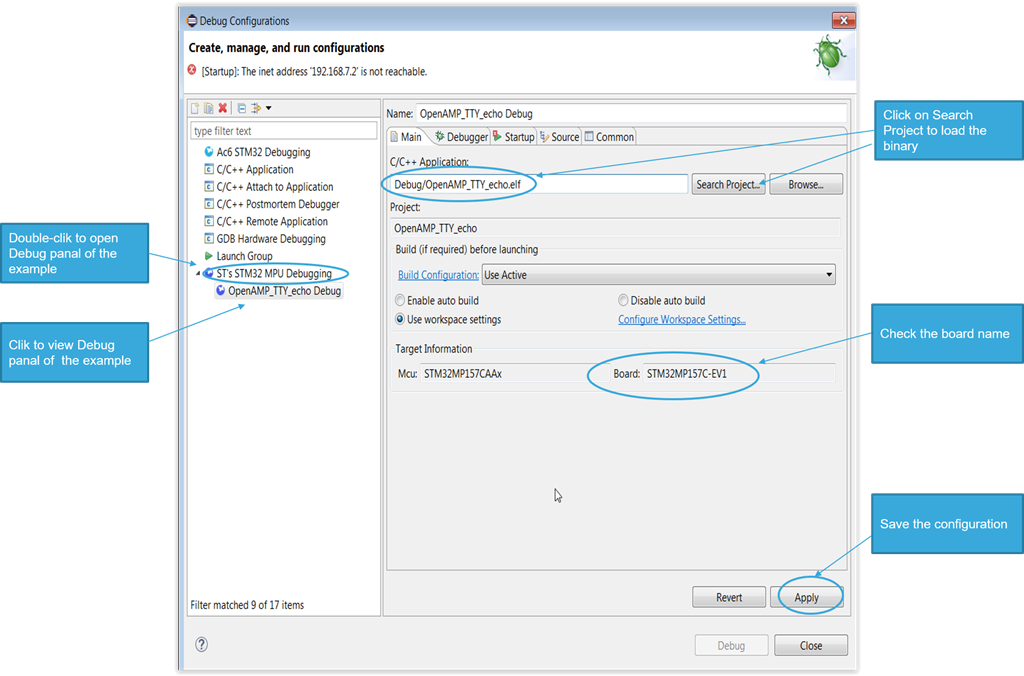
- Configure Main tab of the Debug Configurations panel to add the firmware binary
- Menu > Run > Debug configuration... / [ Main ] tab
- Configure Startup tab of the Debug Configurations panel
- Menu > Run > Debug configuration... / [ Starter ] tab
- Unselect Load image
- Load the Arm Cortex-M4 firmware in the target
- - Connect ADB to the remote target board via USB OTG through Android Studio
- - Check for the adb link:
adb devices List of devices attached 004000353338511934383330 device
Load the Arm Cortex-M4 firmware on the target
- Following rules must be respected about the Arm Cortex-M4 firmware with co-processor service path:
- - Must be under /vendor/firmware/copro directory
- - Firmware name should be the same as the current directory where it is loaded
- Example for STCoproM4Example firmware:
- Note: root access right required for creating directory in /vendor to be able to create any new directory in /vendor
- Following rules must be respected about the Arm Cortex-M4 firmware with co-processor service path:
adb root; adb remount
adb shell mkdir /vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example
adb push <path_to>/STCoproM4Example.elf /vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example/
6.3.4. How to start/stop the example[edit source]
Via the console in the IDE
- Start the example:
console:/ # cd /vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example console:/vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example/ # fw_cortex_m4_eval.sh start fw_cortex_m4_eval.sh: fmw_name=STCoproM4Example/STCoproM4Example.elf
- Stop the example:
console:/ # cd /vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example console:/vendor/firmware/copro/STCoproM4Example/ # fw_cortex_m4_eval.sh stop fw_cortex_m4_eval.sh: fmw_name=STCoproM4Example/STCoproM4Example.elf
6.3.5. How to debug an example[edit source]
Ensure the example firmware is running on the target.
Run the debug mode on IDE side.
IDE attach the current running firmware on the Arm Cortex-M4. It is then possible to break software execution and make step by step debug.
7. How to go further[edit source]
Now that your developments are ready, you may switch to the STM32MP1 Distribution Package for Android in order to create your own distribution and to generate your own SDK and image.