1. Purpose[edit | edit source]
STM32MP Signing Tool is a key tool that guarantees a secure platform, it ensures the signing of binary images using ECC keys generated by KeyGen tool. The signed binary images are used during the STM32 MPU ROM code secure boot sequence that supports a trusted boot chain; this action ensures an authentication and integrity check of the loaded images .
2. STM32MP Signing Tool overview[edit | edit source]
The STM32MP Signing Tool software generates a signed binary file from:
- Binary image file : contains the binary data to be programmed for the STM32MP1 series device.
- Public key file: contains the generated ECC public key in PEM format (generated with the KeyGen tool).
- Private key file: contains the encrypted ECC private key in PEM format (generated with the KeyGen tool).
If the image entry is an .stm32 file that already contains STM32 header and info, it is also possible to generate a signed binary file from the given .stm32 file with the batch file mode. In that case, the parameters Entry point of image, Load address of image, and Image version are not mandatory.
Signing tool usage block diagram:
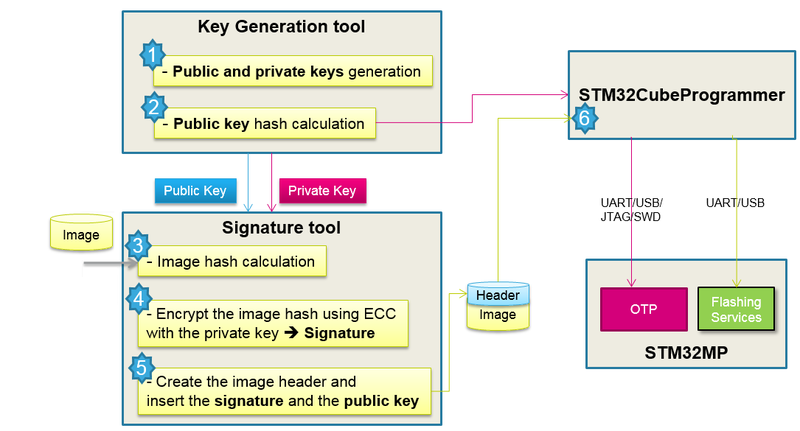
3. STM32MP Signing Tool install[edit | edit source]
This section describes the requirements and procedure to use the STM32MP Signing Tool software.
3.1. Linux install[edit | edit source]
The STM32MP Signing Tool is tested on Ubuntu 14.04 and 16.04 32-bit and 64-bit and should work on any distribution.
To install the STM32MP Signing Tool, the installation of STM32CubeProgrammer is needed.
To run the STM32MP Signing Tool, launch the ./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI.
3.2. Windows install[edit | edit source]
To install the STM32MP Signing Tool, the installation of STM32CubeProgrammer is needed.
To run it, launch the executable STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI.exe.
4. Command line options[edit | edit source]
Available options are:
- --binary-image (-bin), --input (-in)
- Description : binary image file path
- Syntax 1: -bin /home/User/binaryFile.bin
- Syntax 2: -in /home/User/binaryFile.bin
- Description : binary image file path
- --public-key -pubk
- Description : Public key files paths
- Syntax : -pubk <File_Path{1..8}>
- For header v1: use just one key path for STM32MP15xx products
- For header v2: use 8 key paths for STM32MP13xx products
- Description : Public key files paths
- --private-key -prvk
- Description : private key file path
- Syntax : -prvk <File_Path>
- Description : private key file path
- --password -pwd
- Description : password of the private key
- Syntax : -pwd <Password>
- Description : password of the private key
- --load-address -la
- Description : load address of image, value in hex format
- Syntax : -la <Load_Address>
- Example : -la 0x2ffe0000
- Description : load address of image, value in hex format
- --entry-point -ep
- Description : image entry point, value in hex format
- Syntax : -ep <Entry_Point>
- Example : 0x2ffe4000
- Description : image entry point, value in hex format
- --image-version -iv
- Description : image version, Default is 0
- Syntax : -iv <Version>
- Description : image version, Default is 0
- --algorithm -a
- Description : used algorithm : 1. (P-256 NIST) 2. (Brainpool 256), 1- P256NIST is the default algorithm
- Syntax : -a <AlgoNbr>
- Description : used algorithm : 1. (P-256 NIST) 2. (Brainpool 256), 1- P256NIST is the default algorithm
- --option-flags -of
- Description : option flags of image, default is 0 (For more information, check Option flags in STM32_header_for_binary_files)
- Syntax : -of <Option_Flags>
- Example: 0x00000001
- Note : -of option flag is an extension to pass a device settings
- for STM32MP13 (b0=1: Authentication Enable and/or b1=1: FSBL encryption Enable)
- For Authentication: -of 0x00000001, -of 0x00000001
- For Authentication + FSBL Encryption : -of 0x00000003, -of 0x00000003
- If the command "--option-flags" is not mentioned, the tool will not create a signed image (Default: Authentication Disable)
| MP13 | b0=1 (Enable authentication) | b0=0 (Disable authentication) | No -of command |
| Input contains STM32 header: Yes | Sign | Nothing | Nothing |
| Input contains STM32 header: No | Sign | Add header without signing | Add header without signing |
- for STM32MP15 (b0=1: Authentication Disable or b0=0: Authentication Enable)
- Example : -of 0x00000000, -of 0x00000001
- If the command "--option-flags" is not mentioned, the tool will create a signed image (Default: Authentication Enable)
- for STM32MP15 (b0=1: Authentication Disable or b0=0: Authentication Enable)
| MP15 | b0=1 (Disable authentication) | b0=0 (Enable authentication) | No -of command |
| Input contains STM32 header: Yes | Nothing | Sign | Sign |
| Input contains STM32 header: No | Add header without signing | Sign | Sign |
- Signature and authentication are mandatory on secure closed chip
- --output -o
- Description : output file path
- Syntax : -o <Output_File_Path>
- Description : output file path
- --silent -s
- Description : silent mode, no prompt messages
- Syntax : -s
- Description : silent mode, no prompt messages
- --binary-type -type
- Description : identify binary file, possible values : ssbl, fsbl, teeh, teed, teex, copro (For more information, check Binary type in STM32_header_for_binary_files)
- Syntax : --binary-type <type>
- --enc-dc -encdc
- Description: Encryption derivation constant for FSBL encryption [header v2]
- Syntax: -encdc <Deriv_hexVal>
- Description: Encryption derivation constant for FSBL encryption [header v2]
- --enc-key -enck
- Description: OEM secret file for FSBL encryption [header v2]
- Syntax: -enck <Key_Path>
- Description: OEM secret file for FSBL encryption [header v2]
- --dump-header --dump
- Description: Parse and dump image header
- Syntax: -dump <File_Path>
- Description: Parse and dump image header
5. STM32MP Signing Tool usage examples[edit | edit source]
This section presents some examples of how to use the STM32MP Signing Tool software.
5.1. Example 1[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI -bin /home/User/BinaryFile.bin –pubk /home/user/publicKey.pem –prvk /home/user/privateKey.pem –iv 5 –pwd azerty –la 0x20000000 –ep 0x08000000
The default algorithm is selected (prime256v1) and the option flags value is 0 (default value). The signed output binary file (BinaryFile_Signed.bin) is created in the folder /home/user/
5.2. Example 2[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI -bin /home/User/Folder1/BinaryFile.bin –pubk /home/user/publicKey.pem –prvk /home/user/privateKey.pem –iv 5 –pwd azerty –s –la 0x20000000 –ep 0x08000000 –a 2 –o /home/user/Folder2/Folder3/signedFile.bin
BrainpoolP256t1 algorithm is selected in this example.
5.3. Example 3[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI -bin /home/User/Folder1/BinaryFile.stm32 –pubk /home/user/publicKey.pem –prvk /home/user/privateKey.pem –pwd azerty -t <type> –o /home/user/Folder2/Folder3/signedFile.bin
If the image entry is an .stm32 file that already contains header and info the only mandatory options are: public key, private key, password and Binary type.
5.4. Example 4[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI.exe -bin /home/user/input.bin -pubk publicKey00.pem publicKey01.pem publicKey02.pem publicKey03.pem publicKey04.pem publicKey05.pem publicKey06.pem publicKey07.pem -prvk privateKey00.pem -pwd azerty -t fsbl -iv 0x00000000 -la 0x20000000 -ep 0x08000000 -of 0x80000001 -o /home/user/output.stm32
Sign a binary file using header version 2 that includes 8 public keys for authentication flow.
5.5. Example 5[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI.exe -bin /home/user/input.bin -pubk publicKey00.pem publicKey01.pem publicKey02.pem publicKey03.pem publicKey04.pem publicKey05.pem publicKey06.pem publicKey07.pem -prvk privateKey00.pem -iv 0x00000000 -pwd azerty -la 0x20000000 -ep 0x08000000 -t fsbl -of 0x00000003 -encdc 0x25205f0e -enck /home/user/OEM_SECRET.bin -o /home/user/output.stm32
Sign a binary file using header version 2 that includes 8 public keys for authentication + encryption flow.
5.6. Example 6[edit | edit source]
./STM32MP_SigningTool_CLI.exe -dump /home/user/output.stm32
Verify the resulted image by parsing the output file and check each header field.
6. Standalone mode[edit | edit source]
When executing the STM32MP Signing Tool in standalone mode, an absolute path must be entered at first, then enter the password must be entered twice for confirmation.
After specifying one of the two algorithms, enter the image version, image entry point, image load address, and finally the option flags value.
By pressing enter, the output file path proposed by default is selected; if desired, a different output file path can be specified.
7. PKCS#11 solution[edit | edit source]
The signed binary images are used during the STM32MP secure boot sequence that supports a trusted boot chain, this action ensures an authentication and integrity check of the loaded images.
The classic signing command requests to put all public and private keys as input files which are directly accessible by any person who is allowed to execute the signing service, so that can be considered as a security leak. There are several solutions to protect keys against any attempts to steal keys data and based on this context, we will adopt the PKCS#11 solution.
The PKCS#11 API can be used to handle and store cryptographic keys. This interface specifies how to communicate with cryptographic devices such as HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) and smart cards. The purpose of these devices is to generate cryptographic keys and sign information without revealing private-key material to the outside world.
Software applications can call the API to use these objects for:
- Generate symmetric/asymmetric keys
- Encryption and decryption
- Computing and verifying the digital signature
PKCS #11 presents to applications a common, logical view of the device that is called a cryptographic token and it assigns a slot ID to each token. An application identifies the token that it wants to access by specifying the appropriate slot ID.
The STM32SigningTool is used to manage the key objects stored on smart cards and similar PKCS#11 security tokens where sensitive private keys never leave the device.
The STM32SigningTool uses the PKCS#11 interface to manipulate and sign input binaries basing on ECDSA public/private keys which are stored in security tokens (Hardware or Software).
7.1. Additional PKCS#11 commands[edit | edit source]
- --module (-m)
- Description: Specify a PKCS#11 module/Library path to load (dll, so).
- Syntax: -m <Module_Path>
- Description: Specify a PKCS#11 module/Library path to load (dll, so).
- --key-index (-ki)
- Description: List of used keys indexes in hex format. Use 1 index for Header v1 and 8 indexes for header v2(separated by space).
- Syntax: -ki <values>
- Description: List of used keys indexes in hex format. Use 1 index for Header v1 and 8 indexes for header v2(separated by space).
- --slot-index (-si)
- Description: Specify the index of the slot to use (default 0x0).
- Syntax: -si <hexValue>
- Description: Specify the index of the slot to use (default 0x0).
- --active-keyIndex (-aki)
- Description: Specify the actual active key index (default 0).
- Syntax: -aki < hexValue >
- Description: Specify the actual active key index (default 0).
7.2. PKH/PKTH file generation[edit | edit source]
After the processing of the signing operation, the tool will systematically generate the PKH files to be used after for OTP Fuse:
- PKH file named pkcsHashPublicKey0x{active_key_index}.bin for header v1
- PKTH file named pkcsPublicKeysHashHashes.bin for header v2
7.3. Examples[edit | edit source]
The tool can sign input files for both header v1 and header v2 with a minimal difference in the command line:
- Header v1
-bin input.bin -iv <value> -pwd <value> -la <value> -ep <value> -t <type> -of <value> --key-index <value> -aki 0 --module <module_path> --slot-index <index> -o output.stm32
- Header v2
-bin input.bin -iv <value> -pwd <value> -la <value> -ep <value> -t <type> -of <value> --key-index <value0> <value1> <value2> <value3> <value4> <value5> <value6> <value7> -aki <active_index> --module <module_path> --slot-index <index> -o output.stm32
If there’s an error on the command line or if the tool is not able to identify the key objects that match, an error message will be displayed and indicates the problem’s source.
The SigningTool is able only to use preconfigured HSMs and it is not designed to manage or create new security objects, so we need to install and resort to some free software to setup a suitable environment then generates keys and get information about objects.
Error examples:
- Invalid slot index:
- Unknown key object that is mentioned in --key-index command:
The tool treats sequentially the objects and if it is not able to identify the key objects that match at the first time, the signing operation will stop, and an error message will be displayed to indicate the problem’s source.

