Template:ArticleMainWriter
Template:ReviewersList
Template:ArticleApprovedVersion
SUMMARY
This article introduces how NVMEM Linux® framework manages BSEC OTP data and how to read/write from/to it.
1 Framework purpose[edit source]
The NVMEM Linux® framework provides a generic interface for the device non-volatile memory data such as:
- OTP (one-time programmable) fuses
- EEPROM
It offers kernel space and user space interfaces to read and/or write data such as analog calibration data or MAC address.
2 System overview[edit source]
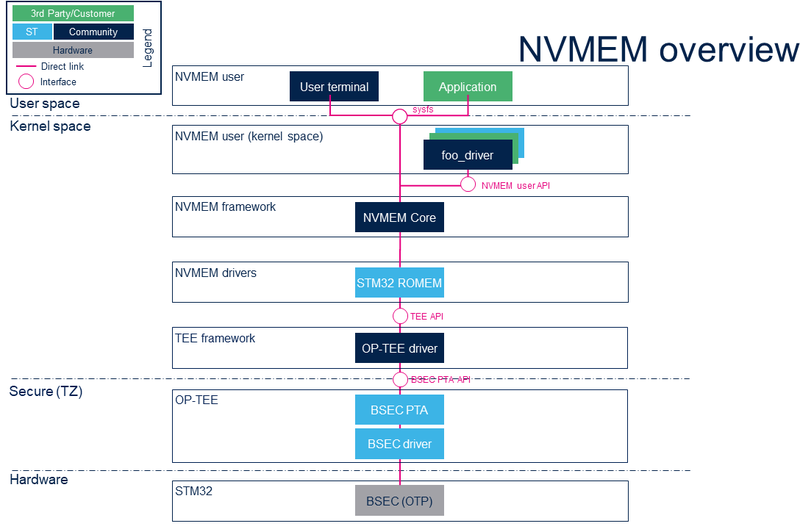
2.1 Component description[edit source]
- NVMEM user (user space)
The user can use the NVMEM sysfs interface, from a user terminal or a custom application, to read/write data from/to NVMEM device(s) from user space.
- NVMEM user (kernel space)
User drivers can use the NVMEM API to read/write data from/to NVMEM device(s) from kernel space (such as the analog calibration data used by an ADC driver).
- NVMEM framework (kernel space)
The NVMEM core provides sysfs interface and NVMEM API. They can be used to implement NVMEM user and NVMEM controller drivers.
- NVMEM drivers (kernel space)
Provider drivers such as BSEC Linux® driver that exposes OTP data to the core.
- NVMEM hardware
NVMEM controller(s) such as the BSEC internal peripheral[1]
2.2 API description[edit source]
The NVMEM kernel documentation[2] describes:
- Kernel space API for NVMEM providers and NVMEM consumers.
- Userspace binary interface (sysfs).
See also sysfs-bus-nvmem[3] ABI documentation.
3 Configuration[edit source]
3.1 Kernel configuration[edit source]
Activate NVMEM framework in the kernel configuration through the Linux® menuconfig tool, Menuconfig or how to configure kernel (CONFIG_NVMEM=y):
Device Drivers ---> [*] NVMEM Support --->
3.2 Device tree configuration[edit source]
The NVMEM data device tree bindings[4] describe:
- The location of non-volatile memory data
- The NVMEM data providers
- The NVMEM data consumers
4 How to use the framework[edit source]
4.1 How to use NVMEM with sysfs interface[edit source]
The available NVMEM devices can be listed in sysfs:
ls /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/ # Example to list nvmem devices
stm32-romem0
The data content of an NVMEM device can be dumped to a binary file:
cat /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/stm32-romem0/nvmem > file # Example to read nvmem data content
The data content of an NVMEM device can be displayed:
hexdump -C -v /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/stm32-romem0/nvmem
The full data content of an NVMEM device can be written as follows:
cat file > /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/stm32-romem0/nvmem # Example to write nvmem data content
Example of 32-bit data word writing (filling it with ones) in OTP n°95:
dd if=/dev/zero count=1 bs=4 | tr '\000' '\377' > file # Create a 4 bytes length file filled with ones, e.g. 0xffffffff)
dd if=file bs=4 seek=95 of=/sys/bus/nvmem/devices/stm32-romem0/nvmem # Write it (32-bits, e.g. 4bytes) to OTP data 95
5 How to trace and debug the framework[edit source]
5.1 How to trace[edit source]
Ftrace can be used to trace the NVMEM framework:
cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing cat available_filter_functions | grep nvmem # Show available filter functions rtc_nvmem_register rtc_nvmem_unregister nvmem_reg_read bin_attr_nvmem_read ...
Enable the kernel function tracer, then start using nvmem and display the result:
echo function > current_tracer echo "*nvmem*" > set_ftrace_filter # Trace all nvmem filter functions echo 1 > tracing_on # start ftrace hexdump -C -v /sys/bus/nvmem/devices/stm32-romem0/nvmem # dump nvmem 00000000 17 00 00 00 01 80 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................| ... echo 0 > tracing_on # stop ftrace cat trace # tracer: function # # _-----=> irqs-off # / _----=> need-resched # | / _---=> hardirq/softirq # || / _--=> preempt-depth # ||| / delay # TASK-PID CPU# |||| TIMESTAMP FUNCTION # | | | |||| | | hexdump-478 [000] .... 423.502278: bin_attr_nvmem_read <-sysfs_kf_bin_read hexdump-478 [000] .... 423.502290: nvmem_reg_read <-bin_attr_nvmem_read hexdump-478 [000] .... 423.515804: bin_attr_nvmem_read <-sysfs_kf_bin_read
6 References[edit source]
- ↑ BSEC internal peripheral
- ↑ Documentation/nvmem/nvmem.txt , NVMEM subsytem kernel documentation
- ↑ Documentation/ABI/stable/sysfs-bus-nvmem , NVMEM ABI documentation
- ↑ Documentation/devicetree/bindings/nvmem/nvmem.txt , NVMEM data device tree bindings